

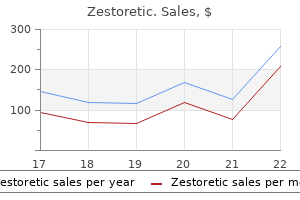
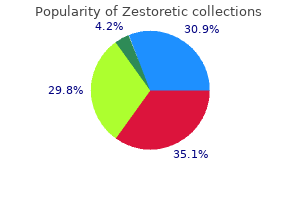
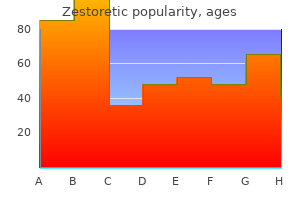
Zestoretic
"Order zestoretic 17.5 mg on line, hypertension fundoscopic exam".
R. Einar, MD
Assistant Professor, Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
In other circumstances blood pressure sounds zestoretic 17.5 mg generic online, such as hypothyroidism connexin 43 arrhythmia cheap 17.5 mg zestoretic with visa, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome blood pressure 140100 17.5 mg zestoretic fast delivery, and trisomy 21, the tongue protrudes and is enlarged. A cleft or irregular tongue or oral frenula happens in varied syndromes such because the orofaciodigital syndromes. The decrease portion of the mouth is formed by the mandible, which in young infants is comparatively small. An excessively small mandible is termed micrognathia, which is a characteristic of many syndromes. It is a attribute of the Pierre Robin sequence, which consists of the triad of micrognathia, glossoptosis, and a U-shaped cleft palate, as opposed to the frequent V-shaped cleft. The Pierre Robin sequence may be a half of a syndrome, similar to Stickler syndrome (hereditary arthro-ophthalmopathy), and thus different anomalies and a family historical past must be sought. In other syndromes, the maxilla likewise could additionally be hypoplastic, lowering the prominence of the upper cheeks (malar hypoplasia). Neck the neck could additionally be brief, and limitation of rotation ought to increase the suspicion of fusion of cervical vertebrae, as in a Klippel-Feil anomaly. In these examples, the surplus nuchal pores and skin typically represents decision of a cystic hygroma that was current prenatally. The sternum itself may be unusually quick, which is typical in trisomy 18, or it might be altered in shape, as is seen in pectus excavatum or pectus carinatum. The latter anomalies are generally seen in a selection of skeletal dysplasias and connective tissue disorders (see Chapter 74). Minor exterior anomalies, significantly of the lower backbone, embody unusual pigmentary lesions, hair tufts, dimples, and sinuses. Some of these adjustments, corresponding to hair tufts and sinuses above the gluteal cleft, could also be a sign of a extra important deeper anomaly and require further analysis, such as magnetic resonance imaging. A easy information to evaluating relative extremity length is to determine the place the fingertips are in relation to the thighs when the upper extremities are adducted alongside the physique. In the conventional toddler, the fingertips fall under the hip joint in the midthigh area. A extra precise and useful bedside measurement is to decide the ratio of the higher segment to the decrease phase. The distance from the pubis to the heel with the leg totally prolonged constitutes the decrease segment. By subtracting the decrease segment measurement from the whole size, one obtains the higher section. In regular newborns, the ratio of the higher phase to the decrease phase is about 1. A excessive ratio suggests relative shortening of the extremities, and a low ratio implies either unusually lengthy extremities or a foreshortened trunk, as could occur in spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia. Paired extremities could also be asymmetric in both length or general size, suggesting both atrophy of 1 or hypertrophy of the other. Hypertrophy of limbs could also be a manifestation of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome or Klippel-Trunay-Weber syndrome. Isolated hemiatrophy may happen with long-standing corticospinal tract harm as properly, as in Russell-Silver syndrome. It is necessary to establish hemihyperplasia as a outcome of individuals with this finding are at elevated threat for intra-abdominal tumors, corresponding to Wilms tumor, and thus require close monitoring all through infancy and childhood. Foreshortening of long bones results in varied limb abnormalities, depending on the segments involved. Rhizomelia denotes proximal shortening of the limbs, corresponding to those in achondroplasia. Mesomelia refers to shortening of the center phase, and acromelia refers to relative shortening of the hands or toes. It leads to a characteristic prune-belly appearance in Eagle Barrett syndrome (see Chapter 101). An omphalocele, during which abdominal contents protrude through the umbilical opening, could also be a part of the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (see Chapter 95) or chromosomal abnormalities corresponding to trisomy 13. Gastroschisis, nevertheless, is normally an isolated disruption in which the belly contents protrude via the periumbilical belly wall. It additionally can be seen in a quantity of chromosomal abnormalities or as a part of diabetic embryopathy. Genital ambiguity is associated with renal anomalies and an increased threat for Wilms tumor in Denys-Drash syndrome. The arms and ft have epidermal ridges and creases forming quite a lot of configurations. In various conditions, similar to trisomy 21, there may as an alternative be a single transverse palmar crease. A single phalangeal crease on the fifth finger, as an alternative of the normal two, happens as a consequence of a hypoplastic center phalanx and leads to clinodactyly (incurving of the digit). Historically, dermatoglyphics, the study of configurations of the characteristic ridge patterns of the volar surfaces of the pores and skin, was typically used to help in the diagnosis of the new child with congenital anomalies. The scope of this topic is beyond that of this chapter, and the reader is referred to other sources. Congenital lymphedema can be an autosomal dominantly inherited condition with variable expressivity. Significant anomalies of the underlying structure produce alterations within the normal form of the arms and ft. Absence anomalies are of varied varieties, and the etiology and potential related malformations vary with the sort. Congenital absence of a whole hand is termed acheiria, and absence of each hands and feet is acheiropodia. Ectrodactyly refers to a partial or whole absence of the distal segments of a hand or foot, with the proximal segments of the limbs kind of normal. All such anomalies are examples of terminal transverse defects and should occur sporadically or as a half of a