

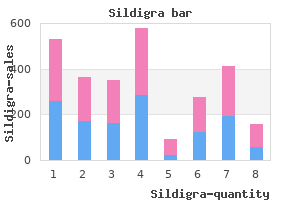
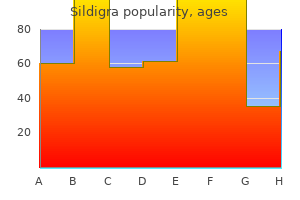
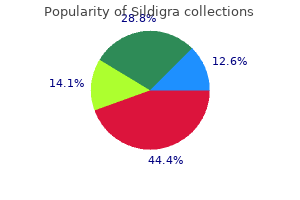
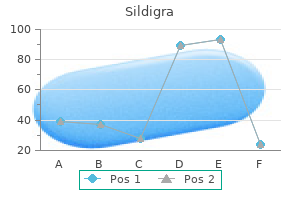
Sildigra
"Sildigra 100 mg generic overnight delivery, causes of erectile dysfunction in 60s".
D. Nerusul, M.A., M.D.
Deputy Director, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Certain vulnerabilities to this alteration erectile dysfunction 60784 sildigra 100 mg purchase online, including age erectile dysfunction causes & most effective treatment generic 50 mg sildigra overnight delivery, illness erectile dysfunction protocol review article order sildigra 100 mg, brain disease, or medication(s), might all play a component in this disorder. In their seminal work on delirium, revealed in 1959, Engel and Romano (41) reviewed indicators of delirium and described "overall slowing of posterior background rhythm" (p. They reported the electrical modifications as reversible and related to the extent of the disturbance. Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is extensively accepted to be produced also by an extrinsic factor, particularly thiamine deficiency. However, a more recent evaluation (104) has advised some attainable genetic contribution in thiamine-inadequate diets. The usually agreed-upon pathological lesions are situated bilaterally within the temporal lobes and contain the associated hippocampus and mammillary body (57, 67). Over time, the anatomical findings (senile plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and granulovacuolar degenerative changes) of the two groups of sufferers have been discovered to be similar (97, 118), as are the medical shows. As these downstream neuropathological changes are being further outlined, the upstream genetics, initiation, evolution, danger elements, and potential therapies are coming extra into focus. Vascular dementia is generally thought to outcome from cerebrovascular disease or trauma. The course is normally associated with the underlying cause and could additionally be fast, stepwise progressive, or plateau with out advance. The association between large strokes and detectable changes in cognition is understandable, but the precise correspondence of sluggish lack of neurons to progression of formal dementia is much less clear. It is likely, however, that refinements in all strategies will improve such correlations in the future. One of the harder decisions physicians must make issues sufferers with delirium or dementia whose behavior raises questions about their psychological capability. Losing or giving away massive sums of cash, writing bad checks, extreme carelessness of gown, unprecedented sexual habits. Dementia complicated by secondary depression is probably considered one of the psychiatric issues related to suicide threat, though it accounts for less than a small portion of suicides (93). The function of dementia-especially that of Alzheimer disease-as an important risk factor for critical falls has also been acknowledged (84). Of observe, nonetheless, substantial numbers of household (19, 20) and linkage (47, 48) research over the past 30 years have shown that less than 5% of dementia instances happen with early onset (prior to age 65), observe an autosomal dominate pattern of transmission, and are linked to three chromosomes (1, 14, and 21) (47, 54). Genome-wide affiliation research have begun to counsel a contribution by other potential danger factors, including cholesterol, inflammatory, and endosomal synaptic vesicle recycling mechanisms (69). Finally, in the largest twin research of dementia conducted on Swedish twins, heritability was estimated at 58%�79% relying on the model utilized (46). Much work remains so as to fully understand the genetic (and environmental) contributions to this dysfunction. The crucial query in every case is whether the affected person exhibits definite inattention, disorientation, or reminiscence impairment. If a affected person with one other psychiatric sickness develops inattention, disorientation, or reminiscence impairment, one ought to suspect that something else has developed: a drug reaction or medical or neurological sickness. When a affected person is unable or unwilling to cooperate within the psychological status examination, a delirium could additionally be suspected. If there has been a sudden change in behavior, speech, or method, and if the behavioral change develops in a medical state of affairs that regularly predisposes to a delirium, the analysis should be thought-about. A definitive analysis should await evidence of inattention, disorientation, or reminiscence impairment; these will usually turn out to be obvious as the patient is noticed fastidiously. At the same time, sure measures typically assist in the management of the neurocognitive dysfunction itself. A calm, sympathetic, reassuring approach can flip a frightened, combative patient into a quiet, cooperative one. Patients with a delirium usually misinterpret stimuli and have unpredictable emotional responses. It is important, therefore, to provide a well-known, stable, unambiguous setting for such patients. Repeated simple explanations and frequent reassurance from acquainted nurses, attendants, or family members could additionally be helpful (86). Patients do higher with fixed gentle; shadows or the darkish simply frightens them. Delirium is, actually, often precipitated by sedatives or hypnotics and may subside when such drugs are discontinued. Usually a relative, friend, or nurse who is prepared to be with the patient constantly-talking to the affected person, explaining things, reassuring him or her-can calm the affected person sufficient to permit appropriate care with out restraints on a general hospital service (86, 87). For sufferers with agitated delirium, bodily restraint could additionally be essential (63), for example, to forestall the confused or frightened affected person from pulling out intravenous traces and urinary catheters or striking