

Kemadrin
"Buy kemadrin 5 mg without prescription, symptoms sinus infection".
W. Lester, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Co-Director, Florida International University Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine
The bony wall of the tympanic bulla is markedly thickened by new bone formation (the layer spanned by the double-headed arrow) and unfastened fibrous connective tissue medications j tube kemadrin 5 mg generic on line. A fibrinopurulent exudate extends from the tympanic membrane (at the top of the image but out of the sphere of view) to the cochlea and has entrapped and immobilized all three ossicles (O) administering medications 7th edition answers effective kemadrin 5 mg. A translucent pure keratin treatment generic kemadrin 5 mg online, crescentshaped fragment of tissue glue used to secure the cannula is entrapped within the tympanic membrane and surrounded by macrophages. The bone forming the cochlea can also be thickened in persistent middle ear irritation. Occasionally the cannula will be enveloped by exuberant fibrous connective tissue, which may permit the proliferating tissue to enter into and impede the cannula. The auditory tube often is relatively unaffected by agents instilled in the center ear, but in some circumstances luminal cellular debris, hypertrophied and hyperplastic epithelium, or increased lymphoid infiltrates in the lamina propria can be identified in the portion of the tube closest to the tympanic bulla. When necrosis ensues the tympanic membrane is crusted in serocellular exudate, its stroma is hypereosinophilic (indicative of extensive matrix degradation), and the inflammatory response might drain outward into the exterior ear canal. The tympanic membrane and its anchoring supports have undergone coagulative necrosis. Inner Ear Ototoxicant-Induced Morphologic Changes the sense of listening to in the inside ear is vulnerable to a number of courses of ototoxicants following systemic exposures. Prototypical ototoxic agents embrace aminoglycoside antibiotics, organic solvents, loop diuretics, quinine, salicylates, cisplatins, organometals, and carbon monoxide. Combinations of ototoxicants and chronically high levels of ambient noise exacerbate the hearing loss that develops following either supply of damage alone. The spherical window membrane (center) is diffusely expanded by edema and is focally thickened within the middle by stromal proliferation. The inside portion of the round window membrane is also thickened adjoining to its attachment to the otic capsule (arrowhead). Ototoxic agents sometimes produce patterns of harm that mimic agerelated hearing loss in that the basal (high frequency) areas of the cochlea are affected earlier than the apical (low frequency) areas. Almost any a half of the cochlea can current with toxicant-induced histologic modifications depending on the agent and the character of the insult. An irritating xenobiotic or car applied to the center ear may produce thickening of the bony otic capsule, which is the exterior construction surrounding the cochlea. Direct middle ear administration of an irritant can also incite inflammatory infiltrates in the spherical window or near the footplate of the stapes within the oval window. In some cases of toxicant-induced cochlear irritation, hemorrhage could also be evident as nicely. The hemorrhage and inflammation may only be current in dependent (ventrally located) portions of the cochlea, keeping in thoughts that dependency could additionally be relative to the place of the cochlea during the trimming and embedding processes. Systemically administered ototoxicants will often have an result on specific portions of the organ of Corti. Such specificity is mostly due both to higher sensitivity of those affected cell populations or to pharmacologic activity. The hair cells of the basal turns of the cochlea, which detect highfrequency sounds, are typically extra sensitive to injury than are those of apical areas, which are sensitive to low-frequency sounds. In these instances, routine histologic sections will reveal a quantity of affected outer hair cells with rounded, shrunken profiles and hypereosinophilic cytoplasm, generally with pyknotic or karyorrhectic nuclei. With extra time after the outer hair cells are lost, the internal hair cells can also be depleted. Microscopic adjustments that might be noticed at the facet of hair cell loss embody reduced cellularity of the spiral limbus, necrosis of spiral ganglion neurons, and axonal degeneration of the cochlear nerve. Fragments of necrotic cells (arrow head) stay where outer hair cells can be expected. Scattered, hypereosinophilic ("pink lifeless") neurons are in preserving with acute necrosis. This may be surmised in some situations from the lack of spiral ganglion neurons in the absence of internal hair cell loss. Whether induced by hair cell loss or direct neuronal toxicity, spiral ganglion evaluation is basically an exercise in standard neuropathology. The normal cellularity of the spiral ganglion varies highly from apex to base; due to this fact, a prognosis of hypocellularity ought to be made with warning on routine microscopic sections until the loss of ganglion tissue is marked. Given the appropriate timing of the evaluation after hair cell loss, the "dying again" phenomenon of axons within the nervous system due to loss of useful synapses within the periphery can be readily obvious in the cochlear nerve. With enough time and intensive depletion of spiral ganglion neurons, changes in the cochlear nerve trunk may be obvious as pallor of the nerve at low magnification with swelling of axons or their glial sheaths, formation of digestion chambers, and empty areas on larger magnification. The stria vascularis is one other structure that has a demonstrated sensitivity to ototoxicants. Injury to the stria vascularis will lead to practical deficits in listening to, because the stria vascularis is the first website for sustaining the charge differential. For instance, loop diuretics have been reported to rapidly