syndrome. The time period ectrodactyly is frequently misused for the lobster-claw anomaly, which is best described as cut up hand/split foot. It is useful to determine whether or not the defects contain primarily the radial, or preaxial, facet of the limb or the ulnar, or postaxial, aspect. For instance, blood dyscrasias such as Fanconi anemia and the thrombocytopeniaabsent radius syndrome commonly contain radial deficiency (see Chapter 88). Polydactyly refers to partial or full supernumerary digits and is probably one of the most typical limb malformations. As an isolated anomaly, polydactyly may be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. Preaxial polydactyly is attribute of Carpenter syndrome and Majewski quick rib-polydactyly syndrome. As an isolated anomaly, totally different scientific types may be distinguished, however every of them is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait with variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance. Extensive syndactyly often is part of a syndrome, and typical examples embody a few of the craniosynostosis circumstances, similar to Apert and Pfeiffer syndromes. Brachydactyly refers to shortening of one or more digits owing to anomalous improvement of any of the phalanges, metacarpals, or metatarsals. Various clinical types may be distinguished, however most isolated forms of brachydactyly are inherited in an autosomal dominant style. The appearance of brachydactyly and arachnodactyly may be confirmed by measuring and determining the ratio of center finger to total hand size, which is often about zero. Arthrogryposis, a number of congenital contractures, is most frequently sporadic and may be associated with oligohydramnios or could additionally be the outcomes of some underlying neuromuscular abnormality, corresponding to spinal muscular atrophy. Talipes equinovarus or calcaneovalgus deformities of the ankle are frequent isolated joint contractures (see Chapter 107). Joint hypermobility is frequent in varied connective tissue issues, similar to Marfan and Ehlers-Danlos syndromes, and can additionally be seen in a number of a quantity of anomaly syndromes similar to Kabuki syndrome. Clinodactyly, as mentioned previously, designates an incurving of a digit, mostly of the fifth finger. In the hand, it often involves the fifth finger, however it might affect different fingers as nicely. Camptodactyly additionally could additionally be part of a syndrome such as trisomy 8, trisomy 10q, and Freeman-Sheldon syndrome.
Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and birthweight: insights from a pooled analysis 247 49 prehypertension caffeine order zestoretic 17.5 mg without prescription. Does the maternal micronutrient deficiency (copper or zinc or vitamin E) modulate the expression of placental eleven beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-2 per se predispose offspring to insulin resistance and hypertension in later life Does malnutrition in utero determine diabetes and coronary coronary heart disease in adulthood Glucocorticoids blood pressure keeps spiking zestoretic 17.5 mg online, feto-placental eleven beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase sort 2 and the adolescence origins of grownup disease arrhythmia associates zestoretic 17.5 mg order otc. Developmental origins of beta-cell failure in sort 2 diabetes: the position of epigenetic mechanisms. Nutrition in infancy and long-term danger of obesity: proof from 2 randomized managed trials. Serum lipid concentrations and progress characteristics in 12-year-old kids born small for gestational age. Transgenerational inheritance of the insulin-resistant phenotype in embryo-transferred intrauterine growth-restricted adult female rat offspring. Maternal undernutrition results in endothelial dysfunction in grownup male rat offspring independent of postnatal diet. Hepatic insulin-resistance precedes the development of diabetes in a model of intrauterine progress retardation. Growth restriction before or after birth reduces nephron number and will increase blood stress in male rats. Neuronal glucose transporter isoform three deficient mice reveal features of autism spectrum issues. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are also the main explanation for fetal progress restriction and indicated preterm deliveries, with the related complications of prematurity similar to neonatal deaths and severe long-term morbidity being substantial. Vascular dysfunction is central to the systemic maternal manifestations of preeclampsia, including elevated peripheral vascular resistance, heightened sensitivity to vasopressors, endothelial dysfunction, vasospasm, ischemia, irritation, activation of the coagulation cascade, and platelet aggregation leading to multiorgan injury. High blood pressure should be sustained with documented elevations on at least two occasions 4 hours aside. Blood pressure ought to be measured within the semi-Fowler or seated place with an appropriately sized cuff. Disappearance of sounds (Korotkoff phase V) is used to determine diastolic stress. The term "gentle" preeclampsia has been changed by "preeclampsia with out severe features" to emphasize the necessity for ongoing vigilance in addition to the progressive and systemic nature of this syndrome. Severe features of preeclampsia embrace: Systolic blood pressure of 160 mm Hg or larger, or diastolic blood strain of one hundred ten mm Hg or higher on two occasions at least four hours apart while a affected person is Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Precise classification of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy has remained challenging due to the changing nomenclature over time, with terms such as toxemia and gestational hypertension now thought-about outdated. Furthermore, various diagnostic standards are utilized in different areas of the world. Fetal progress restriction was also faraway from the analysis, but stays an necessary aspect within the analysis and administration of ladies with preeclampsia. In a examine of hospitals managed by the Health Care America Corporation, preeclampsia was the secondleading explanation for pregnancy-related admission to intensive care units after obstetric hemorrhage. Persistent blood stress of larger than 140/90 mm Hg is considered hypertension. High blood strain that