

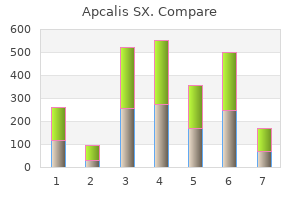
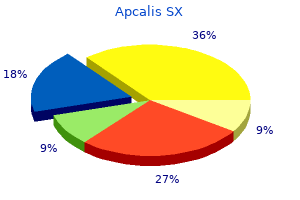
Apcalis SX
"Quality apcalis sx 20 mg, erectile dysfunction pills free trial".
H. Tippler, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of Washington School of Medicine
The extent to which continual erectile dysfunction doterra order 20 mg apcalis sx otc, low-level environmental exposure to cadmium impacts renal function is far less clear impotence injections medications discount apcalis sx 20 mg otc. The Cadmibel Study recruited over 2000 adults from completely different areas of Belgium in an attempt to erectile dysfunction images purchase apcalis sx 20 mg online compare the relationships among hypertension, heart problems, and renal abnormalities with urinary cadmium excretion, a measure of lifetime cadmium exposure. In common, problems come up following uric acid crystallization in the tubules, amassing system, or outflow tract or the deposition of uric acid throughout the interstitium, with ensuing inflammation. Thus as a outcome of uric acid within the tubular lumen is concentrated and exposed to a lower pH within the distal nephron, the chance of precipitation increases in these distal segments. Uric acid stones are a well-recognized entity and are discussed in Chapter 38: Urinary Stone Disease. Claims within the Nineteen Seventies that up to 11% of chronic interstitial illness could presumably be attributed to disorders of uric acid metabolism were challenged within the Eighties because of the problem in figuring out effects of hyperuricemia independent of other risk components, such as hypertension, vascular disease, kidney stones, or aging. Kidney biopsies reveal tubulointerstitial illness and, in some circumstances, glomerular ischemia and glomerulosclerosis. Underlying these mechanisms are repeated episodes of dehydration/volume depletion and maybe episodes of rhabdomyolysis associated with strenuous labor. Further field studies investigating the pathogenesis of this devastating situation are ongoing. Neilson for his or her chapter in the earlier edition of this guide, select parts of which have been carried over for this edition. Interstitial nephritis related to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory brokers and beta-lactam antibiotics: a comparative study of the interstitial infiltrates utilizing monoclonal antibodies. Clinical and pathological characterization of Mesoamerican nephropathy: a brand new kidney illness in Central America. Early steroid treatment improves the recovery of renal operate in patients with druginduced acute interstitial nephritis. Analgesic use and the danger of kidney cancer: a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Relationship between renal function and histological modifications present in renal biopsy specimens from patients with persistent glomerular nephritis. Quantitative analysis of interstitial fibrosis with Sirius Red in IgA nephritis. Significance of tubulointerstitial changes in the renal cortex for the excretory perform and focus capacity of the kidney: a morphometric contribution. The penalties of tubulointerstitial modifications for renal perform in glomerulopathies. The proximal tubule is the first goal of harm and progression of kidney disease: role of the glomerulotubular junction. Tubular obstruction leads to progressive proximal tubular damage and atubular glomeruli in polycystic kidney illness. Expression of apoptosisregulatory genes in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells exposed to high ambient glucose and in diabetic kidneys. Tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen: main construction, expression and role in health and disease. Differential effects of activated human renal epithelial cells on T-cell migration. Pivotal function of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4, its adaptor molecule MyD88, and inflammasome advanced in experimental tubule-interstitial nephritis. Activated renal macrophages are markers of illness onset and illness remission in lupus nephritis. Characterization of inflammatory cells in autoimmune tubulointerstitial nephritis in rats. Alternative pathway complement activation induces proinflammatory activity in human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Plasticity, nuclear diapause, and a requiem for the terminal differentiation of epithelia. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tubular epithelial cells in human renal biopsies. Mycophenolate mofetil prevents the progressive renal failure induced by 5/6 renal ablation in rats. Abnormal contrasuppression facilitates expression of nephritogenic effector T cells and interstitial nephritis in kdkd mice. Involvement of drug-specific T cells in acute drug-induced interstitial nephritis. Dendiritic cells: not just another cell type within the kidney, however a fancy immune sentinel community. Antigen presentation by dendritic cells in renal lymph nodes is linked to systemic and local harm to the kidney. Omeprazole-induced acute interstitial nephritis: a attainable Th1-Th17-mediated harm Tracer research in the rat demonstrate misdirected filtration and peritubular filtrate spreading in nephrons with segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pathways to nephron loss starting from glomerular diseases-insights from animal models. