

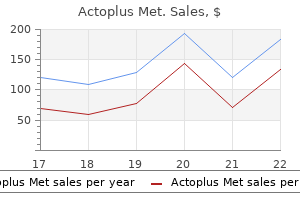
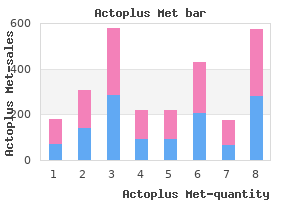
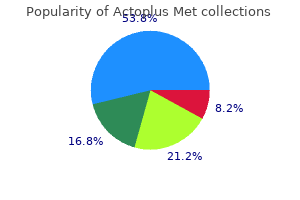
Actoplus Met
"Actoplus met 500 mg generic visa, diabetes type 2 icd".
O. Runak, M.A., M.D.
Professor, CUNY School of Medicine
Less frequent causes of arthritis-induced elbow pain embody collagen vascular ailments diabetes mellitus pronounce actoplus met 500 mg discount mastercard, infection diabetes epidemiology order actoplus met 500 mg fast delivery, and Lyme disease diabetes symptoms ear ringing actoplus met 500 mg cheap on line. Acute infectious arthritis is often accompanied by vital systemic symptoms, including fever and malaise, and must be simply recognized; treatment is with culture and antibiotics quite than injection remedy. The small focus of low sign famous at the proximal end of the ligament might symbolize an avulsion fragment (short arrow). The main complication of intraarticular injection of the elbow is infection, although it should be exceedingly uncommon if strict aseptic method is adopted. The ulnar nerve is very prone to harm on the elbow, and care have to be taken to avoid this construction when performing intraarticular injection. Approximately 25% of sufferers complain of a transient improve in ache after intraarticular injection of the elbow joint, and sufferers must be warned of this risk. Coexistent bursitis and tendinitis might contribute to elbow pain and should confuse the diagnosis. Physical modalities, including local warmth and delicate range-ofmotion exercises, ought to be launched a number of days after the affected person undergoes injection for elbow pain. Sellards R, Kuebrich C: the elbow: prognosis and remedy of common accidents, Prim Care 32(1):1�16, 2005. In Atlas of ache management injection techniques, ed 2, Philadelphia, 2007, Saunders, pp 129�132. The pathophysiology of tennis elbow initially involves microtearing on the origin of the extensor carpi radialis and extensor carpi ulnaris. Secondary irritation may turn into continual because of continued overuse or misuse of the extensors of the forearm. Coexistent bursitis, arthritis, or gout could perpetuate the pain and incapacity of tennis elbow. The most common nidus of ache from tennis elbow is the bony origin of the extensor tendon of the extensor carpi radialis brevis at the anterior side of the lateral epicondyle. Less commonly, tennis elbow ache originates from the origin of the extensor carpi radialis longus on the supracondylar crest; not often, it originates extra distally, on the level the place the extensor carpi radialis brevis overlies the radial head. The olecranon bursa lies within the posterior aspect of the elbow joint and may also become inflamed (bursitis) as a result of direct trauma to the joint or its overuse. Tennis elbow happens in people engaged in repetitive activities corresponding to hand greedy. Tennis players develop tennis elbow by two totally different mechanisms: (1) increased strain grip strain because of taking part in with too heavy a racket, and (2) making backhand pictures with a leading shoulder and elbow quite than keeping the shoulder and elbow parallel to the web. Many sufferers with tennis elbow exhibit a bandlike thickening inside the affected extensor tendons. Radial tunnel syndrome is brought on by entrapment of the radial nerve beneath the elbow. With radial tunnel syndrome, the maximal tenderness to palpation is distal to the lateral epicondyle over the radial nerve, whereas with tennis elbow, the maximal tenderness to palpation is over the lateral epicondyle. Plain radiographs must be obtained in all patients who present with elbow pain to rule out joint mice and different occult bony disease. A total of 1 mL native anesthetic and 40 mg methylprednisolone is drawn up in a 5-mL sterile syringe. After sterile preparation of the pores and skin overlying the posterolateral side of the joint, the lateral epicondyle is recognized. A, Coronal inversion restoration magnetic resonance picture exhibits marrow edema within the lateral epicondyle (arrow) and subtle edema adjacent to the mildly thickened frequent extensor tendon (arrowhead). B, Radiograph shows calcific tendinitis of the common extensor tendon (arrowheads). A Velcro band positioned around the extensor tendons can also help