caregivers, and to avoid falls. Obviously, a restrained affected person should be watched carefully, and the beforehand described measures ought to be continued with the hope of calming the person shortly, making any period of restraint transient (86, 87). The particular remedy for Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is initially parental thiamine followed by oral administration. A substantial variety of these individuals require cautious monitoring within the home or establishment. Too often the impact on family members is overwhelming, and this have to be thought of by the doctor so that acceptable steps can be taken to reduce the burden, a minimum of intermittently (36�38). All have been associated with improvements in international functioning and cognition (30, ninety four, 112, 120). The result of these improvements has been a reduction in impaired behavior, stabilization (albeit temporary) of daily living actions, delay of placement within the nursing home setting, and decreased caregiver burden (32). Report from the Registration Committee of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association. The Oslo research of untreated syphilis; an epidemiologic investigation of the natural course of the syphilitic infection based mostly upon a re-study of the BoeckBruusgaard materials. Risk of dementia amongst white and African American relations of sufferers with Alzheimer disease. Wernicke encephalopathy and beriberi throughout total parenteral diet attributable to multivitamin infusion scarcity. Linkage of an Alzheimer illness susceptibility locus to markers on human chromosome 21. Effect of lorazepam with haloperidol vs haloperidol alone on agitated delirium in patients with advanced most cancers receiving palliative care: a randomized medical trial. Frequency and presentation of depressive signs in patients with major degenerative dementia. Genetic sensitivity to thiamine deficiency and development of alcoholic organic brain illness. Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 affiliation with dementia in a populationbased study: the Framingham examine. Dementia in patients undergoing longterm dialysis: aetiology, differential diagnoses, epidemiology and management. The communication of suicidal intent: a research of 134 circumstances of successful (completed) suicide. Brain harm in continual alcoholism: a neuropathological, neuroradiological and psychological review. Dementia in the acute hospital: potential cohort research of prevalence and mortality. Pharmacokinetic and clinical studies in patients with cimetidine-associated psychological confusion. Occurrence and end result of delirium in medical in-patients: a scientific literature review. Pancreatic encephalopathy and Wernicke encephalopathy in affiliation with acute pancreatitis: a scientific study. Association of postoperative delirium with raised serum ranges of anticholinergic medicine. Isaac Bashevis Singer The purpose of a psychiatric analysis is to study psychological function and to diagnose a psychiatric dysfunction or problems if present.
Language is essential in discussing erectile dysfunction jacksonville doctor sildigra 120 mg buy discount on line, agreeing erectile dysfunction massage sildigra 25 mg cheap on line, and speaking what the rules are erectile dysfunction san francisco safe sildigra 50 mg. Social learning is important in transmitting what the principles are to everybody within the group, and people also can study what occurs when rules are damaged and the likely pay-offs for either co-operating or defecting by observing others. For institutions like this to work, transgressions must be punished, and be seen to be punished, to ensure that compliance with the principles to be maintained and co-operation to be sustained (Ostrom 1990; Boyd and Richerson 1992; Anderies and Janssen 2016). To what extent institutions are possible in non-linguistic species or in species with out our psychological capabilities is an open query (Ak�ay et al. These features certainly make it easier to develop and transmit guidelines, however conceivably mechanisms surrounding reputation (and indirect reciprocity), punishment, and expectations about behaviour and the implications of defecting could be transmitted through social learning in other species to create behavioural patterns that had been comparable in some respects to forty four three How the Dual Inheritance of Genes and Culture Shapes Behaviour institutions. Because they seem to be peculiar to humans, establishments have acquired comparatively little consideration in evolutionary models of co-operation, even when utilized to people. While institutions have been a spotlight of research in several social science fields, understanding how establishments work together with different culturally inherited traits and how both evolve together over time has received much less formal consideration and is a crucial topic for future research in cultural evolution (Currie et al. Features corresponding to institutions and social norms are group-level emergent properties of the interactions between individuals that are made possible by social learning (Smaldino 2014). This has implications for the way selection can act on groups and result in the unfold of co-operative behaviour. However, cultural evolutionary processes might create circumstances under which selection between groups can turn out to be an important pressure. As we saw in a earlier section, frequency-dependent processes and active conformism can act to maintain cultural variation between groups even within the face of physical migration of individuals (Boyd and Richerson 1985b; Bell et al. Individuals can be incorporated inside the victorious group or disperse into other teams. The key point is that the earlier group and its associated norms and establishments no longer exist. Groups may also go extinct if people migrate based on the traits that totally different teams exhibit, or as a outcome of the perceived success