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial harm in the kidney: last widespread pathways to end-stage renal failure. Peritubular capillary loss after mouse acute nephrotoxicity correlates with down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor-A and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha. Deletion of von Hippel-Lindau protein converts renin-producing cells into erythropoietin-producing cells. A transgenic mouse mannequin for uromodulin-associated kidney illnesses shows specific tubulointerstitial damage, urinary concentrating defect and renal failure. Autosomal-dominant medullary cystic kidney illness sort 1: medical and molecular findings in six massive Cypriot households. Clinical and molecular characterization of a family with a dominant renin gene mutation and response to remedy with fludrocortisone. Renal biopsy in patients with unexplained renal impairment and regular kidney measurement. Etiologies and consequence of acute renal insufficiency in older adults: a renal biopsy research of 259 cases. Clinical traits, causes and outcomes of acute interstitial nephritis within the elderly. Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to enhance outcomes in acute kidney injury. Evaluation of medical and histological prognostic markers in drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Drug-induced hypersensitivity nephritis: lymphocyte stimulation testing and renal biopsy in 10 circumstances. Granulomatous interstitial nephritis: a clinicopathologic research of 46 circumstances from a single establishment. Bone marrow-derived myofibroblasts contribute to the renal interstitial myofibroblast inhabitants and produce procollagen I after ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Successful treatment of progressive renal damage as a outcome of granulomatous tubulointerstitial nephritis with uveitis. Changes within the aetiology, medical presentation and management of acute interstitial nephritis, an more and more common cause of acute kidney injury. Sodium losing, acidosis and hyperkalemia induced by methicillin interstitial nephritis. Antitubular basement-membrane antibodies in methicillin-associated interstitial nephritis. Acute interstitial nephritis because of medication: evaluation of the literature with a report of nine cases. Eosinophiluria-a new method of detection and definition of the scientific spectrum. Pathological significance of a panel of urinary biomarkersin sufferers with drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis. Evaluation of urinary biomarkers for the prognosis of drug associated continual tubulointerstitial nephritis. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a possible biomarker for predicting speedy development of drug-induced chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis.
Importantly encore vacuum pump erectile dysfunction order 20 mg apcalis sx overnight delivery, the podocyte quantity in urine correlates with disease exercise (assessed by renal biopsy) and has been proven to decline with treatment gas station erectile dysfunction pills discount apcalis sx 20 mg with visa. Urinary podocalyxin has been reported as a marker of activity in a number of illnesses erectile dysfunction nclex questions 20 mg apcalis sx buy mastercard, together with IgA nephropathy, Henoch-Sch�nlein purpura, diabetic nephropathy, lupus nephritis, poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, membranous nephropathy, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and preeclampsia. Several different studies have seemed at the potential of utilizing urine microscopy in combination with other biomarkers for detecting tubular damage, with varying degrees of success. Urine and serum ranges have been discovered to be elevated in patients with renal tubular diseases. Therefore, a rise within the urinary concentration of 1-microglobulin signifies proximal tubular harm or dysfunction. The normal range in populations younger than 50 years of age is lower than thirteen mg/g of creatinine and, in these 50 years of age and older, is less than 20 mg/g of creatinine. Limited studies have demonstrated that this marker might correlate with disease activity and proximal tubule harm within the setting of diabetic nephropathy, in addition to idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Any pathologic state that impacts kidney tubule perform will result in a rise in 2-microglobulin ranges within the urine due to the impeded uptake of 2-microglobulin by renal tubular cells. For spot urine collections, the concentration of 2-microglobulin in healthy individuals is usually 160 �g/L or less or 300 �g/g of creatinine or less. Because of this, the urine ought to be alkalinized and frozen at -80�C immediately after collection. Hepcidin-25 binds to and induces the internalization and degradation of the transmembrane iron exporter ferroportin. Ho and colleagues202 have identified urinary hepcidin-25 in a nested case-control research of 44 adults who underwent cardiac surgical procedure. They collected serial urine samples from 91 sufferers for 3 days after transplantation. Additionally, they demonstrated that the outcomes were extra promising for the prediction of in-hospital mortality. Lipocalins are extracellular proteins with various functions involving transport of hydrophilic substances through membranes, thereby maintaining cell homeostasis. It is expressed in numerous tissues in the body, such as salivary glands, prostate, uterus, trachea, lung, stomach, and kidney,309 and its expression is markedly induced in injured epithelial cells, together with these within the kidney, colon, liver, and lung. However, this was not considerably totally different from a medical model consisting of age, serum creatinine degree, and severity of sickness scores. It should be famous, nevertheless, that this impact was attenuated after adjusting for urine creatinine and urine albumin. Proteinuria is identified when the entire urinary protein is greater than 300 mg/24 hours. Albumin is a major serum protein with a measurement barely larger than the pores of the glomerular filtration membrane, so albuminuria is best known