relieve the signs. CompliCaTionS and piTfallS the main complication associated with tennis elbow is rupture of the inflamed tendon both from repetitive trauma or from injection instantly into the tendon. To stop inflamed and previously damaged tendons from rupturing, the needle position must be confirmed to be outdoors the tendon before the clinician proceeds with the injection. The injection technique is secure if careful attention is paid to the clinically related anatomy; particularly, the ulnar nerve is vulnerable to harm on the elbow. Clinical Pearls the injection approach described is extremely efficient in the treatment of pain secondary to tennis elbow. Cervical radiculopathy and radial tunnel syndrome may mimic tennis elbow and should be excluded. In Atlas of pain management injection techniques, ed 3, Philadelphia, 2009, Saunders, pp 137�144. Wilhelm A: Lateral epicondylitis: evaluation and current ideas, J Hand Surg 34(7):1358�1359, 2009. Secondary inflammation might become continual because of continued overuse or misuse of the flexors of the forearm. These actions have in common repetitive flexion of the wrist and strain on the flexor tendons ensuing from extreme weight or sudden arrested movement. The olecranon bursa lies in the posterior side of the elbow joint and may turn out to be infected as a end result of direct trauma to the joint or its overuse. Using strict aseptic technique, a 1-inch, 25-gauge needle is inserted perpendicular to the medial epicondyle by way of the pores and skin and into the subcutaneous tissue overlying the affected tendon. The needle is then eliminated, and a sterile pressure dressing and ice pack are applied to the injection web site. In Atlas of pain management injection methods, ed 3, Philadelphia, 2009, Saunders, pp 148�153. CompliCaTionS and piTfallS the major problems associated with this injection method are associated to trauma to the inflamed and beforehand damaged tendon, which can rupture if injected directly. Therefore, the needle position should be confirmed to be exterior the tendon earlier than the clinician proceeds with the injection. Proximal rupture of the tendon of the long head of the biceps tendon accounts for more than 97% of biceps tendon ruptures, whereas ruptures of the distal portion of the biceps tendon occur less than 3% of the time. Falls on a flexed and supinated elbow have also been related to tears and rupture of the distal biceps tendon, as has abuse of anabolic steroids in athletes. The biceps muscle and proximal and distal tendons are intimately involved in shoulder and elbow perform and are vulnerable to trauma and to put on and tear. SignS and SympTomS In most sufferers, the ache of distal biceps tendon tear happens acutely, is commonly fairly extreme, and is accompanied by a pop or snapping sound. The ache is fixed and extreme and is localized to the area surrounding the antecubital fossa. Patients with full distal biceps tendon tear experience weakness of upper extremity flexion and supination. An obvious defect is palpable within the antecubital fossa in sufferers with full rupture of the distal biceps tendon. A comparative research of 22 sufferers handled with both nonoperative administration or early anatomical restore, Injury 39[7]:753�760, 2008. B, Axial image with seen hemorrhage surrounding the insertion website on the bicipital tuberosity of the proximal radius. However, coexisting bursitis or tendinitis of the elbow from overuse or misuse may confuse the analysis. In some clinical situations, consideration must be given to major or secondary tumors involving the elbow. Injection for distal biceps tendon tear is carried out by placing the affected person within the sitting place with the elbow flexed to approximately ninety levels. If intact, the distal biceps tendon is definitely recognized by palpation on the antecubital fossa. The previously marked point is palpated, and the distal biceps tendon or space of defect is reidentified with the gloved finger. The needle is fastidiously superior at this level via the pores and skin and subcutaneous tissues until it impinges on the distal biceps tendon or enters the realm of defect. The needle is then withdrawn 1 to 2 mm out of the substance of the tendon, and the contents of the syringe are gently injected.