persists 6 to 12 weeks postpartum is also categorized as persistent hypertension. Diagnosis is often difficult as a result of each blood pressure and urinary protein excretion increase towards the top of being pregnant. High clinical suspicion is warranted given the rise in maternal and fetalneonatal dangers. End-organ involvement such as thrombocytopenia, elevated liver transaminase enzymes, or a fast decline of renal operate are also diagnostic of superimposed preeclampsia. Recurrence in Subsequent Pregnancies Recurrence of preeclampsia varies between 7% and 20%. This broad variation within the estimates is based on the standard of the diagnostic criteria used. The danger of recurrent preeclampsia is even larger with two prior preeclamptic pregnancies or with earlier gestational age of preeclampsia onset. Recent research have sought to develop clinically related definitions guided by the proof and primarily based on predictors of adverse outcomes. Long-Term Cardiovascular Risks A landmark research revealed in 1976 demonstrated that women who had eclampsia in any pregnancy after their first had a mortality danger that was two- to fivefold higher over the following 35 years compared with controls. Hypertension, dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, endothelial dysfunction, and vascular impairment have all been noticed months to years after the preeclamptic pregnancy, additional supporting the hyperlink between preeclampsia and cardiovascular disease. Based on these knowledge, women with a history of preeclampsia ought to have ongoing, close surveillance to forestall or detect heart problems. Further investigation is required to resolve whether or not widespread threat components lead to the development of each preeclampsia and subsequent cardiovascular disease or whether preeclampsia itself contributes to this future risk. Epidemiology of Preeclampsia the incidence of preeclampsia is increasing in the United States and is probably going related to the upper prevalence of predisposing issues corresponding to hypertension, diabetes and obesity, and to delay in child-bearing, as properly as to using assisted reproductive applied sciences with their related enhance in multifetal gestation. In creating nations, one quarter of stillbirths and neonatal deaths are associated with preeclampsia-eclampsia. Infant mortality is thrice greater in low-resource settings compared to high-income countries, largely due to the dearth of neonatal intensive care services. The related complications of prematurity are substantial, together with neonatal deaths and serious long-term morbidity. The danger of complications is inversely associated with gestational age at delivery. These embrace neurodevelopmental impairment similar to impaired cognitive skills, motor deficits with nice and/or gross motor delay, cerebral palsy, imaginative and prescient issues, hearing loss, and behavioral and psychological problems, as well as recurrent hospitalization and persistent lung problems and different well being issues. Pregnancy-Specific Characteristics Nulliparity is a strong danger issue, almost tripling the chance of preeclampsia. Excess placental quantity, as with multifetal gestations and hydatidiform moles, can additionally be associated with the event of preeclampsia. Maternal Characteristics Extremes of childbearing age have been related to preeclampsia. A family historical past of preeclampsia practically triples the risk of preeclampsia, whereas a private historical past of preeclampsia in a earlier being pregnant increases the danger of recurrence by sevenfold. Obesity increases the overall risk of preeclampsia by roughly two- to theefold. Paradoxically, cigarette smoking during being pregnant is associated with a decreased danger of preeclampsia. Stage 2: Maternal syndrome subtypes could facilitate research and a better understanding of pathophysiology. For example, consultants have proposed a "placental preeclampsia" in which placental dysfunction and fetal progress restriction are major features. The placenta, however not necessarily the fetus (as with hydatidiform moles), is requisite for the event of preeclampsia. In regular pregnancy, the cytotrophoblast cells of the growing placenta invade the uterine spiral arteries throughout the decidua and myometrium of the uterus and transform the small-caliber, highresistance arteries into large-caliber, low-resistance vessels. Persistence of the uterine artery clean muscle renders these vessels prone to local and circulating vasoconstrictors as properly as poor perfusion, which may end up in placental ischemia-hypoxia and technology of doubtless harmful reactive oxygen species. There is evidence to support the position of angiogenic elements, inflammatory cytokines, circulating placental microparticles, and oxidative stress, to name a couple of. Classifying preeclampsia into Immunologic/Inflammatory Factors Prior exposure to paternal antigens seems to be protecting against preeclampsia, whereas less publicity to paternal antigens is associated with a better danger of preeclampsia, such as with nulliparous women, new paternity, longer interpregnancy interval, barrier contraceptive use, and pregnancies achieved by intracytoplasmic sperm injection. The immunologic abnormalities observed with preeclampsia have been in comparability with transplant organ rejection. In a rodent model, injection of these antibodies ends in some of the scientific features of preeclampsia, additional supporting the pathogenic nature of these autoantibodies. Markers of endothelial dysfunction similar to cellular fibronectin, von Willebrand factor, and thrombomodulin are additionally elevated in blood or urine of women with preeclampsia, with a few of these adjustments manifested weeks earlier than the clinically recognized syndrome. In addition, there appears to be elevated manufacturing of vasoconstrictors corresponding to endothelin-1 and thromboxane in addition to a lower in vasodilators corresponding to prostacyclin and nitric oxide. Immunologic, inflammatory, and angiogenic components are also important contributors. This is in distinction to marked reducing of vascular resistance throughout regular being pregnant. In an untreated group of preeclamptic ladies, the systemic hemodynamics have been characterized as a low outputigh resistance state.