of different groups (Boyd and Richerson 2010). More usually, there also appears to be a confusion around how terms are outlined and utilized in totally different analysis traditions: What are probably the most salient units of analysis, and what are acceptable measures in making an attempt to assess these fashions This has consequences for understanding the extent to which culture might have shaped genetic evolution (see below) in relation to the evolution of genetic traits that would help canalize prosocial behaviours. For example, researchers have used cross-national survey knowledge to assess the extent to which sufficient variation in traits exists between groups (Bell et al. However, some authors have conducted empirical studies of co-operation in numerous populations that problem the assumptions in regards to the degree of variation within and between groups, and the extent to which competition between teams is related to in-group co-operation (Lamba and Mace 2011; Mace and Silva 2016). The outcomes of this study counsel that between-group competitors can select for increasing group size which is facilitated by the adoption of pricey institutions concerned in complicated social organization. We have already discussed how genes hold cultural evolution on something of an extended leash, and that genes will construct organisms that may on average learn from others in ways that are adaptive. In this section, I give further consideration to the possibility that the 2 can coevolve such that organic evolution can have important consequences for cultural evolution and vice versa, a course of we can call gene�culture coevolution (Lumsden and Wilson 1980; Cavalli-Sforza and Feldman 1981; Boyd and Richerson 1985b; Durham 1991; Feldman and Laland 1996; Laland et al. The adoption of a model new cultural follow can expose genes to new selection pressures in two methods (Richerson et al. First, cultural traits can make survival and copy potential in novel environments and facilitate migration into environments to which genes had not beforehand been uncovered. Here genes, tradition, and the surroundings are represented in an artificially summary method as collections of specific models at completely different points in time (t0, t1. Changes in different aspects of these techniques are represented by modifications in color. Aspects of 1 system can completely alter or cause evolutionary change in another system. Examples are given of (a) a cultural innovation making a novel selection pressure on a gene, (b) a genetic mutation that facilitates a new cultural trait, (c) a cultural modification of the environment, that (d) feeds back and causes a response in a unique side of culture. Exposure to these new environments selected for genetic modifications related to extra robust physiques and lighter skin pigmentation, that have been better tailored to colder temperatures and decrease mild ranges. Under this mechanism, the relationship between cultural evolution and biological evolution is considerably indirect, and may be more precisely termed culture-mediated genetic evolution. Second, the adoption of cultural practices can even lead to extra direct selection pressures whereby the effectiveness of a cultural adaptation is supported or enhanced by subsequent genetic adjustments. Perhaps probably the most studied instance of direct gene�culture coevolution is the adoption of dairy farming and the evolution of lactose tolerance (Holden and Mace 1997; Tishkoff et al. This is because the manufacturing of the enzyme for digesting milk (lactase) is switched off in most individuals after infancy. The capacity to drink and digest milk supplies certain adaptive benefits � it offers a daily source of energy and essential nutrients corresponding to vitamin D and calcium. The frequency of individuals possessing the lactose tolerance allele is higher in cultures that have a historical past of keeping sheep, goats, or cattle and commonly drink milk from these animals. Yam farming includes chopping down forests, which leads rain to acquire and create standing bodies of water, which is an surroundings conducive to malaria-bearing mosquitoes. It is argued that this drove subsequent selection on genes that trigger sickle cell anaemia, which may lead to premature demise but additionally offers safety in opposition to malaria (Durham 1991) (but see below). The genetic adjustments that happen in both culturally mediated genetic evolution and direct gene�culture coevolution can of course end in further feedback processes such that the cultural change is stabilized by the genetic adjustments. The theoretical risk of gene�culture coevolution is lengthy established, and may be extra typically linked to the ideas of area of interest development (Odling-Smee et al. Whilst there was a lot of theoretical development of the idea of gene�culture coevolution (including a giant number of mathematical models), empirical research and concrete examples of gene�culture coevolution have been fewer. The evolution of lactose tolerance stays very a lot the go-to example of gene�culture coevolution as a result of the twin facts that the genetics underlying lactose tolerance are comparatively simple and it relates to a cultural innovation that occurred comparatively lately in certain parts of the world. Recent years have seen an explosion in our data of human genetics and this will help to provide evidence for gene�culture coevolution. Genetic and genomic methods allow us to determine regions of the genome that present statistical signatures of having undergone selection (Hawks et al. The perform of many putatively chosen genes can be inferred primarily based on earlier information or inferences about genotype�phenotype relationships. A sample emerges from these analyses (Tishkoff 2015) in that they commonly relate to diet (detoxification of plant secondary compounds, alcohol metabolism, digestion of milk and dairy products, processing of excessive levels of dietary fat in