

Finast
"Finast 5 mg lowest price, hair loss kittens".
J. Silvio, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, University of Florida College of Medicine
Upper panel: cat 2 hair loss in men 101 cheap finast 5 mg without a prescription, with an evolving infarct; decrease panel: cat 5 hair loss cure wiki buy discount finast 5 mg line, with reversal of the ischaemia hair loss brush finast 5 mg order overnight delivery. These findings verified the sequence of events that had been deduced from single examinations in man at totally different post-stroke survival occasions. The depolarized neurons trigger more calcium inflow and glutamate launch leading to local amplification of the preliminary ischaemic insult. The repeated depolarizations also exhaust the marginal energy supplies throughout the penumbra, which may remodel from non-lethal to irreversible harm. The demarcated areas reveal a gradient from the ischaemic core (red) via to the penumbra and oligaemic tissue (blue) to usually perfused tissue (grey). The penumbra is severely hypoperfused, non-functional, but nonetheless viable cortex surrounding the irreversibly broken ischaemic core; with elapse of time, extra of the penumbral region is recruited into the core until the tissue is reperfused. The pictures (from inset regions in b and c) present status of neurons and white matter inside the ischaemic core (d,g,j), poor penumbral area (e,h,k) and unaffected tissue (f,i,l). Continued a hundred and forty four (g) Chapter 2 Vascular Disease, Hypoxia and Related Conditions (h) (i) (j) (k) (l) 2. Insets show status of neurons and white matter within the ischaemic core (d,g,j), poor penumbral region (e,h,k) and unaffected tissue (f,i,l). Differential spatial patterns of focal improve in markers in course of the infarct core (I) by way of the hypoperfused region (P, penumbra) and normal (N) showing cortex in a neurosurgical biopsy. The microcirculation within the penumbral zone could also be restructured or turn into progressively impaired. Because the penumbra lies subsequent to irreversibly injured tissue, reactive inflammatory adjustments might occur in the penumbral microvessels. These may cause occlusion of the hypoperfused vessels by leukocytes or platelet aggregates adhering to endothelium, which is stimulated by ischaemia to specific adhesion molecules and additional pro-inflammatory components (see later). Pre- and Post-Conditioning and the Induction of Ischaemic Tolerance Prior sublethal transient ischaemic episodes cause brain cells to acquire tolerance to subsequent, otherwise detrimental, ischaemia. Reprogramming of the Toll-like receptor signalling has also been implicated in neuroprotection after preconditioning. However, the medical utility of ischaemic preconditioning remains to be demonstrated. These include endothelial swelling, perivascular oedema, increased blood viscosity and intravascular adjustments that involve inflammatory cells, platelets and clotting elements. Complement activation additionally appears to be an essential part of reperfusion damage. Experimental studies counsel that irritation contributes to ischaemic mind harm,1066 with higher morbidity after post-stroke inflammation. However, recent findings present that inflammatory processes may also have beneficial results,600 depending on the kind and measurement of stroke damage, diploma of vascularisation and pre-existing systemic infection or inflammatory problems. Perivascular macrophages � unlike microglia, repeatedly replenished from haematogenous precursors. These cells have a quantity of completely different features including cytolysis, antigen presentation, immunoregulation and manufacturing of progress components. Perivascular macrophages, mast cells and dendritic cells, originating in vascular walls or the meninges, also drive the innate and adaptive immune processes. The cytokine setting favours a Th1 helper T-cell response, stimulating macrophage and dendritic cell activity. Experimental studies have additionally proven that regardless of the early deleterious effects of irritation, the inflammatory reaction and removing of mobile particles are necessary for later expression of neurotropic and protective factors, regeneration and neurovascular remodelling. However, recent developments indicate that significant cell death happens by apoptotic as properly as hybrid mechanisms along an apoptosis�necrosis continuum (see earlier). Although the infarcted core is necrotic, inside the penumbra caspase-mediated apoptosis is activated, though secondary necrosis could outcome from failure to implement the apoptotic signalling pathways absolutely, as they require vitality. The intrinsic pathway originates with mitochondrial launch of cytochrome c and subsequent stimulation of caspase-3 whereas the extrinsic pathway is