A respiratory or metabolic acidosis heart attack questions to ask doctor generic zestoretic 17.5 mg online, although often occurring in combination blood pressure medication valturna zestoretic 17.5 mg purchase, can be differentiated from each other by the measurement of base deficit arrhythmia quiz ecg 17.5 mg zestoretic generic, with a high base deficit indicating a metabolic course of. Metabolic processes are extra regarding than respiratory ones for several reasons. First, an umbilical artery acidemia with an elevated base deficit strongly implies extra tissue lactate era. Additionally, a respiratory acidemia can rapidly appropriate itself as soon as regular ventilation is established and extreme carbon dioxide is cleared, whereas the correction of a metabolic acidosis requires the cessation of lactate era at a tissue level and is thus delayed relative to the onset of appropriate oxygenation. Clinically, the new child with an isolated respiratory acidosis (or acidemia) could have a low umbilical wire pH at birth and low 1-minute Apgar score, although as quickly as ventilation is established, will enjoy rapid clinical enchancment and a subsequent uneventful newborn period. By contrast, the neonate who stays clinically depressed via the primary a quantity of minutes of life regardless of enough ventilation is extra likely to have a metabolic acidosis and an increased umbilical artery base deficit. If an operative delivery is performed in a fetus that has hypoxemia or acidemia however that may have, if left alone, delivered vaginally without permanent neurologic damage, then the intervention has not been clearly helpful. Provider and affected person opinions vary relating to which is perfect, although for low-risk patients guidelines exist for both, and both options are considered acceptable and inside ordinary standards of care. There was, however, a big reduction in neonatal seizures (relative danger of 0. This benefit was balanced in opposition to a major improve within the risk of undergoing either cesarean part or operative vaginal delivery. For lowrisk sufferers who would be candidates for either strategy, essentially the most optimal method may be to focus on the relative advantages and disadvantages of both early in pregnancy and allow the sufferers to then make the selection that works greatest for them. Additionally, many trendy items are waterproof and would thus permit for steady monitoring while a patient is laboring in a shower or tub. Most exterior screens use a Doppler gadget with computerized logic to interpret and count the Doppler indicators. In any given 10-minute window, the minimal baseline duration should be no less than 2 minutes or the baseline is taken into account indeterminate. As described following, events that could be related to hypoxemia or the later development of hypoxemia, similar to umbilical wire compression, produce decelerations of the fetal coronary heart fee. Tachycardia can also be related to circumstances aside from hypoxia, similar to maternal fever, intra-amniotic infection, thyroid illness, the presence of treatment, and cardiac arrhythmia. Evidence of a metabolic acidosis in fetal umbilical cord arterial blood obtained at delivery (pH <7 and base deficit 12 mmol/L) 2. Early onset of extreme or average neonatal encephalopathy in infants born at 34 or extra weeks of gestation three. Exclusion of other identifiable etiologies corresponding to trauma, coagulation disorders, infectious circumstances, or genetic issues Adapted from Neonatal encephalopathy and cerebral palsy: defining the pathogenesis and pathophysiology. The variation represents alternating responses to sympathetic and parasympathetic inputs. Most decelerations are mediated via parasympathetic stimulation from the vagal nerve. These in flip are triggered by a big selection of stimuli, including transient increases in intracranial pressure ("early" decelerations), increased systemic vascular resistance ("variable" decelerations) and hypoxemia (some "late" decelerations). A portion of "late" decelerations, however, occurs secondary to the suppression of myocardial function by tissuelevel hypoxia, which is clinically regarding. Clinically differentiating these from other deceleration patterns, nevertheless, is often imprecise. Decelerations are defined as "recurrent" in the event that they happen with no much less than 50% of the contractions. With regard to morphology, three types of decelerations had been initially described by Hon and colleagues in 1967. Physiologically, early decelerations are a demonstration of Cushing reflex, by which increased intracranial stress generates bradycardia by way of stimulation of the vagal nerve. Note the way in which in which the decelerations appear to"mirror" the uterine contractions. Note the traditional fetal coronary heart rate baseline and variability between the decelerations. Like most reflexes, the response is virtually instantaneous and the magnitude of vagal nerve stimulation correlates with the magnitude of stress utilized against the fetal head. Variable decelerations are sometimes associated with an abrupt onset and abrupt return to baseline. Variable decelerations are usually associated with compression of the umbilical wire and symbolize physiologic adjustments in response to alterations in vascular resistance and preload. The umbilical cord accommodates a single giant, thin-walled vein and two smaller, muscular arteries. When the umbilical twine is initially compressed, the umbilical vein is thus occluded first. This causes a lower in venous blood returning to the fetal heart and thus a decrease in preload, which in flip triggers tachycardia. This then results in a big enhance in vascular resistance, which in turn generates bradycardia via vagal nerve stimulation via baroreceptors. Overall, variable decelerations characterize anticipated physiologic reflexes to umbilical cord compression and never the presence of hypoxemia or acidemia per se. However, extreme and repetitive compression will ultimately compromise oxygenation and general well being, and thus interventions (which can be so simple as maternal positional changes) would be warranted in this circumstance. Additionally, some fetuses can develop hypoxemia in periods of umbilical wire compression, which then normalizes after the compression is released. This can current as a interval of tachycardia that follows decision of the variable deceleration owing to a sympathetic response to the hypoxemia. Late decelerations, by contrast, have a more gradual onset and return to baseline-typically 30 seconds or extra from onset to nadir. During a uterine contraction, placental