produce reversible swelling of this tissue. Loop diuretics could potentiate the injury induced by different ototoxicants, such as aminoglycosides, when the brokers are given at the similar time. Injury to the stria vascularis, typically elicited by high doses and persistent administration of such brokers as aminoglycosides, could result in permanent atrophy with transformation to a thinner and less complex construction. In these cases the ability to generate the endocochlear potential may be lowered but not ablated. In the vestibular system the cristae ampullaris and the sensory areas of the utricle and saccule are the primary targets of ototoxicants. The macula has coagulative necrosis as shown by diffuse eosinophilia in affiliation with pyknosis and karyorrhexis of nuclei. Gentamicin, kanamycin, and neomycin, among others of this antimicrobial class, have lengthy been recognized as ototoxicants. The aminoglycosides have varying propensities to have an result on either the auditory or vestibular hair cells, however with sufficiently high doses or long schedules they all will affect each populations of sensory cells. Amikacin tends to have an effect on the cochlea more than the vestibular system, whereas streptomycin impacts the vestibular system greater than the cochlea. Gentamicin and tobramicin equally have an result on both the auditory and vestibular techniques. In the organ of Corti, aminoglycosides are inclined to have an effect on outer hair cells before internal hair cells. Some species, such as mice, are notably "resistant" to aminoglycoside antibiotics since dosing produces lethality from renal effects before ototoxicity may be demonstrated. However, ototoxicity may be produced in mice when local or systemic aminoglycoside administration is mixed with systemic delivery of a loop diuretic. The toxicity of aminoglycosides is due to generation of reactive oxygen species, with iron being a key participant. The basal flip of the ear typically has lower levels of glutathione and different antioxidants, which makes it more vulnerable to oxidative harm. Systemic treatment with antioxidants and iron chelators has been proven to attenuate the toxicity of aminoglycosides. The lack of hair cells observed with aminoglycosides appears to be largely by apoptotic necrosis and is everlasting. Aminoglycosides enter the cochlea by way of the blood vessels of the stria vascularis, which are part of the barrier (analogous to the blood�brain barrier) making the ear a protected website. It was initially thought that aminoglycosides accumulate within the inner ear; nevertheless, pharmocokinetic studies have demonstrated that the focus within the endolymph and perilymph are very low compared to that in the serum. The uptake into the internal ear is dose-dependent and has rapid saturation kinetics. However, aminoglycosides are cleared very slowly from the fluids of the cochlea, so even broadly spaced doses will result in an extended exposure half-life. Aminoglycosides are known to block a big selection of ion channels, together with Ca11-activated K1 channels and transducer channels. At low doses the mechano-electrical transducer channels on hair cell bundles are thought to be permanently blocked by aminoglycosides. These ports may also be one route of antibiotic entry into the outer hair cell; selective pharmacological blockade of these channels prior to dosing with aminoglycosides reduces the extent of ototoxicity. Aminoglycosides are additionally taken up by hair cells through endocytotic activity at the apical membrane.
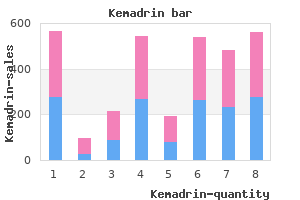
Intratumoral lymphocytes are indicative of an immune reaction and makes an attempt of the person to rid the body of tumor cells medications kosher for passover 5 mg kemadrin cheap amex. Of the approximately 20 medications emts can administer kemadrin 5 mg discount on-line,000 genes in the mammalian genome medications 3605 kemadrin 5 mg order with amex, tons of are known or proposed as oncogenes; however, relatively fewer are tumor suppressor genes. Other basic mobile alterations happen, including limitless replicative potential, capability to set off sustained angiogenesis, and the flexibility to invade and metastasize; these, too, are concerned within the multistep process of neoplastic transformation. Multistage models of carcinogenesis have proven useful for defining these occasions in the neoplastic process, and type the cornerstone of current hypotheses of organic mechanisms of carcinogenesis. These fashions have been used to show the multistep strategy of transformation in quite so much of organ techniques, such as the pores and skin, liver, urinary bladder, lung, kidney, intestine, mammary gland, and pancreas. They have utilized varied methods, in order to categorize various brokers as initiators, promoters, and complete carcinogens able to each initiating and selling. The operationally outlined phases of carcinogenesis-initiation, promotion, and progression-are useful for discussion and understanding of carcinogenesis, however in fact every of these phases within the strategy of neoplastic transformation could doubtless encompass multiple and overlapping stages. Proto-oncogene and tumor suppressor gene mutation assays have become a well-liked software for investigating tumor etiology in people utilizing rodent models primarily because mutations tend to be chemical specific. These findings help the belief that subclone precursor cells can progress via the processes of promotion and development toward malignant transformation. Panel B is a low magnification photomicrograph of a male B6C3F1 mouse demonstrating multiple, nodular metastases within the lung (arrows) originating from a primary hepatoblastoma. In some cases, there are even similar patterns of oncogene activation to those documented in human neoplasms. The B6C3Fl mouse liver is a mannequin in which many genotoxic and nongenotoxic chemical substances induce hepatocellular tumors. The frequency and pattern of activating mutations could be compared between tumors that are