initiated by the activation of cell floor death receptors, which belong to the tumour necrosis issue superfamily, by Fas ligand, resulting in the stimulation of caspase-8. There is some evidence that ischaemic cell death may be mediated by autophagy, which is activated throughout cerebral ischaemia for the bulk removing of damaged neuronal organelles and proteins. Oxidative and endoplasmic stresses in cerebral ischaemia are stimuli for autophagy in neurons. Subsequent to stroke harm, the severity of depletion of energy and the disruption of the blood�brain barrier affect the inflammatory and excitotoxic responses from glia in the ischaemic core and the penumbra. The launch of diffusible components by broken cells and the activation of caspases can induce an apoptotic cascade in cells surrounding necrotic core, rising the extent of injury in response to the ischaemic event. Infarct Progression Experimental research in rodents and non-invasive imaging methods in people have shown that infarcts enlarge with time. In absence of early reperfusion, ongoing subacute harm to cells within the ischaemic penumbra resulting in growth of the infarcted core over about 4�6 hours. Cell death through the subacute phase is related mainly with peri-infarct spreading despair, which exacerbates the imbalance between metabolic demand and haemodynamic capability within the penumbra. The nucleus initially appears pyknotic but later reveals reduced basophilia and ultimately disappears. Consequences of Cerebrovascular Disorders and Impact on Brain Tissues 149 Zone of Transition the transition from poorly to adequately perfused tissue is comparatively abrupt. Similarly, the transition from infarcted to surviving tissue in histopathological sections is surprisingly sharp. The earliest morphological changes associated with infarction had been documented in the classical research of Brown and Brierley145,146 however require electron microscopic examination of perfusion-fixed tissue for dependable evaluation. Within minutes, neuronal mitochondria swell and unfastened their cristae, giving the cells a micro-vacuolated appearance. At the same time, the cytoplasm of the neurons begins to condense to become electron-dense. Over the next minutes and hours the nucleus turns into increasingly pyknotic with clumping of chromatin, and the nucleoli disappear. They are detectable by standard (H&E) staining, but with acid fuchsin stand out more prominently. Swelling of astrocytes results in perineuronal and perivascular vacuolation, which turns into more marked during the hours after onset of ischaemia. Reactive astrocytes start to surround the necrotic tissue after about 5 days, when the elevated density of capillaries also becomes apparent. The significance of reperfusion in the genesis of early ischaemic neuronal adjustments is highlighted by the difference between the structural modifications in incomplete and/or momentary ischaemia (a situation that all the time prevails in focal ischaemia) and people in full and/or everlasting ischaemia. Complete permanent ischaemia offers rise to swollen neurons that stain only weakly with eosin and different acidic dyes. In patients with first-time infarcts, haemorrhagic transformation was found in 14. Two typically accepted mechanisms by which an infarct becomes haemorrhagic are: (i) reperfusion of necrotic, leaking blood vessels and (ii) occlusion of venous drainage. Reperfusion happens when the embolus fragments or is broken down by fibrinolytic enzymes, both naturally or by way of thrombolytic therapy. Perilesional cytotoxic and vasogenic oedema are maximal at 24�72 hours after ischaemic stroke. Consequences of Cerebrovascular Disorders and Impact on Brain Tissues (a) 151 2 2. Dilated astrocytic cell bodies are seen on electron microscopy, and the extracellular (interstitial) space is decreased in cytotoxic oedema, in contrast to vasogenic oedema (see later). Activation of inotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors in neurons, and impairment or reversal of glutamate transporter exercise in neurons and astrocytes, results in the influx of Ca2+, Na+, Cl- and water, exacerbating cytotoxic oedema. It predominantly impacts the white matter and is characterized microscopically by increased separation of myelinated fibres, particularly round blood vessels, and decreased depth of staining with dyes such as Luxol quick blue and solochrome cyanine. Enlarged extracellular areas are occupied by protein-rich fluid, and immunohistochemistry discloses exudation of albumin and different plasma proteins, together with immunoglobulins. Astrocytes show 152 Chapter 2 Vascular Disease, Hypoxia and Related Conditions elongated perivascular foot processes. With time, hypertrophy and hyperplasia of astrocytes and loss of oligodendrocytes and myelin happen.