Inuit populations), immunity or responses to pathogens. There are numerous explanation why tradition may not exert sufficient of a selective force on genes for coevolution to be important. Here again is a possible cause why lactose tolerance is a convincing instance; the physiological ability to digest lactose in later life is a organic course of for which a cultural response is harder (although certain milk-processing techniques similar to cheese making and ageing forty eight three How the Dual Inheritance of Genes and Culture Shapes Behaviour scale back lactose content). Another potential issue affecting the power of choice on genes is the speed at which tradition evolves. This is to not say that all cultural change is extremely fast, and tons of cultural traditions can persist over many generations. We have lots of proof that human genes have been underneath choice in latest human historical past and we are able to make believable arguments for the position of culture in either mediating or driving such adaptations. Future work will need to go beyond such plausible narratives and extra rigorously take a look at gene�culture coevolutionary hypotheses against competing explanations. Ideas relating to earlier stages of human evolution could prove difficult to assess in this respect. A gene�culture coevolution account of the emergence of the human language faculty is plausible, however is difficult to test as we all know so little concerning the early phases of language evolution. However, our capability to assess such hypotheses can enhance if we all know extra about more modern examples and the situations under which gene�culture coevolution is most likely to happen. This has implications for understanding the potential importance of the effects of culture or social studying on genetic evolution in other species. There are currently few convincing examples of gene�culture coevolution in non-human animals. This, nevertheless, represents correlated evolution between genes and tradition somewhat than proof that any explicit alleles have been selected due to this sponging behaviour. Situations the place socially discovered behaviours have enabled species to move into novel environments or be uncovered to new foodstuffs, or where social studying has led to environmental modifications may symbolize potential candidates for assessing the existence of culturally influenced genetic selection in different species. The human reliance on tradition as a way of adaptation and our capacity for cumulative culture, with high-fidelity transmission and long-lasting behavioural traditions, could imply that gene�culture coevolution is extra doubtless in people than different species.
Once shortly erectile dysfunction zinc supplements discount sildigra 25 mg visa, a curious thing might happen: a person may recall things that happened during a earlier ingesting period that had been forgotten when sober what age can erectile dysfunction occur buy sildigra 50 mg free shipping, such as hiding cash or alcohol erectile dysfunction treatment by yoga generic sildigra 100 mg with visa, forgetting about it when sober, and remembering it again during the next drinking episode. Sometimes she would jot down notes for a letter and begin writing it however not end it. After rapport is developed and the examiner is prepared to turn to this section, the scientific strategy could additionally be direct ("Tell me about your current and past use of alcohol") or indirect ("Has alcohol ever interfered along with your social, work, interpersonal or authorized affairs Even though the screening components of those instruments may be useful to the clinician in creating a set of questions and even perhaps a mode of strategy, the reader is reminded that temporary surveys neither capture all circumstances nor diagnose sickness. The clinician should take the time to develop rapport and talk with the patient to get hold of a specific history of alcohol consumption patterns and adequate info for diagnostic assessment of problem consuming. Arcus senilis-a ringlike opacity of the cornea-occurs commonly with age, causes no visible disturbance, and is taken into account an harmless situation. Alcohol will increase fats in the blood and extra patients with alcohol addiction have the ring than others their age (9, 38). A purple nostril (acne rosacea) suggests the owner has a weak point for alcoholic drinks. Often, nevertheless, folks with pink noses are teetotalers and even rabid prohibitionists, they usually resent the insinuation. Red palms (palmer erythema) are additionally suggestive, but not diagnostic, of alcoholism. Cigarette burns between the index and center fingers or on the chest and contusions and bruises should raise suspicions of alcoholic stupor. Painless enlargement of the liver could suggest a larger alcohol intake than the liver can process. Severe, fixed upper belly ache and tenderness radiating to the again indicates pancreatic inflammation, and alcohol sometimes is the trigger. Reduced sensation and weak point in the toes and legs may happen from excessive consuming. These checks are hampered by low sensitivity and specificity and variable performance in numerous populations. In their seek for indicators of excessive alcohol use, physicians sometimes slip right into a moralistic attitude that alienates the patient. For private causes, physicians may imagine any drinking is wrong, but they nonetheless should pay attention to analysis suggesting that average ingesting may actually confer specific well being benefits and even contribute to longevity (96, 99). The lowest mortality from all causes is associated with consumption of one (for women) to two (for men) alcoholic drinks per day. The risk of cancer, however, increases with any quantity of alcohol consumed, even at the lowest levels. Greater amounts of alcohol consumption are especially associated with danger for breast, liver, esophageal, colon, and head and neck cancers (79, 99). The potential advantages