chemically induced and spontaneous to assist in determining potential mechanisms by which chemical compounds induce tumors. When H-ras harbors a mutation, similar to a base substitution in codon 61, particular mutant forms of H-ras protein remain within the activated state with its partner Raf and stimulates cell proliferation. There are a quantity of ras codons and mutant codon sequences that may activate ras and contribute to tumor development. In widespread human cancers, multiple tumor suppressor genes may be affected, supporting the notion that most cancers improvement includes perturbation of a quantity of ranges of progress management. Thus, inactivation or loss of tumor suppressor genes, working in concert with the activation of oncogenes and with a big selection of endogenous and exogenous stimuli, performs an necessary half in the advanced strategy of carcinogenesis. Uncontrolled mobile proliferation is the hallmark of neoplasia, and heaps of most cancers cells reveal injury to genes that regulate their cell cycles immediately. Epigenetics Epigenetics refers to reversible changes in gene expression that happen with out alteration to the underlying genetic code. Indeed, it has become evident in the course of the previous few years that tumor suppressor genes are sometimes silenced by hypermethylation of promoter sequences somewhat than by mutation. Hypomethylation is believed to influence the regulation of transcription and gene expression and could additionally be associated with mobile differentiation. Cancer Stem Cell Theory There is in depth evidence that a number of kinds of cancers arise from transformation of stem and/or multipotent progenitor cells during carcinogenesis. Self-renewal is a course of by which a stem-cell pool maintains its numbers through symmetric and asymmetric division. In symmetric cell division, the progeny is equivalent to the preliminary stem cell; in uneven stem-cell self-renewal, one of many two progenies is equivalent to the initial stem cell, whereas the opposite cell is a committed progenitor cell, which ultimately undergoes mobile differentiation. The traditional clonal origin of carcinogenesis states that transformation occurs via a series of sequential mutations resulting in preneoplastic lesions that progress to neoplasia and, finally, metastasis. On the opposite hand, through the tightly regulated means of self-renewal, regular stem cells are able to function over the lifespan of the host, and thus their longevity and continued mitotic exercise makes them a major goal, and potential reservoir for, the accumulation of the quite a few genetic mutations needed for transformation. Furthermore, many similarities between normal stem cells and tumor cells exist, together with indefinite proliferative potential and the flexibility to give rise to new tissues (although disorganized and atypical in the case of tumorigenesis). In addition, both stem cells and varied neoplastic cells categorical telomerase (which imparts longevity), have antiapoptotic mechanisms to forestall cell dying, share frequent embryonic and developmental metabolic pathways, and have elevated membrane transporter activity (allowing them to efflux chemical compounds from the intracellular compartment). In many ways, neoplastic cells differ from stem cells in phrases of their unrestricted and disordered progress and genetic alterations. Perhaps the major difference between these two cell sorts is that the method of tumorigenesis in lots of kinds of most cancers entails dysregulation of embryonic and developmental pathways, cell differentiation, and stem-cell upkeep. Some of those key pathways embrace Wnt, Notch, and Sonic Hedgehog, all very important for regular embryogenesis and stemcell upkeep. However, identification of those cells could be problematic, as a end result of stem cells characterize a very small proportion of the overall cell inhabitants in an organ. A main explanation for cancer-related dying, metastasis, is currently thought of to occur via sequential acquisition of mutations leading to choice of clones with metastatic potential. However, it has been proven that in certain cancers a small number of particular person most cancers cells disseminate and lie dormant at distant websites in a state of quiescence for up to several years, until triggered to outbreak. Alternatively, some disseminated tumor cells never activate to trigger formation of metastatic tumors and finally endure anchorage-dependent cell dying (anoikis). Treatment of most cancers as a homogeneous population of proliferative clones with limitless development potential is problematic as a outcome of many tumors may initially respond to therapy only to recur, often months to years later in life. Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis Current information strongly suggest that cell demise may be as important as cell proliferation in carcinogenesis. The ratio between cell "birth" and counterbalancing cell dying determines tumor progress. Two types of cell dying are commonly noticed in most cancers growth: necrosis and apoptosis. Necrosis typically occurs when a growing cancer outgrows its blood supply, resulting in hypoxia and deprivation of vitamins essential for tumor cell survival. Apoptosis is an energy-dependent course of that involves lively gene transcription and translation and relatively intact cellular metabolic machinery. Enhanced apoptosis could additionally be triggered in experimental in vivo fashions by chemical exposure; meals deprivation; sure cytokines, growth elements, and tumor suppressor gene actions; and withdrawal of mitogenic brokers. For instance, it has been reported that the expansion of dioxin-promoted preneoplastic liver foci in rats is secondary to inhibition of apoptosis, quite than enhanced cell proliferation. In addition, an underlying precept of most cancers chemotherapy is the selective induction of apoptosis in neoplastic cells. Some compounds, corresponding to these categorised as nongenotoxic carcinogens (see later), typically act via enhancement of cell