Diseases
This potential house descends to the level of the tenth rib within the midaxillary line hair loss cure stem cells generic 5 mg finast fast delivery. Its existence must be stored in thoughts when doing a splenic needle biopsy hair loss in men xxy buy finast 5 mg mastercard, or when injecting radiopaque material into the spleen for visualization of the hepatic portal vein (splenoportography) hair loss types buy 5 mg finast free shipping. Blockage of Hepatopancreatic Ampulla and Pancreatitis Because the principle pancreatic duct joins the bile duct to type the hepatopancreatic ampulla and pierces the duodenal wall, a gallstone passing along the extrahepatic bile passages may lodge within the constricted distal end of the ampulla, the place it opens on the summit of the major duodenal papilla. However, bile may back up and enter the pancreatic duct, normally resulting in pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). A comparable reflux of bile sometimes outcomes from spasms of the hepatopancreatic sphincter. Normally, the sphincter of the pancreatic duct prevents reflux of bile into the pancreatic duct; nonetheless, if the hepatopancreatic ampulla is obstructed, the weak pancreatic duct sphincter could additionally be unable to stand up to the extreme strain of the bile in the hepatopancreatic ampulla. If an adjunct pancreatic duct connects with the primary pancreatic duct and opens into the duodenum, it might compensate for an obstructed main pancreatic duct or spasm of the hepatopancreatic sphincter. This technique produces detailed photographs of the hepatobiliary and pancreatic techniques, including the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, pancreas, and pancreatic duct. First, a fiberoptic endoscope is passed through the mouth, esophagus, and stomach. Then the duodenum is entered and a cannula is inserted into the main duodenal papilla and superior beneath fluoroscopic management into the duct of choice (bile duct or pancreatic duct) for injection of radiographic contrast medium. Utilizing the fluoroscopic visualization offered by the contrast medium, devices operated via the endoscope are then utilized for the intervention. Pancreatic harm can result from sudden, extreme, forceful compression of the abdomen, such as the force of impalement on a steering wheel in an car accident. Because the pancreas lies transversely, the vertebral column acts as an anvil, and the traumatic drive may rupture the friable pancreas. Rupture of the pancreas regularly tears its duct system, permitting pancreatic juice to enter the parenchyma of the gland and to invade adjoining tissues. Subtotal Pancreatectomy Pancreatectomy, partial or complete surgical elimination of the pancreas, is mostly performed when pancreatic tumors are detected (see "Pancreatic Cancer" below). However, subtotal or partial pancreatectomy is utilized to remove ruptured parts of the pancreas and for the treatment of persistent pancreatitis after nonsurgical choices have failed. Subtotal pancreatectomy reduces pancreatic secretion by reducing the scale of the pancreas. While surgical removal of the body and tail is less difficult, the anatomical relationships and blood supply of the head of the pancreas, bile duct, and duodenum make it unimaginable to take away the whole head of the pancreas with out removing the duodenum and terminal bile duct (Skandalakis et al. Usually, a rim of the pancreas is retained along the medial border of the duodenum to protect the duodenal blood supply. Because of the posterior relationships of the pancreas, most cancers of the head often compresses and obstructs the bile duct and/or the hepatopancreatic ampulla. Obstruction of the biliary tract, usually the widespread bile duct or ampulla, leads to the retention of bile pigments, enlargement of the gallbladder, and obstructive jaundice. Cancer of the neck and physique of the pancreas may trigger hepatic portal or inferior vena caval obstruction because the pancreas overlies these massive veins. The Whipple process for cancer of the pancreas and biliary tract (pancreatoduodenectomy) is probably the most commonly carried out for tumors of the pancreas. It is a posh operation to remove a half of the pinnacle of the pancreas, a half of the duodenum, and the gallbladder. Tumors that develop within the body and tail of the pancreas are eliminated by a subtotal process known as distal pancreatectomy. The particular person is asked to take a deep breath as the examiner presses posterosuperiorly with the right hand and pulls anteriorly with the left hand (Bickley, 2016). Subphrenic Abscesses Peritonitis may end result within the formation of localized abscesses (collections of purulent exudate, or pus) in various elements of the peritoneal cavity. A common website for pus to acquire is in the best or left subphrenic recess or area. Subphrenic abscesses are more common on the best side because of