as a biomarker of glomerular dysfunction; its appearance in massive amounts in urine represents compromised integrity of the glomerular basement membrane. Using microalbuminuria as a marker, Levin and colleagues have demonstrated that N-acetylcysteine could attenuate contrast-induced glomerular and tubular damage. Any injury to proximal tubular cells can impede the reabsorption and improve the urinary excretion of cystatin C. Several medical research have sought to perceive the potential of urinary cystatin C ranges for the prediction of kidney harm and its prognosis. However, the small associations were completely attenuated after adjusting for the scientific mannequin. Advantages are that the commercially available immunonephelometric assay provides rapid automated measurement of cystatin C, and outcomes are available in minutes. Although very like the other associations, these must be validated in separate cohorts. This finding was then validated in a potential worldwide multicenter observational research of 728 subjects. For more in-depth discussion around specific markers for glomerular diseases, cystic diseases, diabetes, and inherited forms of renal illness, please see the individual chapters masking these matters. Several critiques on the ability of renal fibrosis markers to predict affected person outcomes have been printed. However, acute and chronic kidney ailments are complicated, with multiple underlying causes. A single biomarker may not be optimum to make an early prognosis and predict the longer-term outcome of the illness course of. Thus, it is important to contemplate the scientific utility of a panel of biomarkers for acute and persistent kidney diseases. Proteinuria and albuminuria can be used in combination with these two markers of glomerular function to diagnose and risk-stratify people further. There has not been a consensus for the statistical methods for combining biomarkers, and this remains an area of continued investigation. More current research have acknowledged the aforementioned premise that individual biomarkers will have their own specific kinetics, and that combining biomarkers from totally different time factors could enhance their predictive capabilities. As increasingly biomarker data are amassed, we anticipate advances in novel strategies for assessing biomarker combinations. For some, quite so much of additional work continues to be wanted, however, to deliver the biomarkers successfully to medical follow. Because kidney disease is advanced, with multiple causes, and often presents in the setting of systemic diseases, a single biomarker may be insufficient for early diagnosis, perception into pathophysiology, and prediction of scientific course and end result. In some circumstances, a single biomarker may suffice, however in others, benefit will come from using multiple biomarkers in plasma, urine, or each to provide early proof of risk and injury, and to distinguish between varied forms of kidney ailments. Many of these biomarkers can be grouped in accordance with their affiliation with a selected sort of harm. Understanding the relationships between these different biomarker categories may assist us better understand disease processes. Until just lately, the usage of newly emerged biomarkers in preclinical and scientific studies and drug growth has been hindered by lack of regulatory acceptance. This public-private partnership was designed to foster collaborations to optimize the evaluation of medication, devices, biologics and meals products within the higher kidney group. This initiative is meant to facilitate the delivery of those products to the U. Plasma biomarkers and kidney function decline in early and established diabetic kidney disease. Perioperative heart-type fatty acid binding protein is related to acute kidney damage after cardiac surgical procedure. Additive value of blood neutrophil gelatinaseassociated lipocalin to clinical judgement in acute kidney harm analysis and mortality prediction in sufferers hospitalized from the emergency division. Derivation and validation of cutoffs for clinical use of cell cycle arrest biomarkers. Validation of cell-cycle arrest biomarkers for acute kidney injury using scientific adjudication. Development and standardization of a furosemide stress take a look at to predict the severity of acute kidney harm. Urinary connective tissue progress issue is associated with human renal allograft fibrogenesis. Circulating bone morphogenetic protein-7 and reworking growth factor-beta1 are better predictors of renal finish factors in sufferers with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The end result of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-positive subclinical acute kidney damage: a multicenter pooled evaluation of potential studies. Early postoperative serum cystatin C predicts extreme acute kidney harm following pediatric cardiac surgery. Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney harm and poor outcomes after grownup cardiac surgical procedure. Improved performance of urinary biomarkers of acute kidney damage in the critically ill by stratification for injury period and baseline renal operate. Association between peritransplant kidney damage biomarkers and 1-year allograft outcomes. The severity of acute kidney harm predicts development to continual kidney disease. The burden of persistent kidney illness on developing nations: a twenty first century challenge in world health. Surveillance of persistent kidney illness around the world: monitoring and reining in a global drawback. Urine proteomics in kidney and urogenital ailments: moving towards medical purposes. Metabolomics for early detection of druginduced kidney damage: evaluation of the current status.