proliferation or interference with apoptosis by way of mechanisms unrelated to adjustments in genomic sequence. Confirmation of whether altered cell turnover alone is a realistic explanation for noticed carcinogenicity of nongenotoxic carcinogens would require carefully carried out research that demonstrate enhanced cell turnover. These undesirable consequences are influenced by the kind and dose of xenobiotics, and show considerable species differences in susceptibility and severity that must be understood for assessing the potential results on human health from related exposures to specific xenobiotics. Hormones Hormones are chemical messengers that bind to particular mobile receptors and form a hormone�receptor complicated that triggers a mobile response. The target-cell response to hormone stimulation is often a rise or decrease in cell division, or an acceleration or deceleration in differentiation. There has been recently almost continual discovery of new endogenous messenger substances and development components that match the broad definition of "hormone. A main difference between hormones and progress components is that hormones are produced in an endocrine tissue and act on cells at a distant website, whereas progress factors are secreted by a variety of normal and irregular tissues and act on close by responsive cells. Endogenous and exogenous hormones have long been known to be related to the development of particular neoplasms. Hormones or hormone imbalances undoubtedly play a major causative role in cancers of certain hormone-sensitive tissues (ovary, uterus, prostate, testes, and endocrine organs). Through the usage of two-stage animal models for mammary and thyroid cancer, hormones have been demonstrated to operate as tumor promoters of certain neoplasms. Whether the assorted forms of hypertrophy are thought of physiological, adaptive, or pathological is dependent upon the philosophy of the particular person making the judgment. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia may occur collectively, and several elements link hypertrophy to rodent hepatocarcinogenesis. Hypertrophy is underneath varied regulatory controls, and thus is proscribed in quantity and period. Hypertrophy may be categorized in a manner just like how hyperplasia is classed. Compensatory, or adaptive, hypertrophy represents a physiological response to a stimulus, such as is seen with muscle hypertrophy subsequent to extended train or hepatocellular hypertrophy due to enzyme induction in the liver following exposure to chemical inducers such as phenobarbital. Along with degenerative changes, such as necrosis and vacuolization, hepatocyte hypertrophy is associated with the development of hepatocellular neoplasms in rats and mice. However, hypertrophy may not be constantly noticed in the growth of other types of neoplasms. Exposure of animals to liver enzyme inducers results in a signature of toxicological adjustments characterized by a rise in liver weight, hepatocellular hypertrophy, cell proliferation, and incessantly hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic 2-year studies.
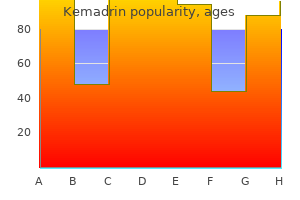
In some classification schemes symptoms viral infection kemadrin 5 mg for sale, the number of types of foci is expanded by additional subdividing these 4 basic classes of foci treatment lower back pain generic 5 mg kemadrin mastercard. Foci of cellular alteration could also be detected by a big selection of specialised histochemical and immunohistochemical markers symptoms enlarged prostate cheap kemadrin 5 mg overnight delivery. These and similar markers even have been used to characterize foci in mice, although outcomes have tended to be more variable. In both species, the looks of some markers may be correlated to the altered staining characteristics detected in H&Estained sections. The characterization of foci using H&E staining traits and marker evaluation means that the mode of motion of a carcinogen might exert a profound affect upon the prevalence of certain phenotypes. However, the mechanistic explanation for these sorts of observations stays incomplete. In mice, intravascular protrusion of hepatocytes from basophilic foci has been noticed following nitrosamine administration. These projections could also be contained in subendothelial locations, however in some cases appear to prolong beyond the endothelial lining of the veins. Some of the earlier literature debated whether or not this finding represented an invasive process linked to metastatic potential. Foci of cellular alteration are considered to characterize potential precursors to hepatocellular neoplasms. Hepatocellular neoplasms are divided into benign lesions referred to as adenomas and malignant lesions known as carcinomas. Hepatocellular adenomas are very related in appearance to foci of cellular alteration. The key difference is that adenomas are inclined to be bigger and cause a larger diploma of compression of adjacent hepatic parenchyma, whereas foci tend to be smaller and merge with adjoining parenchyma, inflicting only modest, if any, compression. Hepatocellular adenomas also should be distinguished from focal hyperplasia of hepatocytes that might be associated to previous or ongoing liver injury or other liver lesions. Unlike adenomas and foci, the lobular construction in focal hyperplasia is normally maintained, even if in some cases it could be distorted. Although hepatocytes in focal hyperplasia could additionally be enlarged, they often stain similarly to hepatocytes in the surrounding liver, and are usually acknowledged as a result of compression of adjacent tissues. They are readily recognized as main lesions, and the metastatic potential varies. Especially wide trabecular structures tend to endure central (presumably ischemic) necrosis, and lack of necrotic centers may end in a pseudoglandular sample of growth. Some hepatocellular carcinomas are characterized by rarer mobile arrangements together with sheets, glands, and combined cholangiocellular patterns. Occasionally, some