the frequency of ruptured appendices and perforated duodenal ulcers. Because the best and left subphrenic recesses are continuous with the hepatorenal recess 1191 (the lowest [most gravity-dependent] elements of the peritoneal cavity when supine), pus from a subphrenic abscess may drain into one of the hepatorenal recesses. A subphrenic abscess is often drained by an incision inferior to , or through, the mattress of the 12th rib (Ellis, 2013), making it unnecessary to create an opening within the pleura or peritoneum. An anterior subphrenic abscess is usually drained through a subcostal incision situated inferior and parallel to the proper costal margin. More lately, especially because the introduction of the cauterizing scalpel and laser surgery, it has become potential to carry out hepatic segmentectomies. This process makes it attainable to remove (resect) only those segments that are affected by a tumor. The right, intermediate, and left hepatic veins serve as guides to the planes (fissures) between the hepatic divisions. These injuries are normally managed by eradicating the foreign material and packing or embolization (deliberate blocking of blood vessels to control bleeding) when needed. Every effort is made to avoid resection of the liver for trauma; resection is a last resort. In such cases, the surgeon must determine whether or not to perform a segmentectomy or lobectomy. Aberrant Hepatic Arteries the extra frequent variety of right or left hepatic artery that arises as a terminal branch of the hepatic artery proper. The most typical source of an aberrant left hepatic artery is the left gastric artery. Variations in Relationships of Hepatic Arteries In most people, the best hepatic artery crosses anterior to the hepatic portal vein. Hepatomegaly the liver is a soft highly vascular organ that receives a considerable amount of blood immediately earlier than it enters the guts. Marked short-term engorgement stretches the fibrous capsule of the liver, producing ache around the lower ribs, particularly in the right hypochondrium. In addition to illnesses that produce hepatic engorgement such as congestive coronary heart failure, bacterial and viral ailments such as hepatitis trigger hepatomegaly (liver enlargement). When the liver is massively enlarged, its inferior edge could additionally be readily palpated beneath the right costal margin and will even attain the pelvic brim in the right decrease quadrant of the abdomen. The liver is a typical website of metastatic carcinoma (secondary cancers spreading from organs drained by the portal system of veins. Cancer cells may move to the liver from the thorax, especially from the best breast, because of the communications between thoracic lymph nodes and the lymphatic vessels draining the naked space of the liver. Although many industrial solvents, such as carbon tetrachloride, produce cirrhosis, the situation develops most incessantly in persons suffering from chronic alcoholism. Alcoholic cirrhosis, the commonest of many causes of portal hypertension, is characterized by hepatomegaly and a "hobnail" look of the liver floor. The liver has nice practical reserve; therefore, the metabolic proof of liver failure is late to seem. Fibrous tissue surrounds the intrahepatic blood vessels and biliary ducts, making the liver agency and impeding the circulation of blood through it (portal hypertension). Liver Biopsy Hepatic tissue could additionally be obtained for diagnostic purposes by liver biopsy. Because the liver is situated in the best hypochondriac area the place it receives protection from the overlying thoracic cage, the needle is commonly directed through the right tenth intercostal space in the midaxillary line. Before the physician takes the biopsy, the individual is requested to maintain his or her breath in full expiration to scale back the costodiaphragmatic recess and to reduce the risk of damaging the lung and contaminating the pleural cavity. Mobile Gallbladder In most people, the gallbladder is carefully connected to the fossa for the gallbladder on the visceral floor of the liver. In roughly 4% of individuals, however, the gallbladder is suspended from the liver by a short mesentery, rising its mobility. Mobile gallbladders are topic to vascular 1197 torsion and infarction (sudden insufficiency of arterial or venous blood supply). As a result, the bile duct is brief and lies posterior to the superior a part of the duodenum, or even inferior to it. In different circumstances, the cystic duct spirals anteriorly over the frequent hepatic duct earlier than becoming a member of it on the left aspect. Awareness of the variations in arteries and bile duct formation is essential for surgeons after they ligate the cystic duct during cholecystectomy (surgical removal of the gallbladder). An accessory duct is a standard segmental duct that joins the biliary system outside the liver instead of within it.