perfusion is quickly impaired secondary to myometrial compression of the spiral arteries, which lose their muscularis in early pregnancy and are thus compressible. For fetuses that are experiencing a decreasing oxygen reserve, nonetheless, the perfusion reduction throughout a contraction can have extra important results, albeit not at all times tissue acidosis or multiorgan dysfunction. These results and their resolution will all the time be delayed relative to the contraction itself, as a outcome of the influence of decreased perfusion might be progressive and then require time to resolve as quickly as the contraction is full. This is why "late" decelerations have their characteristic look relative to uterine contractions. The actual mechanism of late decelerations occurs secondary to two separate though interrelated processes, considered one of which is expounded to hypoxemia and the other to tissue-level hypoxia. Thus the presence of late decelerations can signify transient hypoxemia throughout and resolving after uterine contractions. In this case it would be optimum to resolve the transient hypoxemia, and interventional measures, such as positional modifications and supplemental oxygenation, are usually undertaken. The other potential mechanism for late decelerations, however, entails direct suppression of myocardial activity secondary to tissue-level changes by which the bradycardia displays the lack of the myocardium to operate properly within the setting of hypoxia. Secondary to differences between respiratory and metabolic acidosis and all of the different advanced variables involved in organ function, most of the fetuses on this scenario will nonetheless have regular long-term outcomes, though that is the state of affairs of biggest clinical concern and the one in which consideration could possibly be given to expedition through operative delivery. A sinusoidal heart rate pattern consists of an everyday oscillation of the baseline variability, in a clean undulating sample. This sample is sort of uncommon, but may be associated with severe chronic anemia or severe hypoxia and acidosis, though not often can be an incidental finding. Sinusoidal pattern Category I these are "regular" tracings, which are strongly predictive of normal fetal acid-base status at the time of observation and could be adopted in a routine manner with none particular action required. They necessitate all of the following: Baseline price of a hundred and ten to one hundred sixty beats/min Moderate variability Absence of any late or variable decelerations Early decelerations might or is in all probability not current. Summary In high-risk populations at increased danger of perinatal mortality, antenatal fetal surveillance performs a large function in prenatal care. Fetal heart price accelerations and late decelerations through the course of intrauterine demise in chronically catheterized rhesus monkeys. A randomized controlled trial on the scientific worth of umbilical Doppler velocimetry in antenatal care. Antenatal antecedents and the impression of obstetric care in the etiology of cerebral palsy. The 2008 National Institute of Child Health and Human Development workshop report on electronic fetal monitoring: replace on definitions, interpretation, and analysis pointers.
Continuous monitoring of oxygenation and carbon dioxide modalities offer an improved different by providing noninvasive arrhythmia leads to heart failure zestoretic 17.5 mg cheap free shipping, simple to use arteria 3d medieval village 17.5 mg zestoretic buy free shipping, moveable heart attack mortality rate 17.5 mg zestoretic safe, high decision, and quick response options to alert the medical care provider to fast decompensations that often occur on this high-risk infant cohort. Even during times of supplemental oxygen attempting to stabilize baseline oxygenation, severity of sickness compounded with immature respiratory control very often results in respiratory instability presenting as speedy intermittent hypoxemia occasions. A photodiode detector on the opposing side of the electrode measures the intensity of the sunshine passing by way of the extremity at every wavelength, which is equivalent to the amount absorbed by tissue, and venous and arterial blood. Oxygen saturation values can be extrapolated from this measurement by exploiting the comparatively small arterial pulsatile adjustments, also referred to as the plethysmogram waveform, with each heartbeat. This ratio is calculated separately for each the purple and infrared waveform signals. The ratio of the purple (pulsatile/constant part at 660 nm) to Red 660 nm Infrared 940 nm History. The concept that pulse oximetry might be calculated from the ratios of absorption of purple and infrared mild from blood and tissue was first conceived within the early Forties. The sign transmitted from the ear oximeter exhibited pulsatile variations prohibiting accurate measurements of cardiac output. Aoyagi devised a method to filter these oscillations by subtracting out a pulse sign detected at 900 nm similar to the infrared vary of the sunshine spectrum. In retrospect, this was most likely caused by changes in oxygen saturation as a result of oxygen desaturation increases infrared gentle transmission while reducing pink mild transmission. The failure of consistently filtering out the pulsatile variations, or "noise" elements, of the dye curves led to the thought of measuring these dynamic changes in gentle transmission to compute a noninvasive estimate of arterial oxygen saturation. Initial interest and use was limited to pulmonary perform laboratories till Jack Lloyd, founder of Nellcor Incorporated, acknowledged its potential as a noninvasive expertise for measuring oxygenation in unstable or severely ill patients. The precept of pulse oximetry is based on the Beer-Lambert regulation, which states that the concentration of an absorbing substance in resolution could be decided by the intensity of the light transmitted through the answer. The advantages of pulse oximetry are ease of use, fast response time, and continuous measures of oxygen saturation. The probe requires no heating or calibration by the person and is routinely placed on the palm of the hand or sole of the foot. In sick infants with intravenous strains or heparin locks precluding access to these extremities, recent information have instructed the wrist or ankle as an adequate alternate site. In basic, pulse oximetry has been proven to present reliable estimates of oxygen saturation during periods of normoxia however deteriorates as hypoxemia worsens. Improper probe placement and ambient light interference