hepatocellular neoplasms might have the everyday look of adenomas aside from one or few select areas within the lesion, where a nodule of neoplastic hepatocytes compresses the adjacent adenoma tissue, and accommodates a trabecular pattern and/or possesses a distinct, often more basophilic, cytoplasm staining. Current diagnostic conventions designate these lesions as hepatocellular carcinomas. In rats and mice, hepatocellular neoplasms could happen spontaneously and are often noticed as incidental findings in getting older untreated animals in standard laboratory environments. However, in mice, some strains such as the C3H are identified to have a reasonably high incidence (30%�50% in males) while different strains such because the C57Bl/6 have a reasonably low incidence (,5% in males). Rats occasionally have spontaneous hepatodiaphragmatic nodules of the median lobe, with the incidence varying by pressure. They are composed of hepatic lobular parenchyma, usually with hepatocytes possessing uncommon linear chromatin patterns. A uncommon lesion that could be confused with hepatocellular neoplasia is glandular metaplasia of hepatocytes. This lesion could have a variable appearance, with formation of a few too many glands of various size that are lined by cells resembling hepatocytes or cuboidal epithelial cells which resemble bile duct epithelium. The partial replacement of hepatic parenchyma by glandular buildings with features resembling hepatocytes has been observed in continual research of some pentachlorobiphenyls. Hepatoblastoma is a distinct form of hepatic neoplasm that has been described in aging mice as a spontaneous lesion, or in some instances attributed to a check article. Among aged untreated control B6C3F1 mice, the incidence of hepatoblastoma was roughly 2% in males and,1% in females. Hepatoblastomas are normally detected in mice with concurrent hepatocellular adenoma or carcinoma. When related to a check article, affected therapy groups with an elevated incidence of hepatoblastoma often even have an increased incidence of hepatocellular neoplasia. The lesions usually embody endothelial-lined cystic areas that include blood and/or eosinophilic material. Central areas of necrosis with hemosiderin-laden macrophages, calcium deposits, and cholesterol crystals may be present. On occasion, there are focal areas with cells arranged in an embryonal-like organoid pattern or kind rosettes and ribbons. In some studies, focal areas of squamous differentiation or osteoid differentiation have been noted. Biliary Neoplasia Neoplasms of the biliary epithelium may be apparent by gross inspection. Typically, they kind raised, pale, white to beige lots that could be cystic or comprise areas of necrosis. Cholangiomas have scant connective tissue stroma and may have a skinny connective tissue capsule. Although the person bile ducts could also be barely irregular in shape, the epithelium lining these ducts is normally homogeneous in cell dimension and form. Cystic cholangiomas are characterized by irregular cystic cavities often lined by a uniformly low cuboidal to squamous epithelium. Cholangiofibroma Cholangiofibroma is a benign liver tumor that has some characteristics in common with the cholangiocarcinoma. The cholangiofibroma has an extensive collagenous connective tissue stroma surrounding atypical bile ducts composed of a number of completely different cell types. Most cells have bile duct epithelial characteristics, together with a basophilic cytoplasm and vesicular nucleus, and goblet cells are observed incessantly. The duct-like structures are often full of necrotic mobile debris from sloughed epithelial cells and mucous substances. In the middle of cholangiofibromas, the bile duct epithelium could also be completely denuded from the floor of the gland-like structure, leaving a mucus-filled cyst surrounded by connective tissue. Cholangiocarcinoma Cholangiocarcinomas are malignant neoplasms of biliary epithelium. The malignant biliary epithelium is pleomorphic, with an elevated nuclear�cytoplasmic ratio and basophilic cytoplasm. The malignant biliary epithelium may form ducts, glandular constructions (often with papillary projections), or stable sheets of neoplastic cells. These tumors tend to be fairly agency as a outcome of the presence of abundant scirrhous response. The differential analysis of bile duct neoplasms is regularly tough, no much less than compared with different primary liver neoplasms. The malignant lesion is recognized primarily by proof of invasion into vessels or by metastasis. Extreme atypia of the cells could also be helpful however has limited diagnostic significance because the cells of cholangiofibromas additionally display appreciable atypia. Two options, the smaller quantity of collagen in the stroma and the much less abundant accumulation of mucus in neoplastic glands, aid in differentiating the cholangiocarcinoma from the nonneoplastic lesion of cholangiofibrosis. The unitized structure of the lesion with distinct borders, significantly the presence of a skinny capsule, helps distinguish the cholangioma. The biological potential, as properly as the pathogenesis of the assorted bile duct proliferative lesions, has generated a reasonable amount of research interest and an even greater diploma of hypothesis. Cholangiofibrosis, cholangiofibromas, and cholangiocarcinomas are generally believed to characterize a steady spectrum of lesions. Neoplasms of bile duct epithelium are extraordinarily rare as spontaneous lesions within the rodent, although bile duct proliferation is comparatively widespread. Endothelial Cell Neoplasia Hemangiomas are benign neoplasms fashioned by endothelial cells. They form fairly well circumscribed but rarely encapsulated lots of vascular channels lined by a single layer of well-differentiated endothelial cells. Hemangiomas could assume a capillary form composed of multiple smallcaliber vessels compressed into a mass. By gross inspection, hemangiosarcomas could appear as single or multiple raised, darkish red, strong to fluidfilled lots.