Buy cheap apcalis sx 20 mg line. NoFap Benefits for Erectile Dysfunction (Pornography Addiction).
Normally impotence zoloft apcalis sx 20 mg cheap mastercard, the kidneys reabsorb 96% of filtered magnesium212 and regulate magnesium homeostasis (see Chapter 18) erectile dysfunction lotion 20 mg apcalis sx buy mastercard. The maintenance of a slender vary of serum Pi levels is critical for numerous mobile features erectile dysfunction genetic apcalis sx 20 mg cheap on-line, together with power metabolism and bone formation, or as a constituent of phospholipids and nucleic acids. Older adults are extra prone to develop acid-base dysregulation for several reasons. First, age-related structural and useful modifications in the kidney result in decreased adaptive responsiveness to dietary and/or environmental changes. Administration of an acute acid load in 26 wholesome men of varied ages has demonstrated that regardless of a immediate improve in acid excretion in all of them, the older topics excreted a a lot lower share of ingested acid. Additional studies in four younger and four older subjects who, along with acid load, acquired glutamine, confirmed equivalent responses of young and old kidneys to glutamine. Additional insights from this study have been the increased exercise of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger and decreased phosphate transport in isolated proximal tubules in each age groups. The age-related perturbations of acid-base homeostasis seem to influence electrolyte stability. A Swedish study of eighty five wholesome older people has shown an association between net acid excretion and potassium-adjusted magnesuria, no matter magnesium intake. A research of nearly 10,000 participants in the common population has found that a higher dietary acid load is related to lower serum bicarbonate concentrations; the affiliation is much stronger in middle-aged and older than younger people. The large majority of glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in the proximal tubules and descending skinny limbs of the loop of Henle. Both most urinary focus and diluting capacity are decreased by growing older,274 resulting in the next risk for hypernatremia and hyponatremia, respectively. Findley has proposed an age-related dysfunction of the hypothalamic-renal axis based on scientific observations of elevated vasopressin secretion in older age. Due to the combined impact of age-related modifications in body composition, progressive microstructural modifications in the kidney, and changes in plasma osmolality and fluid volume, some older adults are extra prone to creating disturbances in water homeostasis. One of the main adjustments in body composition is a rise in whole fraction of body fats by 5% to 10% and an equal lower in whole body water, in order that an older man on common has 7 to 8 fewer liters of whole body water than a young man with the identical physique weight. A examine comparing plasma osmolality in older and younger individuals earlier than and after an identical extent of water deprivation has confirmed this presumption. Water homeostasis is also influenced by the beforehand described microstructural changes that occur with the getting older kidney. However, within the event of stress, acute disease, quantity load, or dehydration, the combined effects of age-related loss of renal mass. Vasopressin secretion, the renal response to vasopressin, and thirst management are additionally affected by getting older. Vasopressin secretion in the hypothalamus is under the fragile management of osmoreceptors in and across the organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis and the anterior wall of the third ventricle in the mind. Most research have found that basal vasopressin concentrations within the wholesome older are usually higher than in younger controls. Animal research have provided potential explanations for the reduced renal response to vasopressin, which embrace lowered expression of vasopressin receptors within the collecting ducts and impaired second messenger response to vasopressin receptor signaling. Other animal studies have proposed that lowered vasopressin receptor signaling considerably hinders the medullary concentrating gradient required for urine focus. It has been proposed that they may have the next osmolal set point for thirst-that is, for a given plasma osmolality, older adults have a lowered degree of perceived thirst, thus leading to less water consumption. For instance, at a Uosm of ninety mOsm/ kg H2O (maximum dilution in older adults) and a daily osmolal excretion of 360 mOsm/day (about half of normal levels), the maximal electrolyte free water consumption could be about four L/day. Any free water consumption in excess of this worth would lead to dilutional hyponatremia. Water conservation (urinary concentrating ability) is primarily affected, although a gentle form of impaired diluting capacity can also be present. This is important to keep in mind, not solely during the diagnostic course of, but additionally while taking care of older adults and planning for various scientific, surgical, or pharmacologic interventions. Aldosterone manufacturing and serum and urinary aldosterone ranges are lower in older adults in contrast with younger persons,296 and there may also be reduced aldosterone responsivity to elevations in serum potassium ranges. Thus, manufacturing rates of cystatin C are troublesome to assess and can differ in many states. However, serum cystatin C ranges have a tendency not be affected significantly by muscle mass or gender, and by no means by ancestry. All formulation incorporating a cystatin C measurement exhibited consistent improvements in accuracy compared with the corresponding creatinine-based equations. This is usually displayed as a multicolored heat map of the rising threat of events-green, no added threat; pink, high risk-often decided from large-scale epidemiologic studies. These research describe a pattern of a threshold (nonlinear) relationship, by which the brink varies in accordance with age. The basic phenomenon of getting older can work together with these pathologic processes in numerous ways that are very troublesome to disentangle unambiguously. Certain glomerular and vascular illnesses have a predilection to have an result on older adults (Box 22. Obstructive uropathy can be the consequence of ureteric involvement in gynecologic most cancers in older women and bladder dysfunction associated with neurologic illnesses and diabetes. Modulating Klotho expression pharmacologically might need helpful results, through decreased oxidative stress. Armed with new tools, however, corresponding to nephron number quantification, it may be attainable to check a number of the most promising strategies instantly in humans. Kidney function in early diabetes: the tubular speculation of glomerular filtration. So far, no elixir of life or "fountain of youth" has been discovered, but several promising avenues have been recognized. It is possible that all three of those approaches converge on mitochondrial energy production to gradual growing older. Performance of cystatin C- and creatinine-based estimated glomerular filtration fee equations is decided by affected person traits. The mixed contribution of albuminuria and glomerular filtration rate to the prediction of cardiovascular mortality in older men. Risks for all-cause mortality: stratified by age, estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria. Clinical and pathology findings associate constantly with larger glomerular volume. Association of kidney perform and metabolic danger factors with density of glomeruli on renal biopsy samples from living donors. Age-dependent reference intervals for estimated and measured glomerular filtration price. A longitudinal evaluation of the pure price of decline in renal operate with age. Tubulointerstitial illness in getting older: proof for underlying peritubular capillary damage, a potential role for renal ischemia. The age-associated loss of ischemic preconditioning in the kidney is accompanied by mitochondrial dysfunction, elevated protein acetylation and decreased autophagy. Telomere length, cardiovascular threat and arteriosclerosis in human kidneys: an observational cohort study. Klotho, the Holy Grail of the kidney: from salt sensitivity to persistent kidney disease. Association between soluble Klotho and change in kidney operate: the well being aging and body composition study. The human urinary proteome reveals excessive similarity between kidney getting older and continual kidney disease. Evolutionary conservation and modulation of a juvenile growth-regulating genetic program. Kidney dimensions at sonography: correlation with age, intercourse, and habitus in 665 grownup volunteers. Is the diverticulum of the distal and collecting tubules a preliminary stage of the straightforward cyst within the grownup Hygroma renale: pararenal lymphatic cysts related to renin-dependent hypertension (Page kidney). Prevalence of renal artery and kidney abnormalities by computed tomography among healthy adults. Detection and scientific patterns of nephron hypertrophy and nephrosclerosis among apparently wholesome adults.