However diabetes impact factor actoplus met 500 mg online buy cheap, in some spindle cell tumors diabetes symptoms double vision cheap actoplus met 500 mg, cytologic options could be deceptively bland focally blood glucose reading chart actoplus met 500 mg mastercard. Abundant cytoplasmic intermediate filaments likely account for the distinctive cytologic options. Tumors in the latter exhibited a extensive range of cell measurement and shape, frequent loss of mobile cohesion, marked nuclear atypia, a high mitotic fee (>5 mf/10hpf), and a imply survival of 7 months in distinction to 23 months for the low-grade group. In the 2 examples within the Ord��ez (2013) research, the signet-ring cells accounted for 15�25% of the tumors that have been otherwise of epithelioid sort with tubulopapillary and stable patterns. The vacuoles in the signet-ring cells were sometimes clear but occasionally contained a bluish granular materials; mucicarmine staining was negative. Unusual histologic variants and findings Typical pathologic findings 632 � Tumor-like lesions and Tumors of the PeriToneum (non-m�llerian) Multicystic sample. Unusual cell sorts that could be present in striking numbers embrace tumor cells with plentiful clear (glycogen-rich) or foamy (lipid-rich) cytoplasm, hobnail-type cells, or cells resembling these of extrarenal rhabdoid tumors. Tumors with these elements, which may embrace rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, are normally sarcomatoid or biphasic (Klebe et al. Omental biopsy confirmed a single layer of minimally atypical mesothelial cells with rare foci of superficial invasion. Tumors with fusions occurred in young individuals and not using a history of asbestos publicity, and exhibited typical epithelioid morphology. Tumor-like lesions and Tumors of the PeriToneum (non-m�llerian) � 633 Differential prognosis Florid mesothelial hyperplasia (see corresponding heading). This analysis is favored when the lesion is solitary, small, comprised of exclusively bland mesothelial cells, and noninvasive. With cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy, Yan et al. Favorable prognostic elements embody an age <60 years, localized tumor, no deep invasion, low nuclear grade, low mitotic rely, distinguished lymphocytic host response, complete/near full tumor resection, and hyperthermic intraoperative peritoneal chemotherapy with cisplatin (Alexander et al. The nuclear atypia rating (graded 1, 2, or 3) was added to the mitotic rating (1: 0�1 mf/10hpf; 2: 2�4 mf/10hpf; three: 5 mf/10hpf) for an general score. Although most are intra-abdominal, related tumors additionally occur within the pleura and rarely at a distance from mesothelial surfaces (parotid gland, central nervous system). Laparotomy typically discloses a normally large, intra-abdominal mass or more often lots of varying measurement; tumor may be confined to the pelvis. Treatment (debulking and postoperative chemotherapy, irradiation, or both) could lead to an initial response, however >90% of patients die from tumor progression. The tumor tends to stay inside the peritoneal cavity, but extra-abdominal metastases occur in some patients. On gross examination, the tumors, which may attain 40 cm in maximal dimension, have easy or bosselated Pathologic features (figs. Usual microscopic features: � Sharply circumscribed aggregates of small epithelioid cells are delineated by a cellular desmoplastic stroma. The aggregates differ from tiny clusters (or even single cells) to rounded or irregularly formed islands. Tumor cells with eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusions and an eccentric nucleus, leading to a rhabdoid appearance, are additionally frequently present. Irregular nests and cords of neoplastic cells are separated by a desmoplastic stroma. Cords of cells may raise the differential analysis of metastatic breast carcinoma. High-power view exhibiting small cells with malignant nuclear function and mitotic figures. Follicle-like spaces, a uncommon function of this tumor, could additionally be diagnostically confusing. Unusual microscopic features: � Architectural options that will predominate and lead to diagnostic problems embrace a strong pattern, tubules, follicle-like spaces, glands (sometimes with luminal mucin), cysts, papillae, anastomosing trabeculae, cords mimicking lobular breast carcinoma, adenoid cystic-like foci, and a sparse desmoplastic stroma. Desmin and vimentin immunoreactivity (particularly intense within the rhabdoid cells) is usually paranuclear and globular. The stromal cells are typically immunoreactive for vimentin and muscle particular actin. Cell junctions have