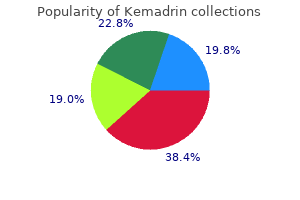
Selection of follicles to continue onto the preovulatory stage is decided by follicles having granulosa cells capable of medications you can give your cat 5 mg kemadrin purchase mastercard express the required gonadotropin receptors at the time of elevated gonadotropin levels symptoms of flu kemadrin 5 mg generic. The estrogen and androgen secreted from growing follicles promote cell proliferation and maturation in both the uterus and vagina symptoms quitting weed kemadrin 5 mg purchase mastercard. Under the influence of estradiol and androgens, the stromal fibroblasts and epithelial cells of the endometrium proliferate and improve in dimension. Estrogen and androgen additionally promote the synthesis of actomyosin and glycogen in clean muscle cells, leading to hypertrophy of the myometrium. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration in the uterus, which can be causally related to intercellular edema and hyperemia, is also attributed to the impact of estrogen. In the vagina, estrogen not solely stimulates cell proliferation but additionally induces epithelial cornification. The ovarian steroid hormones, including estrogens, progestins, and androgens, exert their affect on the uterus and vagina, and different elements of the body, through the circulatory system. However, in rats, prolactin has been identified as the luteotropic factor, whereas in rabbits, estrogen is the only recognized luteotropic issue. The interval during which the corpus luteum is practical is named pseudopregnancy. In canine, luteinization of the preovulatory follicles is accompanied by progesterone secretion previous to ovulation. Due to the long luteal life span in canines, pseudopregnancy is common however not at all times clinically apparent. If being pregnant occurs, the embryonic trophoblast secretes chorionic gonadotropin as early as 8�9 days after fertilization, thus maintaining the corpus luteum all through early being pregnant. Progesterone inhibits cell division and maturation but promotes secretion by the endometrial glands. With prior estrogen priming, it can additionally cause the endometrial stromal cells to change from the small inactive type with fusiform nuclei to giant cells with ovoid nuclei. Progesterone causes myometrial cells to turn into hypertrophic with distinguished myofibrils. In the vagina, when estrogen can be present, progesterone induces mucification by increased production and intracytoplasmic accumulation of sialic acid. The solely clearly demonstrated luteolytic issue is prostaglandin F (2-), produced by the endometrium. Experimental data indicate that this prostaglandin is answerable for luteolysis in large home species corresponding to cattle and sheep and in pseudopregnant rodents corresponding to rat and hamster. The reader is referred to the just lately revealed rodent guidance for female reproductive system terminology (see Dixon et al. Response to Injury the response of the reproductive system to insult is comparable amongst totally different species of laboratory animals due to the similarity of reproductive operate control. As described earlier, reproductive finish organ growth and development are dependent on numerous trophic elements produced by the pituitary, ovary, and within the nonrodent, the adrenal gland. These trophic components modulate cell development, metabolism, and differentiation throughout the varied compartments of the ovary, uterus, vagina/cervix, and clitoral glands. Not solely is the level of individual components essential but the ratio of things is also critical. Atrophy and hypertrophy/hyperplasia could result from will increase or decreases in cell proliferation or apoptosis, both essential and regular physiologic processes in the cycling female reproductive tract. As discussed beforehand within the endocrinology sections, hormones produced by the hypothalamus, pituitary, ovary, and in nonrodents, the adrenal gland, modulate the balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis within the reproductive tract. The trophic hormones are tumor promoters and potential nongenotoxic carcinogens due, partially, to their results on cell proliferation in the feminine reproductive tract of animals and girls. For this reason, potential shifts in the incidence of spontaneous tumors from hormone responsive tissues (pituitary, mammary gland, vagina, uterus, cervix, ovary, and clitoral gland) may happen in animal mannequin techniques. Of course, a toxicant may also produce neoplasms via a genotoxic pathogenesis. The estrous and menstrual cycles in healthy adult animals and women are synchronous; the reproductive tissues comply with a selected pattern manifested by coordinated morphologic and practical changes. Toxicity could alter estrous or menstrual cycle length or trigger asynchronous modifications in feminine reproductive tissues. These adjustments could also be harder to acknowledge without particular study designs that assess cycle length because of a number of factors together with the long, variable estrous cycle within the beagle dog; the small variety of nonrodents per group used in toxicology studies (generally three or 4); and the use of peripubertal nonrodents. However, for rodent studies, the variety of animals and study designs provides a possibility for the pathologist to recognize toxicitymediated shifts within the number of animals in several levels of estrous or a scarcity of coordination between the expected morphologic look of the uterus, vagina, and ovary for any particular stage of the cycle. The vaginal mucosa (B) is skinny (two or three layers thick) and the superficial epithelial cells have distinguished, mucoid cytoplasm. Direct toxicity of components of the feminine reproductive tract is less widespread; however, there are some specific examples of degenerative, inflammatory, and immune-mediated responses to damage within the reproductive tract. These embrace vaginal epithelial degeneration and inflammation on account of irritation, and degeneration and necrosis of ovarian follicles secondary to chemical toxicants or radiation that focus on rapidly dividing cell populations. The causes are based on our expertise and literature stories and are limited to patterns within the rat due to paucity of data due to the usage of immature or peripubertal nonrodents. The examples listed include those cited in the literature and unpublished observations. In virtually each case, we only record changes in the rodent as a end result of usually the nonrodent toxicologic research have