The kidney-renal lymph node-system contributes to cross-tolerance against innocuous circulating antigen impotence lexapro apcalis sx 20 mg buy with amex. Characterization of mononuclear cell subsets in renal cellular interstitial infiltrates impotent rage order apcalis sx 20 mg visa. Tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation mechanisms in proximal tubule cells erectile dysfunction pills from canada apcalis sx 20 mg cheap online. Fate tracing reveals the stromal pericyte and never epithelial origin of myofiboblasts in the obstructive mannequin of kidney fibrosis. The angiopoietin/Tie-2 system regulates pericyte survival and recruitment in diabetic retinopathy. Renal ischemiareperfusion induces a dysbalance of angiopoietins, accompanied by proliferation of pericytes and fibrosis. Progressive adriamycin nephropathy in mice: sequence of histologic and immunohistochemical occasions. Colony-stimulating factor-1 promotes kidney progress and restore via alteration of macrophage responses. Selective depletion of macrophages reveals distinct, opposing roles during liver damage and repair. Regulatory T cell lineage specification by the forkhead transcription issue foxp3. Increased single-nephron protein excretion after renal ablation in nephrotic rats. Mechanism of furosemide resistance in analbuminemic rats and hypoalbuminemic patients. Plasma binding and disposition of furosemide in the nephrotic syndrome and in uremia. Intratubular albumin blunts the response to furosemide-a mechanism for diuretic resistance within the nephrotic syndrome. N-desulfated/acetylated heparin ameliorates the progression of renal illness in rats with subtotal renal ablation. Vitamin D metabolites and calcium metabolism in patients with nephrotic syndrome and regular renal function. Osteomalacia and hyperparathyroid bone illness in sufferers with nephrotic syndrome. Absence of metabolic bone disease in grownup sufferers with the nephrotic syndrome and regular renal function. Lowered protein content material of tissue fluid in patients with the nephrotic syndrome: observations during illness and restoration. Structural and useful elements of intercellular junctions in vascular endothelium. The effect of albumin infusion upon plasma norepinephrine concentration in nephrotic youngsters. Foxp3-transduced polyclonal regulatory T cells defend towards chronic renal harm from adriamycin. Bone marrow-derived cells contribute to podocyte regeneration and amelioration of renal disease in a mouse model of Alport syndrome. Notch activation differentially regulates renal progenitors proliferation and differentiation toward the podocyte lineage in glomerular issues. Retinoids augment the expression of podocyte proteins by glomerular parietal epithelial cells in experimental glomerular disease. Albumin metabolism within the nephrotic syndrome: the effect of dietary protein consumption. Micropuncture studies of the filtration and absorption of albumin by nephrotic rats. Albumin absorption and catabolism by isolated perfused proximal convoluted tubules of the rabbit. Slope of serial glomerular filtration price and the progression of diabetic glomerular illness. Observations on edema formation in the nephrotic syndrome in adults with minimal lesions. Blunted excretory response to atrial natriuretic peptide in experimental nephrosis. Atrial natriuretic peptide and the renal response to hypervolemia in nephrotic humans. Cellular basis for blunted volume enlargement natriuresis in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Interstitial irritation, sodium retention, and the pathogenesis of nephrotic edema: a unifying hypothesis. Concentrating defect in experimental nephrotic syndrone: altered expression of aquaporins and thick ascending limb Na+ transporters. Impaired aquaporin and urea transporter expression in rats with adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrome. Relationships between blood lipid and blood protein ranges within the nephrotic syndrome. Apolipoprotein gene expression in analbuminemic rats and in rats with Heymann nephritis. Defective lipolysis persists in hearts of rats with Heymann nephritis within the absence of nephrotic plasma. Proteinuria, not altered albumin metabolism, affects hyperlipidemia in the nephrotic rat. Catabolic defect of triglyceride is related to irregular very-low-density lipoprotein in experimental nephrosis. Lovastatin therapy in nephrotic hyperlipidemia: effects on lipoprotein metabolism. Studies on the turnover of triglyceride and esterified cholesterol in subjects with the nephrotic syndrome. Low density lipoprotein metabolism in rats with puromycin aminonucleoside-induced nephrotic syndrome. Molecular mechanisms of altered cholesterol metabolism in rats with spontaneous focal glomerulosclerosis. Role of elevated lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesteryl ester switch protein actions in abnormal lipoproteins from proteinuric sufferers. Relationship between platelet aggregation, thromboxane synthesis and albumin focus in nephrotic syndrome. Effects of statins on nonlipid serum markers associated with heart problems: a scientific evaluate. Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome of the grownup with asymptomatic thrombosis of the renal vein. Thromboembolic problems within the nephrotic syndrome: pathophysiology and clinical management. Asymptomatic renal-vein thrombosis in adult nephrotic syndrome ultrasonography and urinary fibrin-fibrinogen merchandise: a prospective study. Hemostasis and thromboembolism in kids with nephrotic syndrome: variations from adults. Serious adverse incidents with the usage of low molecular weight heparins in patients with persistent kidney disease. Decreased serum factor B focus associated with decreased opsonization of Escherichia coli in the idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Decline of vaccine-induced antipneumococcal antibody in youngsters with nephrotic syndrome. Lipid nephrotoxicity in continual progressive glomerular and tubulo-interstitial disease. The effect of angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibition and dietary protein restriction within the treatment of proteinuria. Hypercoagulability, renal vein thrombosis, and different thrombotic complications of nephrotic syndrome. Thrombus formation and platelet-vessel wall interaction in the nephrotic syndrome beneath move conditions.