of moderate drinking have to be weighed in opposition to potential for improvement of alcohol use issues and data demonstrating that alcohol contributes to car accidents, hypertension, breast most cancers, adverse outcomes for sufferers with hepatitis C, and start defects related to drinking throughout pregnancy (128, 130). Unlike opioids and nicotine, alcohol has no identified receptor within the human mind (35). Alcohol impacts numerous neurotransmitter techniques in numerous mind regions that are identified to play a role in reward and reinforcement processes thought-about fundamental to addictions. The dopamine system is taken into account to be central in the development and upkeep of alcohol dependence. Alcohol increases the amount of dopamine on this pathway, and the quantity of dopamine increase is associated with the level of high or euphoria reported from alcohol ingestion. With alcohol habit, alcohol-conditioned cues by themselves immediate will increase in striatal dopamine, much more than with actual alcohol ingestion. Once habit to alcohol has developed, the dopamine response to alcohol ingestion is blunted. During protracted withdrawal in people with alcohol use problems, dopamine receptors lower within the striatum, and this is additional associated with decreased operate of the salience attribution areas of the orbitofrontal cortex and also of inhibitory controls within the anterior cingulate gyrus. The dopamine circuits concerned in reward and conditioning thus become imbalanced with mind circuits concerned in govt capabilities (emotional management and decision-making). This imbalance is postulated to contribute to the compulsion to drink and loss of management that are the medical hallmarks of alcohol use disorder (140). Dysregulation of serotonin pathways has been demonstrated to be related to impulsive alcohol consumption and with ingesting for the needs of self-medication of tension, contributing to excessive and compulsive drinking, sensitivity to the negative reinforcing effects of alcohol, and relapse conduct. Genotypic variations in mind serotonin circuitry might properly contribute to many different pathways to the development of alcohol use disorders (87). If they do, the physician should be alerted to the potential of a major mood disorder or mind disease. Alcohol use problems have been studied less extensively in women than in men, but the evidence means that the course of the dysfunction is more variable in girls. In girls, the onset typically happens later (23, 61) and spontaneous remission apparently is less frequent (30). Women with the dysfunction are more likely than their male counterparts to have a history of depressive and nervousness issues (55). The patterns are fairly variable, and no explicit pattern is related solely with alcohol use dysfunction. Overall, alcohol dependence is a chronic remitting and relapsing dysfunction with intervals of remission lasting for variable lengths of time. Alcohol use disorder has a higher "spontaneous" remission rate than is usually recognized. The incidence of first admissions to psychiatric hospitals for alcohol problems drops markedly in the sixth and seventh decades, as do first arrests for alcohol-related offenses. Although the mortality rate among people with alcohol use disorder is probably two to 3 times that of reasonable drinkers, attrition by way of death might be insufficient to account for the obvious decrease in downside ingesting in center and late middle life (51, 137). Based on questionnaire knowledge obtained from sufferers with alcohol use problems, Jellinek promulgated earlier views that manifestations of the disorder observe a natural chronological order, with blackouts being one of many early "prodromal" symptoms of the sickness (64). Frequently, after years of heavy problem-free consuming, a person might experience numerous problems in a short period. In 1960, Jellinek (65) developed a typology subdividing alcoholism along observable consuming patterns. Subsequent analysis by Edwards and Gross in 1976 (34) moved the sector towards establishing a reliable foundation for prognosis of alcohol dependence syndrome through the use of criteria. By the time individuals with alcohol problems seek the advice of a physician, many have developed medical and social complications from consuming. High charges of marital separation and divorce accompany alcohol use problems (27). People with alcohol use disorder usually have job troubles, together with frequent absenteeism and job loss. They also have a excessive frequency of accidents-in the home, on the job, and while driving vehicles. More than one-third of highway fatalities in the United States involve a driver who has been consuming, however with national programs carried out to address this problem, the charges have dropped substantially over the last three decades (102). Nearly half of convicted felons have an alcohol use disorder (45), and about half of police actions in large cities are related to alcohol-related offenses. Medical complications fall into three categories: 1) acute effects of heavy drinking, 2) chronic results of heavy ingesting, and 3) withdrawal effects. Consumption of very giant quantities of alcohol can lead on to demise by miserable the respiratory center in the medulla. Acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis occasionally happens from a single heavy consuming episode. Nearly each organ system may be affected, instantly or indirectly, by persistent, heavy use of alcohol. The gastrointestinal system is particularly susceptible to damaging effects of alcohol. Chronic gastritis might occur, though persistent Helicobacter pylori an infection has been found to be causal in most alcoholic gastritis and not the direct effects of alcohol itself. The most damaging effect of alcohol on the gastrointestinal tract is to the liver. Exactly how alcohol damages the liver remains to be not totally understood, regardless of a long time of research.