been done in immature or pubescent beagle canine or cynomolgus monkeys. These courses of compounds include intercourse hormone receptor ligands, other nuclear hormone receptor ligands, and centrally energetic neurohormone receptor agents. Examples include bisphenol A for which evidence suggests opposed effects on ovarian meiosis and oocyte high quality and the organophosphate pesticide, methoxyclor and its metabolites, which target antral follicles in the rodent and primate ovary resulting of their atresia. As might be talked about later, xenobiotics that pharmacologically target rapidly dividing cell populations will negatively influence ovarian follicular growth, leading to atresia. Stress, Negative Energy Balance, and Senescence A widespread pattern of reproductive adjustments noticed in toxicology research is secondary to the results of stress and lowered food consumption, both widespread outcomes of administrating excessive doses of check brokers to younger, rapidly growing animals used in safety evaluation studies. The organ weight, gross, and histologic changes related to this frequent sample of nonspecific toxicity are listed in Table 18. Morphologic changes are easiest to determine within the vagina as a outcome of the uterine epithelium that lines the luminal and endometrial glands is just a single cell layer that can bear limited morphological adjustments beneath the influence of estrogen, androgens, and progesterone. In contrast, the vaginal epithelium from the anterior 2/3 of the vagina, owing to its multilayered structure and excessive turnover price, is in a position to bear a selection of adjustments and is a very delicate indicator of the hormonal status of the animal. The morphology of the ovarian interstitial glands additionally adjustments quickly with negative vitality balance. During the in-life portion of toxicity research, lodging may occur to the acute stress and meals consumption results. In these studies, there may be a combined phenotype at necropsy whereby the histologic pattern of previous cycle cessation is combined with a pattern of normal biking. In these situations, cycle asynchrony within the reproductive tract will be the predominant change. The toxicologic pathologist ought to carefully consider the meals consumption and clinical indicators in individual animals to appropriately interpret these varieties of postmortem changes within the feminine reproductive system. Differentiating cycle disruption on account of stress or unfavorable energy balance and primary take a look at agent�related results can be challenging. It is necessary that the toxicologic pathologist intently look at the doseresponse of the cycle disruption relative to the effects on animal meals consumption, scientific signs, and thymic weights and histology, the latter, in our expertise, being probably the most sensitive indicator of earlier or ongoing stress in animals. If cycle disruption is only observed at doses that produce decreased food consumption or vital clinical signs or postmortem changes indicative of stress, one may not be ready to assess whether or not there are primary results on the female reproductive system. However, if this sample of cycle disruption is noticed at doses that trigger little or no or no changes in meals consumption or clinical signs, a primary effect of the test agent should be considered. These changes can confound the evaluation of xenobiotic-related therapy results. Hyperprolactinemia Another common feminine reproductive toxicity pattern that toxicologic pathologists will likely expertise is that manifested by hyperprolactinemia in rats. Female rats are particularly delicate to the effects of hyperprolactinemia, and there are a number of lessons of take a look at brokers that induce a hyperprolactinemia phenotype in animals. The most common mechanism of hyperprolactinemia is the excessive prolactin secretion that happens when dopamine is depleted or antagonized by compounds corresponding to reserpine or phencyclidine hydrochloride. The constellation of adjustments related to hyperprolactinemia is printed in Table 18. It is necessary to notice that the histologic manifestations of xenobiotic-induced hyperprolactinemia might change with the chronicity of the publicity. The subsequent decline in ovarian steroid production ends in uterine and vaginal atrophy.
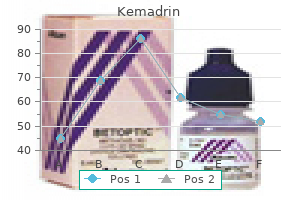
This process medicine dictionary pill identification 5 mg kemadrin purchase otc, and the extent of the resulting diarrhea symptoms kidney failure kemadrin 5 mg cheap mastercard, is best demonstrated with cholera toxin medicine lodge treaty purchase kemadrin 5 mg amex. This process leads to severe diarrhea and death, with little morphological proof of mucosal damage. Malabsorptive diarrheas related to loss of enterocytes, crypt cells or both, often accompanied by Gastritis and gastric ulceration Esophageal, stomach, and intestinal cancer, and/or acute gastritis Ulcerative, hemorrhagic, and necrotic gastroenteritis and/or colitis Ulcerative, hemorrhagic, and necrotic gastroenteritis Table adapted from Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology, second ed. These lesions perhaps site-specific, however, providing a clue to the type of toxicant concerned. By causing distension, these compounds elicit contractions that happen in either course along the bowel. In a couple of cases, for example, organophosphate-insecticide toxicosis, diarrhea is via prolonged stimulation of muscarinic receptors due to inhibition of acetylcholinesterase at the synapse. The consequences of diarrhea are systemic in nature, and embrace dehydration, acidosis, and electrolyte alterations. Intracellular hydrogen ion concentrations increase and potassium concentrations lower. This electrolyte imbalance results in improper upkeep of intracellular pH ranges, and reduces the exercise of multiple enzyme systems. Reduced intracellular potassium is the result of a failure in mobile electrolyte transport. Vomiting possibly stimulated by direct mucosal irritation or by stimulation of the vomiting center within the central nervous system. Vomiting can also happen if the esophageal or pyloric lumen is obstructed by a scar or neoplasm. Bilateral belly vagotomy and bilateral splanchnic nerve transection completely inhibit emesis induced by these anticancer medication. Agonists of dopamine D2 receptors similar to apomorphine, L-dopa, and bromocryptine act in the chemoreceptor set off zone of the brainstem area postrema. Phenothiazine medication with vital dopamine D2 antagonists