various from scant and primitive to more distinguished ones together with intermediate, desmosomal, and tight types. Paranuclear intermediate cytoplasmic filaments and basal lamina surrounding tumor nests are sometimes distinguished. The typical age of the patient, confinement to the stomach, and the everyday microscopic and immunohistochemical options facilitate distinction from other malignant small cell tumors. A diagnosis of sarcoma was usually thought of within the above examine, however the follow-up was uneventful, suggesting a hamartomatous origin. The lesions usually occur in patients <20 years of age who present with a mass, fever, development failure or weight reduction, hypochromic anemia, thrombocytosis, and polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia. Microscopic examination reveals myofibroblastic spindle cells, mature plasma cells, and small lymphocytes. All of the sufferers have had an uneventful postoperative course with disappearance of the clinical manifestations. There is a loose association of tumor cells that vary from epithelioid to spindled with scattered inflammatory cells and a myxoid matrix. Their options were similar to those of uterine origin (Chapter 9) � Additionally, Salviato et al. Rare malignant vascular tumors, including epithelioid hemangioendothelioma and epithelioid angiosarcoma, might have a peritoneal origin. In addition to ependymomas of the broad ligament (Chapter 11) and ovary (Chapter 15), rare ependymomas presenting with both ovarian and peritoneal involvement (Liang et al. Immunoreactivity for sex wire markers and exclusion of other neoplasms facilitated the diagnosis. Peritoneal involvement by metastatic tumor usually displays spread from a major tumor arising throughout the stomach or pelvis, most commonly the ovary. Peritoneal serous tumors (Chapter 19) during which the ovaries are normal or solely minimally concerned might arise from tubal or endometrial serous carcinomas, which can be microscopic. Other tumors which will unfold to the peritoneum with some frequency embody carcinomas of the breast and gastrointestinal tract (colon, stomach, pancreas), a few of which can have an exclusive or prominent component of signet-ring cells. The glands of mucinous adenocarcinomas could also be focally lined by deceptively benign-appearing epithelium Peritoneal involvement by low-grade mucinous tumors (sometimes in the type of pseudomyxoma peritonei, see subsequent heading) is usually of nonovarian origin. The tumor cells, which are barely seen at this magnification, are broadly scattered via a reactive fibrous stroma. The extent of the mucinous epithelial element is highly variable from case to case and from region to area inside an individual case. The typical presentation is gradual painless stomach enlargement, but in some instances with distinguished ovarian unfold the scientific presentation is that of a slowly rising ovarian neoplasm. Orange to brown to light-yellow lots of jelly-like material are present inside the peritoneal cavity and are normally no less than focally densely adherent to the peritoneum. Rarely jelly-like mucoid material extends past the peritoneal cavity into the retroperitoneal space or not often the pleural cavity. Pools of sometimes basophilic or sometimes eosinophilic mucin vary from acellular to those surrounded by mucinous epithelium or have epithelium suspended within the mucin. As previously famous, the mucinous epithelium can range from morphologically benign to atypical to low-grade carcinoma. A giant mass of mucoid tissue with a outstanding jelly-like consistency has been evacuated from the abdomen. Classic appearance seen in cases of involvement by low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasms. Mucin, some surrounded by neoplastic mucinous epithelium, some not, dissects in a hyaline stroma (dissecting mucin with fibrosis). Generally well-delineated aggregates of mucin, a couple of containing neoplastic glands or strips of neoplastic epithelium, are current in this case which was that of a low-grade mucinous adenocarcinoma of appendiceal origin. Patients with low-grade mucinous adenocarcinomas had 3- and 5-year survivals of 90% and 44%, respectively. In distinction, sufferers with spread of a high-grade appendiceal or colorectal adenocarcinoma have a poor prognosis. Intraperitoneal India ink deposits showing as endometriosis in a patient with chronic pelvic ache. Sclerosing mesenteritis: A actual manifestation or histologic mimic of IgG4-related disease
Generic 500 mg actoplus met mastercard. VIA DULCE DULCE VITA Omnilife Beneficios para que Sirve. Como ayuda con La DIabetes. TESTIMONIO..