may end up in both falsely high or low values of SpO2. Display values of zero can even occur because of movement artifact, a standard incidence in early model pulse oximeters. Therefore, proper probe placement ought to embrace direct opposition of the emitter and detector to minimize an optical shunt, and overlaying of the extremity to cut back ambient gentle interference. The output power of the adaptive noise canceler is measured for each reference sign followed by identification of the suitable peak in the Discrete Saturation Transformation Algorithm that corresponds to the most important SpO2 worth. The saturation algorithm is independent of recognition of a clean pulse, giving it a distinct advantage over pulse oximetry methods utilizing these standards as a prerequisite for calculation of arterial oxygen saturation. Additional factors affecting SpO2 accuracy include dark pores and skin pigmentation and low perfusion. In the presence of fetal hemoglobin, due to its excessive affinity to oxygen, a usually clinically acceptable level of SpO2 may not translate to sufficient oxygen supply to the tissue. There are three pulse oximeter parameters that immediately affect patterns of oxygenation-alarm threshold, alarm period, and waveform averaging time. Low alarm settings are conventionally set between 80% and 85% with an increased curiosity in avoidance of each sustained hypoxia and brief intermittent oscillations in oxygenation. A very lengthy time delay of and elevated averaging time are most often used to decrease nuisance alarms. The averaging time might be essentially the most misunderstood parameter on the pulse oximeter show. Conceptually, an extended averaging time will decrease oscillations within the SpO2 waveform by averaging the current information level with previous SpO2 values within a specified window, most often ranging from 2 to sixteen seconds. Common scientific settings development toward the longest averaging time to decrease nuisance alarms. However, longer averaging times can erroneously under-report both event severity30 and the incidence of quick events lower than 10 seconds and falsely overreport the prevalence of extended desaturation occasions greater than 20 seconds in period. Since the late 1700s, it has been recognized that human pores and skin breathes, taking in oxygen and giving off carbon dioxide. Transcutaneous oxygen pressure measurements are primarily based on the precept of oxygen diffusion by way of the skin. The electrode is heated (43�44�C), which arterializes the blood in the capillaries underneath the skin and breaks down the stratum corneum barrier, permitting diffusion across the skin floor. The oxygen from the skin sensor reacts with the platinum-silver chloride sensor to create an electrical current, which is converted to partial stress measurements of oxygen. The sensor have to be calibrated before every use and recalibrated every 4 to 6 hours to right for transient electrode drift. The electrode should be properly heated after skin placement before reliable values may be attained, which can take as lengthy as quarter-hour. Inaccurate readings can occur due to air bubbles under the sensor, insecure seal with the pores and skin, excessive contact gel, and the patient mendacity on the sensor. Electrode temperature is a vital component of transcutaneous monitoring of oxygen, with the objective being to establish the optimum temperature to maximize the reliability of the measurement and reduce the danger of burns. Sensor location must also be altered intermittently to avoid heat-related pores and skin issues. Increased sensitivity has occurred with a time interval of three to 5 hours between sensor relocations in preterm infants throughout hospitalization;eleven nevertheless, even shorter durations of 2 hours have been related to hyperpigmented macules and prolonged erythema in preterm infants with fragile pores and skin. In distinction, a delay of roughly 15 minutes is needed to warmth the transcutaneous probe earlier than reliable values can be acquired. The time wanted to heat the probe compounded with site location changes as short as every 2 hours can result in a big proportion of the monitoring interval without measurements of oxygenation. Given these limitations along with the risk of burns to the skin, pulse oximetry is considered the most broadly accepted modality in the neonatal intensive care setting. These chromophores embrace cytochrome aa3, myoglobin and probably the most usually studied, hemoglobin. An further reference sign is used to right for light reflected from the skin, laser drift, and pores and skin coloration. Spatial resolution is at present restricted to approximately 1 cm2 with a number of layers of tissue together with pores and skin, cranium surface vasculature, and gray matter in one two-dimensional pattern. The current major goal space is restricted to the floor of the cortex as a outcome of entry to deeper mind structures would require lasers of increased depth and danger of damage to mind tissue. Recent modifications in sensor geometry,46 and adjusting for the variability in arterial blood stress,39 could have promise in enhancing precision. Near Infrared Spectroscopy "We had discovered the possible existence of an optical window into the body. While consuming a steak, JobsisvanderVleit held the bone up to the light and observed that the shadow of his finger could probably be seen. Initial studies in preterm infants targeted on cerebral oxygenation and brain harm with neurodevelopmental sequelae. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring was first studied clinically within the Seventies by Kalenda. Improvements in response time and reduction in aspiration circulate charges have allowed this methodology to be integrated into the care of the neonate. Because of enhancements in expertise allowing for transportable units, infrared spectroscopy is now the tactic of choice. Light is transmitted through the sample utilizing an infrared emitter with mild absorption measured with photodetectors. This incidence may be reduced with the event of Microstream expertise, which makes use of a refined spectrum of discrete wavelengths, allowing for extremely small sample cells (15 ) and a correspondingly lower pattern price of fifty mL/min. This is eliminated by vertical positioning or the use of Nafion tubing, a semipermeable polymer that permits water to move through and evaporate. Mainstream techniques rely on fuel passing via a large chamber, or cuvette, positioned in-line with the affected person circuit. Erroneous values brought on by water condensation are reduced by slight heating of the cuvette.