In termites erectile dysfunction types sildigra 100 mg cheap with mastercard, modifications in aggression following alterations to the bacterial communities with antibiotic remedy seem to be mediated by disruption of faecal odour cues which may be used in nest-mate recognition (Matsuura 2001) impotence 35 years old generic 50 mg sildigra fast delivery. The impact of the intestine microbiota on aggression levels can even have implications for the establishment success of invasives erectile dysfunction treatment in tampa purchase 120 mg sildigra with visa. In Argentine ants (Linepithema humile), invasion success is expounded to level of aggression and survival that in turn could also be influenced by intestine microbiota. Antibiotic therapy barely increased ranges of interspecific aggression, however resulted in vital lower in survival. This increased mortality may be due to ants participating in aggressive interactions for longer periods of time (Lester et al. In general, the release from old pathogens and/or the unfold of novel pathogens throughout interplay with new competitors in the course of the invasion phase is an important element dictating the success of invasive species. For instance, red hearth ants (Solenopsis invicta) have fewer pathogenic infections of their introduced vary compared to their home range (Yang et al. Invading harlequin ladybirds (Harmonia axyridis) gain a aggressive edge by carrying parasitic microsporidia in their haemolymph which would possibly be deadly to native ladybird beetles (Vilcinskas et al. To what extent the gut microbiota affects this interplay remains to be quantified, however there are tantalizing information suggesting it could play a role. Toxoplasma gondii can solely reproduce sexually in cats, and hence this behavioural alteration leads to elevated transmission of toxoplasmosis as infected mice usually have a tendency to be eaten (Ingram et al. In mice, females that are heterozygous for the t-complex (see above) are less more doubtless to perform exploratory behaviours and eat much less food than homozygous wild-type females, 168 eight the Effect of Non-Self Genes on the Behaviour of Hosts and it has been suggested this can be an adaptive behaviour as heterozygous females live longer than wild-type females (Auclair et al. It is unclear whether or not this could be a aspect effect of lower metabolic fee associated with carrying the t-haplotype. In Aedes triseriatus mosquitos, gregarine endosymbionts have an effect on larval behaviour in a way that has been documented to cut back the risk of predation. Infected larvae change their feeding behaviour, thrash less incessantly and spend extra time in refuges in the presence of predators than uninfected larvae (Soghigian et al. Overall, the impact of lowered predation on contaminated hosts means that gregarines may in reality be mutualistic in some circumstances. Locusts (Locusta migratoria) are well known for his or her ability to shift between gregarious and solitary behaviour based mostly on insect density (Applebaum and Heifetz 1999). Aggregation behaviours are achieved by way of a combination of visual, tactile, and chemical cues, with faecal odour taking part in a big role (Pener and Yerushalmi 1998). Recent work has shown that this behavioural alteration of locusts by microsporidia includes modulation of the host immune response that suppresses the growth of hindgut bacteria that produce aggregation pheromones (Tan et al. The microsporidia also suppress manufacturing of dopamine, which has been implicated in sustaining gregariousness (Shi et al. Behavioural experiments show that these odour cues are important as long-distant attractants to guide flies to suitable meals sources (Venu et al. Healthy locusts positioned in chambers containing scats from microsporidia-infected locusts are much less prone to display swarming behaviours than locusts placed in chambers with scat from uninfected individuals. This is caused by microsporidia suppressing the growth of hindgut bacteria that produce the aggregation pheromones, and by suppressing manufacturing of a neurotransmitter that helps preserve gregariousness. The function of gut bacteria on host feeding and ensuing fitness has been well studied (Wong et al. The intestine is filled with receptors that are immediately connected with the neuroendocrine system, and several other of those receptors are designed to detect microbial metabolites that in flip affect host feeding (Tan et al. Gut bacteria can have an effect on food plan consumption by altering cravings by the host for particular meals varieties and nutrients which would possibly be beneficial for the microbes themselves (Alcock et al. Flies favor helpful bacteria, but these preferences are modified by the intestine microbiota, and early microbial publicity form the precise desire of the adult fly. This signifies that maternal deposition of microbes on eggs, for instance, can affect the feeding choice of their offspring (Funkhouser and Bordenstein 2013). Coevolution between host dietary needs on the one hand and talent of the microbiome to synthesize specific vitamins on the opposite, has formed host�symbiont associations, at times promoting obligate dependence usually leading to highly decreased symbiont genome dimension (Moran and Sloan 2015; Wilson and Duncan 2015; Fisher et al. There can also be a growing realization that the gut microbiota is a key regulator of the host immune system (Rosenberg and Zilber-Rosenberg 2016). For instance, honeybees upregulate gene expression of antimicrobial peptides in the presence of gut microbes that seem to confer pathogen protection (Kwong et al. However, at times the intestine microbiome can have unfavorable influence on host feeding behaviour by resulting in overeating and weight problems or intake of potentially harmful substances (Rosenberg and Zilber-Rosenberg 2016). Host�microbe associations clearly contain each positive and negative feedbacks, emphasizing that this relationship will not be intrinsically parasitic or mutualistic, but will rely upon the fitness outcomes which are more