In some cases managing diabetes pathophysiology actoplus met 500 mg purchase overnight delivery, fat is also present diabetes medications list wiki actoplus met 500 mg order with mastercard, suggesting the potential for uterine perforation diabetes symptoms related to chronic pancreatitis discount actoplus met 500 mg online. Other circumstances are likely due to transtubal unfold from the peritoneal cavity, and thus probably clinically insignificant. Rare cases, however, have been related to persistent myelogenous leukemia or myelofibrosis. This Affected sufferers are often of reproductive age and with symptoms regarding uterine enlargement. Gross examination typically reveals a unilocular myometrial cyst full of clear to amber fluid. The cysts are usually of m�llerian type, situated in the midline of the anterior or posterior uterine wall, with a typical lining of a single layer of columnar cells that may be ciliated (tubal), endometrioid, or endocervical in kind. The differential analysis is with other myometrial cysts, including adenomyotic cysts (which normally have an endometrial stromal component), cystic adenomyoma (which have a leiomyomatous component), echinococcal cysts, and hydrosalpingiotic cysts of the intrauterine portion of the fallopian tube. The amyloid, typically in massive quantities, is discovered inside the endometrial stroma, myometrium, or in vessel walls. Some require hysterectomy or are amenable to embolization; others resolve spontaneously. The lesion is usually grossly hemorrhagic, the appearance various with the extent of involvement (circumscribed or diffuse) and the caliber of the vessels. Microscopic examination reveals variable proportions of muscular vessels admixed with thin-walled capillary-like vessels. The former are arteries and veins with some vessels having an intermediate appearance; intimal fibrosis could also be seen. This term has been applied to submucosal, subserosal, or mural zones of myometrial hypercellularity during which myocytes exhibit an elevated N�C ratio. The process could mimic leiomyomas on scientific and sonographic examination and can lead to grossly seen bulges or ridges on pathologic examination. Microscopic examination reveals quite a few empty cystic areas lined by endometrial stromal cells and occasional histiocytes. Two girls had neurofibromatosis type 1 (one on oral progestins and one with a Mirena coil), the third had a Mirena coil, and the fourth had no associated findings. In another case, a cellular blue nevus shaped a subserosal dark-red 1 cm myometrial nodule in a 48-year-old girl. Most circumstances were related to abnormal bleeding, and barely, uterine enlargement. Pseudolipomatosis has been encountered in as many as 11% of endometrial and endocervical biopsy specimens, together with polyps from these sites, as well as leiomyomas. Awareness of this phenomenon, the scattered and insinuating pattern of the spaces, an absence of nuclei around the areas, and unfavorable S100 staining facilitate the analysis. The discovering is most likely going related to the closed pressure system created as a half of the technique. These artifacts included vascular pseudoinvasion, endometrial disruption, endomyometrial clefts, intratubal contaminants, nuclear crushing, intravascular inflammatory debris, and the next price of optimistic peritoneal washings. History of a process, the presence of typical cautery-related adjustments in the adjoining epithelium, and the absence of malignant features facilitate the prognosis. Squamous morules: Re-examination of a well-known entity � An ultrastructural and immunohistochemistry study. Atypical mucinous metaplasia and intraepithelial neoplasia of the female genital tract � a case report and evaluation of the literature. Mucinous metaplasia of the endometrium: Ultrastructural and histochemical characteristics. Reappraisal of synchronous and multifocal mucinous lesions of the female genital tract: A shut association with gastric metaplasia. Endometrial intestinal metaplasia: A report of two circumstances, together with one related to cervical intestinal and pyloric metaplasia. Papillary mucinous metaplasia of the endometrium as a attainable precursor of endometrial mucinous adenocarcinoma. Endometrial epithelial metaplasias: Proliferations regularly misdiagnosed as adenocarcinoma. Association of endometrial epithelial metaplasias with endometrial carcinoma and hyperplasia in Japanese and American women. The immunohistochemical profile of atypical eosinophilic syncytial modifications vs serous carcinoma. Papillary syncytial metaplasia related to endometrial breakdown displays an immunophenotype that overlaps with uterine serous carcinoma. Endometrial eosinophilic syncytial change associated to breakdown: Immunohistochemical evidence suggests a regressive process. Endometrial papillary syncytial change: A nonspecific alteration associated with active breakdown. Eosinophilic cell change of the endometrium: A possible relationship to mucinous differentiation. Normal and irregular mitoses in the atypical endometrial change related to chorionic tissue impact. Nonneoplastic endometrial signet-ring cells: Vacuolated decidual cells and stromal histiocytes mimicking adenocarcinoma. Optically clear nuclei: An alteration of endometrial epithelium within the presence of