Discount 5 mg finast overnight delivery. How to use tea tree oil for hair growth: how to prevent itchy scalp.
The serial changes that happen throughout the intimal layer throughout development of atherosclerosis are shown from left to right hair loss from wen 5 mg finast buy overnight delivery. The preliminary steps embrace adhesion of blood leukocytes to the activated endothelial monolayer eyebrow hair loss cure finast 5 mg cheap on-line, directed migration of the bound leukocytes into the intima hair loss talk forum purchase 5 mg finast, maturation of monocytes into macrophages and their uptake of lipid, yielding foam cells. Extracellular lipid derived from dead and dying cells accumulates within the central region of the plaque, usually denoted the lipid or necrotic core. Thrombosis, the last word result of atherosclerosis, typically includes a physical disruption of the atherosclerotic plaque, which develops a fibrous cap. This might induce blood coagulation components to come into contact with tissue factors within the inside of the plaque, triggering thrombosis that extends into the vessel lumen, where it can impede blood move. Initially, the circulating lymphocytes adhere to the endothelium solely transiently and roll on it. These interactions end in agency adhesion and extravasation of inflammatory cells. This phenomenon, called reverse ldl cholesterol transport, usually keeps an equilibrium between the influx and efflux of cholesterol in extrahepatic tissues, together with the arterial intima. Development of atherosclerotic Plaques In most instances, nonetheless, the fatty streaks do develop into extra superior lesions, as atherosclerotic plaques (atheroma), over a long time period, even a long time. The plaques are often situated at particular websites, such as on the outer features of the bifurcations of arteries, the place the intima is thickened and laminar blood flow disturbed. They additionally induce the transformation of clean muscle cells from contractile cells into cells that actively synthesize extracellular proteins. Beneath the cap, clusters of easy muscle cells, foam cells and lymphocytes acquire, together with a central core of necrotic cell particles and extracellular lipids, regularly including ldl cholesterol crystals. Even 5 per cent of the cross-sectional area of the lumen might enable blood move enough for normal brain operate. However, the turbulence caused by stenosis might cause endothelial injury and lead to the event of complicated plaques. According to the response to injury/inflammatory hypothesis, an additional prerequisite of atherogenesis is disruption of the endothelial barrier via injury to endothelial cells. These cells are reworked into intimal foam cells, clusters of which form the preliminary lesion visible to the bare eye as yellowish fatty streaks. Both the foam cells and extracellular lipids are stained strongly by widespread methods for demonstrating impartial lipid, corresponding to oil red O and Sudan black B. The efflux of extra ldl cholesterol from cells is mediated by the transmembrane protein adenosine triphosphate Development of Complicated Plaques the chance of thromboembolism rises markedly when the atherosclerotic plaque converts into an unstable difficult plaque, by which the lipid core expands and the fibrous cap thins. Thinning of the fibrous caps results in plaque instability, a course of thought to be modulated by inflammatory cells, that are a constant discovering at sites of ulceration or rupture of an atheromatous plaque. These occasions remodel strong fibrous lesions with small lipid cores and thick caps into lesions with massive lipid cores and skinny caps. Examination of complicated plaques in instances of carotid artery occlusion reveals that the endothelial lining is at all times disrupted. This exposes the blood to tissue elements that activate coagulation, and thrombus types over the plaque, inflicting narrowing of the lumen and predisposing to embolism. An embolus results in abrupt occlusion of the vascular lumen, whereas a neighborhood thrombotic course of is usually slow and may enable time for collateral channels to develop. Endothelial injury also happens if the dimensions of the plaque is increased abruptly by intramural bleeding from new blood vessels fashioned in the fibrous cap and on the margins of the plaque, though extra regularly the blood originates from the circulation by way of defects brought on by rupture of the plaque surface. Over time, haemosiderin might accumulate and, when calcium salts precipitate within the necrotic core, the plaque acquires the attribute onerous consistency. One-third of asymptomatic hypertensive sufferers have been found to have focal or diffuse cerebral hypoperfusion. Sudden and extreme malignant hypertension, precipitated for instance by renal disease, release of catecholamines from a phaeochromocytoma, eclampsia, or