properties, corresponding to chlorpromazine and promethazine, block the emetic actions of dopamine D2 agonists. Emetine, the precept ingredient of ipecac, and opiates, such as morphine, act nonspecifically on the chemoreceptor trigger zone to provoke an emetic response. The space postrema is unprotected by a complete blood�brain barrier, thus permitting chemical substances in blood to penetrate with relative freedom into this brain area. Polyps and neoplastic masses induced by carcinogenic brokers as well as partly or fully circumferential scars may end in bodily obstruction. This activity represents contraction of both longitudinal and round muscle layers. Neuronal networks concerned in peristalsis are complicated and incompletely understood; however, cholinergic excitation mechanisms play a significant position. These compounds trigger intestinal distension and elicit contractions that occur in either path alongside the bowel. Endogenous opioid peptides maybe involved in segmentation motility, since morphine locks the intestine right into a continuous segmentation pattern of motility. In morphine-dependent rats, diarrhea, which is the opposite of the acute results of morphine, is a major withdrawal occasion. Extrinsic nervous input affecting motility contains both stimulatory and inhibitory nerve fibers. Both vagal and sacral innervation to the large intestine is very energetic throughout defecation. Tonically lively inhibitory neurons can account for a low responsiveness of round muscles to myogenic pacemakers. A model toxicity of inhibitory nerve enter that results in suppression of both cholinergic and serotoninergic synaptic transmission is norepinephrine overdose. Spasm is a functional dysfunction, the opposite of ileus, and consists of accelerated exercise of circular muscular tissues with no exercise on inhibitory neurons. In these animals, the terminal section of the big gut lacks inhibitory neurons. However, the inflammatory response is generally much less extreme in primary toxicologic lesions than in main infectious (bacterial and viral) diseases. Gastritis is normally catarrhal (with large amounts of mucus), and may involve ulceration, hemorrhage, and lymphoid hyperplasia. Inflammation of any a half of the intestinal tract could be termed enteritis, but in practice this time period is regularly used to designate only small intestinal inflammation. Direct irritants usually trigger extra severe inflammation of the proximal intestine (duodenum) and fewer irritation of the distal tract (ileum and large intestine). However, mercury could cause lesions of the massive intestinal mucosa as a outcome of transport from the blood into the colonic lumen. Chronic inflammatory reactions is usually a primary or secondary impact in toxicologic lesions. Immunemediated responses are characterised by accumulation of persistent inflammatory cells (lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages), though they might have an energetic mobile element consisting of neutrophils and eosinophils. Diseases that end in chronic irritation or damage to the lamina propria or lymphatic vessels trigger malabsorption of fatty acids and weight loss. Fatty acids and monoglycerides are packaged into chylomicrons by the enterocytes earlier than being exported to the central lacteal and into the lymphatic circulation. Consequently, longstanding damage to the lymphatic circulation may end up in significant malabsorptionrelated issues. The actual frequency of toxicity in commonly used laboratory animals is lower than one might count on, primarily as a outcome of the excessive rate of cellular proliferation that can happen within the reparative response to any lack of mucosal epithelium. Additionally, mixing an injurious compound with luminal contents dilutes the toxin and its effects. Epithelial cells can also bear biochemical adjustments that allow them to functionally reconstitute mucosal integrity after a poisonous insult. Many of these identical enzymes are involved in compound metabolism and biotransformation. Mucosal epithelial cells work together with reactive compounds by way of both membrane-bound and cytoplasmic enzymes. This course of occurs by way of mucosal cell enzymes, together with epoxide hydrolases and glucuronosyl transferases. Unique forms of adaptive mucosal safety occur after publicity of the mucosa to mild irritants. Resealed or healed cells could stay viable for up to 24 hours within the stomach and forty eight hours within the gut. Under normal dietary conditions and well being, the range of proliferation charges for the most actively dividing mucosal cells (stomach to colon) is 3�6 days. When the intestine encounters a noxious agent, enterocyte half-life is lowered to shortly exchange injured cells. If the damage is transient, mucosal alternative, and normal microarchitecture will recuperate within three days. However, prostaglandins of the E collection suppress enzyme release and superoxide anion manufacturing by neutrophils. It produces vasodilation of gastric microvessels and exerts an antiaggregation impact on platelets. It additionally stimulates secretion of mucus by surface mucous cells and helps maintain protection in opposition to luminal acid. Stomach Mucosal protection and protection, initially termed cytoprotection, was initially described as the ability of prostaglandins to forestall macroscopic proof of gastric mucosal injury. This protective phenomenon is partially depending on the antisecretory activity of prostaglandins, and is dose- and route-dependent. It is presently understood that several mechanisms apart from prostaglandin-mediated pathways are answerable for stopping mucosal damage by each regular digestive processes and injurious compounds. These embody increased quantities or modifications of mucous gel covering the mucosal epithelial floor, increased secretion of bicarbonate, increased resistance to acid back-diffusion, and elevated blood flow. Additionally, mucosal protection is mediated in part by lipids (neutral lipids and phospholipids) within the mucous gel layer. These lipids enhance the hydrophobicity of the mucous gel, resulting in repulsion of watersoluble compounds (including many toxicants). These brokers permeate the mucous barrier and immediately damage the underlying epithelium. Since the mucous layer remains intact, it facilitates epithelial repair in these conditions. With persistent mucosal harm, mucous-gel secretion is impaired and mucous-gel loss will exceed production.
Discount kemadrin 5 mg amex. Acupressure Points to Stop Smoking.