trophoblast. Immunohistochemical staining for Ki-67 and p53 helps distinguish endometrial Arias-Stella reaction from high-grade carcinoma, including clear cell carcinoma. Adenoacanthosis of the endometrium: A clinicopathologic study in premenopausal women. Squamous morules are functionally inert parts of premalignant endometrial neoplasia. Endometrial squamous metaplasia: An unusual response to progestin remedy of hyperplasia. Selective progesterone receptor modulator growth and use in the treatment of leiomyomata and endometriosis. Non-neoplastic nuclear atypia in endometrial epithelium in postmenopausal ladies on hormonal remedy. Distinguishing features of endometrial pathology after exposure to the progesterone receptor modulator mifepristone. Arias-Stella reaction in nonpregnant girls: A clinicopathologic research of 9 circumstances. Selective progesterone receptor modulators: Clinical roles and effects on endometrial histology. The spectrum of endometrial pathology induced by progesterone receptor modulators. Endometrial morphology after remedy of uterine fibroids with the selective progesterone receptor modulator, ulipristal acetate. Endometrial histopathology in patients with culture-proven higher genital tract an infection and laparoscopically diagnosed acute salpingitis. Chronic endometritis: A combined histopathologic and scientific review of instances from 2002 to 2007. Florid reactive lymphoid hyperplasia (lymphomalike lesion) Bryant A, Lawton H, Al-Talib R, et al. Intravascular proliferation of reactive lymphoid blasts mimicking intravascular lymphoma � a diagnostic pitfall. Post-hysteroscopic ablation response: A histopathologic examine of the effects of electrosurgical ablation. Idiopathic uterine granulomas: Report of a collection with morphological similarities to idiopathic ovarian cortical granulomas. Postoperative granulomas of the endometrium: Histological features after endometrial ablation. Pathology of endometrial ablation failures: A clinicopathologic study of 164 circumstances. Idiopathic postmenopausal decidual reaction of the endometrium: A clinicopathologic analysis of four circumstances. Asynchronous glands in the endometrium of women with recurrent reproductive failure. Plasma cells in chronic endometritis are simply recognized when stained with syndecan-1. Xanthogranulomatous endometritis: Report of six circumstances and a proposed mechanism for development.
The nuclear features are sometimes bland diabetes in dogs glucose levels actoplus met 500 mg order without prescription, however in 40% of the circumstances rare nuclei are enlarged and hyperchromatic diabetes insipidus neuropathy 500 mg actoplus met fast delivery. The tumors are benign but 30�40% of them recur because of diabetes mellitus type 2 causes 500 mg actoplus met discount incomplete excision, typically a few years later. The stroma of superficial angiomyxoma is rather more myxoid than that of aggressive angiomyxoma. Small bland spindle to stellate cells lie within a myxoid matrix and a few delicate capillaries are seen. The tumors are often <5 cm in dimension, well-circumscribed, nodular or multinodular or polypoid plenty that involve pores and skin or subcutis, with a gelatinous sectioned floor. Microscopic examination reveals sparsely mobile nodules of spindle to stellate cells, delicate capillary-like vessels, and an alcianophilic myxoid matrix. The tumor cells have bland to mildly pleomorphic nuclei, with occasional multinucleated cells; mitotic figures are uncommon to absent. Other findings embrace inflammatory cells, particularly neutrophils, and in some tumors, entrapped cystic epithelial inclusions doubtless of adnexal origin. These tumors happen within the reproductive or postmenopausal eras as a superficial mass, mostly in the vulva; rare tumors have arisen in the vagina, paravaginal area, perineum, inguinal region, or urethra. Microscopic features of typical cellular angiofibromas: � A mobile proliferation is comprised of spindle cells in brief intersecting fascicles; quite a few small to medium-sized, thick-walled, often hyalinized, blood vessels; and short wispy collagen bundles. The spindle cells have scanty eosinophilic cytoplasm, bland nuclei, and uncommon mitoses. A well-circumscribed mobile proliferation of spindled with interspersed small to medium-sized vessels lies inside the superficial dermis. A mobile proliferation of monotonous bland ovoid to spindle cells accommodates many small and medium-sized vessels, some with thick walls. Chen and Fletcher found that ~8% of vulvar cellular angiofibromas contained foci of extreme atypia or sarcomatous transformation. However, unlike most of the latter, they sometimes comprise a distinguished adipocytic component and inconspicuous thin-walled vessels. Microscopic examination reveals a moderately mobile proliferation of bland, mitotically inactive, ovoid, spindle, or stellate cells, often with a wavy nucleus, separated by a finely collagenous stroma. A patternless association of the spindle cells normally predominates, but lace-like, fascicular and storiform patterns, as properly as myxoid, edematous, or hyalinized foci with thick dense collagen bundles are additionally frequent. The deep elements of bigger tumors are often hypercellular, and should even counsel a small round blue cell tumor. Thin-walled blood vessels, typically