likely to range relying on environmental conditions (Wong et al. Infected planthoppers present vital fecundity decrease but also significantly shortened nymphal stage length. Infected people also differ in their feeding behaviour by feeding for longer, presumably to compensate for his or her lower fecundity (Wan et al. Bumblebees contaminated by gut parasites present lowered capacity to use floral information throughout foraging (Gegear et al. Many microbes and endosymbionts instantly target the mushroom our bodies of insect brains that influence sensory learning and reminiscence. Reduced studying capability could be costly since terrestrial crustaceans such as isopods use associative studying in actions such as mating, egg laying, and foraging (Dukas 2008). Similarly, Wolbachia can impair learning and reminiscence in Trichogramma brassicae parasitoid wasps. Infected wasps present reduced capacity to be taught to affiliate a novel odour with a reward (a host egg) (Farahani et al. Previous work has additionally shown that Wolbachia impairs determination making throughout patch exploration on this species, with contaminated wasps being less efficient in assessing the nutritional worth of hosts displaying a decreased capability to discriminate between unparasitized and parasitized hosts, and wanted to forage more frequently than uninfected people (Farahani et al. Collectively, these effects favour transmission of Wolbachia by encouraging contaminated wasps to search out new environments. In honeybees and bumblebees, people with experimentally challenged immune techniques have poorer learning and reminiscence (Mallon et al. This might in part be as a result of the energetic stress imposed by activating the immune system, but in addition because of a compromised gut microbiota (Kwong and Moran 2016; Gomez-Moracho et al. Conversely, reminiscence formation was found to be impaired in germ-free mice missing a gut microbiota, and diets that induced modifications within the microbiota also altered the reminiscence in mice (Gareau et al. Similarly, disruption of the retrotransposon-derived Zcchc16/Mart4/Sirh11 gene in mice leads to irregular behaviours related to cognition and reminiscence (Irie et al. Similarly, many cellular genetic components are able to regulate expression of genes in key regulatory gene networks with large impacts on behaviour. The impacts of Wolbachia and the microbiome on mate choice in Drosophila melanogaster. A selfish genetic element influencing longevity correlates with reactive behavioural traits in feminine home mice. The impact of Wolbachia, male age and mating historical past on cytoplasmic incompatibility and sperm switch in Drosophila simulans. The institution of intracellular symbiosis in an ancestor of cockroaches and termites. Altered mating behavior and pheromone production in feminine Helicoverpa zea moths infected with the insect virus Hz-2v. Wolbachia associations with bugs: successful or shedding against a master manipulator. Mind-altering microorganisms: the impression of the intestine microbiota on brain and habits. Removing symbiotic Wolbachia bacteria particularly inhibits oogenesis in a parasitic wasp. Nutritional interactions in insect-microbial symbioses: aphids and their symbiotic micro organism Buchnera. Quantitative evolutionary genomics: differential gene expression and male reproductive success in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromatin variation related to liver metabolism is mediated by transposable parts. Widespread lateral gene transfer from intracellular micro organism to multicellular eukaryotes. Decrease of memory retention in a parasitic wasp: an impact of host manipulation by Wolbachia Bumble-bee foragers contaminated by a gut parasite have an impaired capability to utilize floral data.
Review the overall patterns of chromosome alignment along the metaphase plate throughout mitotic and meiotic divisions erectile dysfunction solutions pump trusted 50 mg sildigra. Thus erectile dysfunction doctor mn discount sildigra 120 mg with mastercard, for example erectile dysfunction causes treatment buy generic sildigra 100 mg online, the sister chromatids of 1 chromosome will every carry a duplicate of D1. In every of the other three chromosomes, the sister chromatids might be equivalent for one of the other alleles. During mitotic metaphase, chromosomes align in single file and in an arbitrary order alongside the metaphase plate. In meiotic metaphase I, homologs align opposite one another along the metaphase plate. Any order of the four chromosomes in single file along the metaphase plate is a correct order. Homologous chromosomes align reverse one another alongside the metaphase plate in meiotic metaphase I. The consequence of synapsis is that homologs align subsequent to one another and on reverse sides of the metaphase plate in metaphase I. The absence of synapsis in mitosis leads chromosomes to align in any order along the metaphase plate in mitotic metaphase. His screening of flies from the wild and from his laboratory-raised shares yielded occasional flies with a phenotype different from the wild kind. Morgan set up crosses between these suspected mutant flies and wild-type flies to look at the inheritance of mutations. Over several years, Morgan discovered many phenotypic variants that have been due to the inheritance of gene mutations. X-Linked Inheritance While Sutton and Boveri had been observing chromosome actions throughout meiosis, a researcher named Nettie Stevens, who in 1903 became one of the first ladies in the United States to receive a Ph. The cross produced 1237 F1 flies, all with purple eyes-a outcome indicating dominance of the wild kind over the mutant. The surprising end result from this cross prompted Morgan to test eye-color inheritance in a reciprocal cross of his first cross. After perpetuating the white-eye lineage for several generations, Morgan had each men and women with white eyes in his possession, and he mated a white-eyed female with a wild-type, red-eyed male as a reciprocal to his unique cross. The variations between the outcomes of