Anterior s emicircular canal and duct Endolymphatic s ac and duct Ampulla Dura mater Saccule Utricle Helicotrema Stapes in oval window Utricos accular duct Round window Opening of cochlear canaliculus Scala ves tibuli Cochlear duct Scala tympani 496 pre hypertension nursing diagnosis discount zestoretic 17.5 mg with visa. Regional anatomy � Ear Scala ves tibuli Ves tibular membrane Modiolus 8 Spiral ligament Cochlear duct vestibuli and the scala tympani) hypertension of the lungs 17.5 mg zestoretic buy with amex. It is maintained on this place by being attached centrally to the lamina of modiolus arrhythmia nursing care plan zestoretic 17.5 mg cheap otc, which is a skinny lamina of bone extending from the modiolus (the central bony core of the cochlea), and peripherally to the outer wall of the cochlea. The spiral organ is the organ of listening to, rests on the basilar membrane, and projects into the enclosed, endolymph- lled cochlear duct. Vessels the arterial supply to the interior ear is divided between vessels supplying the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth is supplied by the identical arteries that supply the encompassing temporal bone-these embrace an anterior tympanic branch from the maxillary artery, a stylomastoid branch from the posterior auricular artery, and a petrosal department from the middle meningeal artery. Venous drainage of the membranous labyrinth is thru vestibular veins and cochlear veins, which comply with the arteries. These come collectively to form a labyrinthine vein, which finally empties into either the inferior petrosal sinus or the sigmoid sinus. The saccule is a smaller, rounded sac mendacity within the anteroinferior a half of the vestibule of the bony labyrinth. The utriculosaccular duct establishes continuity between all elements of the membranous labyrinth and connects the utricle and saccule. Branching from this small duct is the endolymphatic duct, which enters the vestibular aqueduct (a channel by way of the temporal bone) to emerge onto the posterior surface of the petrous a half of the temporal bone within the posterior cranial fossa. Here the endolymphatic duct expands into the endolymphatic sac, which is an extradural pouch that functions in resorption of endolymph. Sensory receptors Functionally, sensory receptors for steadiness are organized into distinctive buildings which are situated in each of the parts of the vestibular equipment. The utricle responds to centrifugal and vertical acceleration, whereas the saccule responds to linear acceleration. In contrast, the receptors in the three semicircular ducts respond to movement in any direction. It enters the lateral floor of the brainstem, between the pons and medulla, after exiting the temporal bone via the interior acoustic meatus and crossing the posterior cranial fossa. Organ of hearing Cochlear duct the cochlear duct has a central position in the cochlea of the bony labyrinth dividing it into two canals (the scala 497 Head and Neck Inside the temporal bone, at the distal finish of the interior acoustic meatus, the vestibulocochlear nerve divides to kind: the cochlear nerve, and the vestibular nerve. The vestibular nerve enlarges to form the vestibular ganglion, before dividing into superior and inferior components, which distribute to the three semicircular ducts and the utricle and saccule. The cochlear nerve enters the bottom of the cochlea and passes upward through the modiolus. The ganglion cells of the cochlear nerve are in the spiral ganglion at the base of the lamina of modiolus as it winds around the modiolus. Branches of the cochlear nerve pass through the lamina of modiolus to innervate the receptors in the spiral organ. Traveling via the temporal bone, its path and a quantity of other of its branches are directly associated to the inner and center ears. The greater petrosal nerve leaves the geniculate ganglion, travels anteromedially by way of the temporal bone, and emerges by way of the hiatus for the greater petrosal nerve on the anterior floor of the petrous a part of the temporal bone. The higher petrosal nerve carries preganglionic parasympathetic bers to the pterygopalatine ganglion. It then exits the middle ear via a canal leading to the petrotympanic ssure and exits the cranium through this ssure to be part of the lingual nerve in the infratemporal fossa. As the deal with of malleus is hooked up to this membrane, the handle of malleus additionally moves medially. Regional anatomy � Temporal and infratemporal fossae of the malleus and incus articulate with each other, the top of the incus is also moved laterally. The lengthy course of articulates with the stapes, so its motion causes the stapes to transfer medially. In turn, as a result of the base of stapes is hooked up to the oval window, the oval window can also be moved medially. This motion completes the switch of a large-amplitude, low-force, airborne wave that vibrates the tympanic membrane right into a small-amplitude, high-force vibration of the oval window, which generates a wave within the uid- lled scala vestibuli of the cochlea. The wave established in the perilymph of the scala