with perivascular hyalinization, are sometimes concentrated within the heart of the tumor. This lesion, not like myofibroblastoma, lacks an expansile nodular look and a definite margin, is usually much less cellular, usually incorporates multinucleated stromal large cells, and lacks each a Grenz zone and a multipatterned structure. Distinction from mobile fibroepithelial polyps is harder and the lesions could additionally be part of a spectrum. This tumor, not like superficial myofibroblastoma, typically contains perivascular aggregates of epithelioid or plasmacytoid cells, and normally lacks the multipatterned structure of myofibroblastoma. These tumors, in contrast to superficial myofibroblastomas, are often more deeply seated, have infiltrative borders, are extra myxoid and fewer cellular, and have blood vessels which are more outstanding and variable in dimension. These tumors are extra diffusely mobile than superficial myofibroblastomas, comprise many thick-walled vessels and generally fat, and lesional cells that sometimes are desmin-negative. Differential analysis unilateral, subcutaneous vulvar mass (usually in the labium majus) in girls 3�13 years of age. The lesional cells sometimes infiltrate and entrap surrounding vessels, fats, and nerves, and will prolong to the epidermal�stromal interface. About 30% of the tumors have recurred after native excision that was normally incomplete. These tumors happen in a postpubertal age group, are often deeply seated, and have a diffusely myxoid matrix, perivascular smooth muscle, and desmin+ cells. These tumors are nicely circumscribed and comprise perivascular desmin+ epithelioid cells. The tumor consists of hyalinized fibrous tissue, adipose tissue, and blood vessels. Variable proportions of mature adipocytes, bland uni-/ bivacuolated lipoblasts, and spindle cells lie within a myxoid stroma with distinguished branching vessels. Striking dermal lymphangiectasia is usually associated with marked reactive epidermal hyperplasia. Vulvar examples of solitary (sometimes giant) neurofibroma, neurofibromatosis, schwannoma, and paraganglioma have been reported. Adipocytic tumors embody lipomas and lipoma-variants, together with spindle-cell lipoma, pleomorphic lipoma, adenolipoma, and lipoblastoma-like tumors (see corresponding heading). The largest series of this entity involving the female genital tract discovered that 14 of 25 occurred in the vulva. They have been usually well circumscribed with a firm, uniform yellow�tan cut floor. Microscopic features are similar to these seen within the general delicate tissue location � bland spindle cells with no specific pattern related to distinguished branching ectatic blood vessels and a hyalinized stroma. Occasional tumors are hypercellular and uncommon options include fat, myxoid stroma, large cells, and cytologic atypia. In the biggest collection the mitotic rate was 1 per 10 high-power fields in half the cases, brisk activity (up to 15 per 10 high-power fields) being seen in the other cases. Angiomyofibroblastoma could also be considered however it sometimes has a cuff of epithelioid cells around blood vessels of a smaller caliber in distinction to solitary fibrous tumor. In these and different uncommon issues in differential prognosis, staining for stat 6 could additionally be an important diagnostic aid. Especially when multifocal, they could be related to similar tumors in extravulvar sites. Irregular nests and sheets of eosinophilic, granular cells with bland nuclei and usually <2 mf/10 hpf are intermingled with strands of collagen and occasional chronic inflammatory cells. The tumors are nearly always clinically benign, although some tumors recur domestically. In one examine, native recurrence was only related to tumors that had an infiltrative border. Six malignant vulvar granular cell tumors have occurred in ladies 17�56 years of age; 4 had nodal and/or hematogenous unfold. Typical granular cells are shown and show entrapment of skin appendages (left). The underlying neoplasm (best seen lower right) has elicited hanging pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, which could possibly be misdiagnosed as carcinoma. Verruca vulgaris of the vulva in youngsters and adults: A nonvenereal type of vulvar wart. Immunophenotype and viral (human papillomavirus) correlates of vulvar seborrheic keratosis. Histologic correlates of vulvar human papillomavirus an infection in kids and younger adults. Coexistent vulvar condyloma and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion in an immunocompetent girl: From the case consultation committee of the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease. Genital herpes simplex virus infections: Clinical manifestations, course, and problems. Underdiagnosis of genital herpes by current clinical and viral-isolation procedures. Necrotizing fasciitis in gynecologic and obstetric sufferers: A surgical emergency. Vulvovaginal candidiasis as a continual illness: Diagnostic standards and definition. Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) infestation of the vulva: Report of 2 instances of a pseudoneoplastic lesion mimicking squamous carcinoma. Necrotizing fasciitis and progressive bacterial synergistic gangrene of the vulva. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and therapeutic considerations.