the reciprocal crosses confirmed for Morgan that eye color was inherited in another way from other traits he had studied and from traits Mendel had studied. Suspecting that eye-color inheritance was linked to intercourse and to intercourse chromosomes, Morgan proposed diagrams of the 2 reciprocal crosses. In the figure, w represents the recessive mutant allele for white eye and w + the dominant wild-type allele for purple eye. In Cross A, the only X chromosome of a white-eyed male carries a recessive allele designated w. The X chromosomes of the female each carry a dominant allele w + that produces purple eye colour. The F1 of this cross are red-eyed males that are w +Y and red-eyed females which might be w +w. The F2 of this cross include equal proportions of white-eyed (wY) and red-eyed (w +Y) males and red-eyed females which may be, in equal proportions, w +w + and w +w. Cross B between a white-eyed female and a red-eyed male produces red-eyed feminine and white-eyed male F1 progeny in addition to equal proportions of red- and white-eyed men and women in the F2. Specifically, we use the time period hemizygous, a word meaning "half zygous," to refer to male genotypes for X-linked genes. Note also that males can transmit both the X chromosome or the Y chromosome, but that the X chromosome is handed completely to female progeny and the Y chromosome solely to male progeny. � X wY White F1 X w+X w Red F2 � X w+Y Red X w+ Y X w+ X w+X w+ Red X w+Y Red F2 females have pink eyes, males � � are 1 red: 1 white. Q Observing different outcomes in the F1 of Cross A versus Cross B is a trademark of X-linked inheritance. Why are variations not seen in the F1 of reciprocal crosses involving autosomal genes Calvin Bridges, a student of Morgan, provided this validation in an experiment that studied fruit flies with surprising eye-color phenotypes and abnormal chromosome numbers. This experiment confirmed that genes are carried on chromosomes, proving the "chromosome principle of heredity. Nearly all of the progeny from this cross had the expected phenotype and had been both red-eyed females (w +w) or white-eyed males (wY), however about 1 in every 2000 F1 flies had an "distinctive phenotype"-a time period used to determine progeny with sudden characteristics. Specifically, the distinctive flies had been either white-eyed females or redeyed males. The answer to the primary query got here when Bridges checked out chromosomes of the exceptional progeny beneath the microscope. Bridges used comparable logic to recommend that the only X chromosome in distinctive males came from the male mother or father that handed the w + allele. The exceptional males with a single X chromosome expressed the w + allele as red eyes. The intercourse of most animals is identified on two ranges: (1) chromosomal intercourse, the presence of sex chromosomes associated with male and female intercourse in a species; and (2) phenotypic intercourse, the internal and external morphology present in every sex. Chromosomal intercourse is decided in the meanwhile of fertilization and is controlled by the intercourse chromosomes contributed by the mother and father. In distinction, phenotypic intercourse is determined by gene expression and the event of intercourse characteristics throughout gestation or progress. In this part, we look at the patterns and processes of chromosomal and phenotypic intercourse willpower in a quantity of organisms. Sex Determination in Drosophila In Drosophila, the number of X chromosomes in relation to the variety of haploid sets of autosomal chromosomes is a critical component in figuring out intercourse. The cross progeny consists of males with yellow body colour and full-sized wings and females with grey physique colour and full-sized wings. Give genotypes for parental flies and the male and suggesting potential X-linkage for that trait (p. Pure-breeding females are homozygous for X-linked alleles, but males are hemizygous (p. Identify the topic of this problem and the type of information the answer should include. The patterns of transmission of two Drosophila traits and the genotypes of organisms are to be determined primarily based on the phenotypes of male and female F1 progeny. Pure-breeding parental phenotypes are given together with the phenotypes of female and male progeny in the F1. All F1 progeny have full-sized wings and none have vestigial wings, suggesting that full-sized wing is dominant. The F1 males are solely yellow-bodied, whereas F1 females are completely gray-bodied. Hypothesize the modes of inheritance of body colour and wing type from the F1 information. The statement of one body color in F1 males and one other in females suggests that is an X-linked trait. The F1 results for wing form are the same for both sexes, suggesting that this trait is autosomal. The pure-breeding full-winged parent transmits the dominant alleles to all progeny, and the pure-breeding vestigial mother or father transmits the recessive allele. The sex-dependent difference in physique color amongst F1 women and men strongly suggests this trait is X-linked. F1 females inherit a recessive allele on the maternal X chromosome and a dominant allele on the paternal X and are heterozygous, thus displaying the dominant phenotype. The genotypes of pure-breeding parents are X y/X y; v +/v + for yellow-bodied, full-winged females; and X y + /Y; v/v for gray-bodied, vestigial-winged males. Use X y+ for yellow body, X y for gray body, v + for full wing, and v for vestigial wing. At the molecular level, we now know that Drosophila intercourse is determined by regulatory proteins that relay the number of X chromosomes present in nuclei of cells in Drosophila embryos. As we focus on within the Case Study at the end of Chapter 8, Sxl protein controls the expression of extra genes that drive intercourse improvement. Unlike Drosophila, however, sex willpower in placental mammals is dependent upon the presence or absence of the Y chromosome.
Purchase sildigra 120 mg without a prescription. How A Pos-T-Vac Vacuum Therapy System works for Male Impotence/Erectile Dysfunction.