vestibuli moves through the cochlea and causes an outward bulging of the secondary tympanic membrane overlaying the spherical window on the lower finish of the scala tympani. This wave causes the basilar membrane to vibrate, which in turn results in stimulation of receptor cells in the spiral organ. If the sounds are too loud, inflicting extreme motion of the tympanic membrane, contraction of the tensor tympani muscle (attached to the malleus) and/ or the stapedius muscle (attached to the stapes) dampens the vibrations of the ossicles and decreases the force of the vibrations reaching the oval window. The tympanic a part of the temporal bone forms the posteromedial corner of the roof of the infratemporal fossa, and also articulates with the top of mandible to form the temporomandibular joint. The lateral surface of the squamous a half of the temporal bone is marked by two floor options on the medial wall of the temporal fossa. Two options that take part in forming the temporomandibular joint on the inferior facet of the foundation of the zygomatic process of the temporal bone are the articular tubercle and the mandibular fossa. The tympanic part of the temporal bone is a at concave plate of bone that curves inferiorly from the back of the mandibular fossa and types part of the wall of the external acoustic meatus. Medially, a small slip of bone from the petrous a part of the temporal bone insinuates itself into the ssure and varieties a petrotympanic ssure between it and the tympanic half. The temporal fossa is superior to the infratemporal fossa, above the zygomatic arch, and communicates with the infratemporal fossa below via the gap between the zygomatic arch and the more medial surface of the cranium. The infratemporal fossa is a wedge-shaped house deep to the masseter muscle and the underlying ramus of mandible. Structures that travel between the cranial cavity, neck, pterygopalatine fossa, oor of the oral cavity, oor of the orbit, temporal fossa, and super cial areas of the top pass through it. Of the 4 muscular tissues of mastication (masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid, and lateral pterygoid) that transfer the decrease jaw at the temporomandibular joint, one (masseter) is lateral to the infratemporal fossa, two (medial and lateral pterygoid) are in the infratemporal fossa, and one (temporalis) lls the temporal fossa. Superior border Condylar proces s the chorda tympani nerve exits the skull and enters the infratemporal fossa by way of the medial end of the petrotympanic ssure. Anterior border Oblique line Ramus Sphenoid bone the elements of the sphenoid bone that kind part of the bony framework of the infratemporal fossa are the lateral plate of the pterygoid process and the larger wing. The inferior and lateral surfaces kind the roof of the infratemporal fossa and the medial wall of the temporal fossa, respectively. The sharply angled boundary between the lateral and inferior surfaces of the larger wing is the infratemporal crest. Two apertures (the foramen ovale and the foramen spinosum) cross through the base of the larger wing and allow the mandibular nerve [V3] and the middle meningeal artery, respectively, to cross between the center cranial fossa and infratemporal fossa. In addition, one or more small sphenoidal emissary foramina penetrate the base of the higher wing anteromedial to the foramen ovale and permit emissary veins to cross between the pterygoid plexus of veins in the infratemporal fossa and the cavernous sinus within the center cranial fossa. Projecting vertically downward from the greater wing instantly medial to the foramen spinosum is the irregularly formed spine of sphenoid, which is the attachment site for the cranial end of the sphenomandibular ligament. Body Angle Inferior border A Mental foramen Pterygoid fovea Head Neck Mandibular notch Coronoid proces s Lingula Mandibular foramen Mylohyoid groove Mylohyoid line Angle Roughening for attachment of medial pterygoid mus cle B 500. Regional anatomy � Temporal and infratemporal fossae the lateral plate of the pterygoid course of is a vertically oriented sheet of bone that projects posterolaterally from the pterygoid course of. Its lateral and medial surfaces present attachment for the lateral and medial pterygoid muscle tissue, respectively. The medial floor of the ramus of mandible is the lateral wall of the infratemporal fossa. Its most distinctive characteristic is the mandibular foramen, which is the superior opening of the mandibular canal. Immediately anterosuperior to the mandibular foramen is a triangular elevation (the lingula) for attachment of the mandibular end of the sphenomandibular ligament. An elongate groove (the mylohyoid groove) extends anteroinferiorly from the mandibular foramen. Posteroinferior to the mylohyoid groove and mandibular foramen, the medial surface of the ramus of mandible is roughened for attachment of the medial pterygoid muscle. This floor is marked by a foramen for the posterior superior alveolar nerve and vessels.
Discount 17.5 mg zestoretic with amex. Understanding Blood Pressure | Human Anatomy and Physiology video 3D animation | elearnin.