as a rebound effect after discontinuation of antihypertensives, may cause acute hypertensive encephalopathy. These may be adopted by focal neurological abnormalities, such as visual disturbances and seizures, and a progressive decrease within the level of consciousness. Clinical expertise reveals that the same holds true for the human cerebral circulation. Symptoms of cerebral hypoperfusion develop when the mean arterial blood stress falls to about 40 per cent of baseline levels. The acute rise in the arterial blood stress was induced by clamping the belly aorta in a rat for 10 minutes adopted by survival for two hours. The leakage is seen as small perivascular accumulations of albumin within the cortex. Diffuse spread of the oedema fluid to the encircling parenchyma has already occurred within the deep gray matter, hippocampus and hypothalamus (anti-albumin antibody and haematoxylin counterstain). The wall of the small artery (arrow) is thickened by the deposited plasma proteins. The lumen of the bigger artery is crammed by thrombus and there was leakage of plasma proteins into the surrounding cortical parenchyma (anti-fibrinogen antibody and haematoxylin counterstain). At these sites the basal lamina beneath the broken or regenerated endothelial cells becomes thickened or reduplicated. First, it aggravates atherosclerotic adjustments in extracranial and intracranial larger arteries. The leptomeningeal arteries over the convexities are normally spared in normotensive atherosclerotic topics, whereas in hypertensive sufferers they stand out as hardened, non-collapsed, yellowish blood vessels. Lesions similar to those in large vessel atherosclerosis might develop in arterioles all the means down to a hundred m in diameter (see later). Since they have been first reported648 the pathogenesis of lacunar infarcts has been a subject of intensive analysis. Small cerebral arteries and arterioles may be affected by many different illnesses, such as hereditary angiopathies, inflammatory and infective vasculitides and toxic issues (see later). The homogeneous eosinophilia in haematoxylin- and eosin (H&E)-stained sections may end result from both fibrinoid change or collagenous fibrosis. Arteriolosclerosis tends to be associated with ischaemic white matter illness and vascular dementia somewhat than lacunar infarcts. The significance of micro-aneurysms in hypertensive haemorrhage has been questioned. However, definitive identification of microaneurysms in routine diagnostic evaluation may be very uncommon. Venous Collagenosis Venous collagenosis is mostly seen in older brains and increases in tandem with white matter disease. In some respects, atherosclerosis additionally has some features of an inflammatory illness (see earlier). The American College of Rheumatology has printed clinical diagnostic criteria for a number of vasculitides. Deciphering the micro-aneurysms According to the standard view, Charcot�Bouchard or miliary micro-aneurysms arise within the context of hypertension, at weakened sites in vessel partitions. Inset exhibits the excellence between the actual size and straight distance between two factors alongside the vessel. Periventricular venous collagenosis is invariably present in older topics, although the extent and severity differ. Revascularization of the obstructed carotid arteries can cause a marked transient hyperperfusion syndrome. There is multifocal destruction of elastic lamellae within the aorta and of easy muscle cells within the carotid arteries. In uncommon deadly instances, it has been possible to analyze the topography of the irritation in detail. The inflammation fades as the affected arteries perforate the dura, at which level the quantity of elastic in the arterial wall can also be markedly diminished. The key symptom is headache, and a serious sequel is blindness: transient amaurosis fugax in about 10�12 per cent of sufferers and permanent blindness in about eight per cent. The blindness is usually due to extension of the illness into the ocular, mostly, or the ophthalmic arteries or their branches but can also be caused by occipital infarction, probably because of emboli from thrombosed vertebral arteries. The inflammation impacts primarily the tunica media, inflicting destruction of the elastic lamellae and inducing the formation of overseas body big cells, a standard finding wherever elastic tissue is destroyed by inflammation. Secondary fibrosis of all layers causes thickening and lack of compliance of the blood vessel partitions, leading to attribute lack of carotid pulsations. The affected arteries are finally remodeled into Diseases Affecting the Blood Vessels (a) (b) 103 2 (c) 2. The inflammatory modifications might extend alongside the size of the artery however are sometimes focal. Marked proliferation of intimal cells has thickened the intima and severely narrowed the lumen.
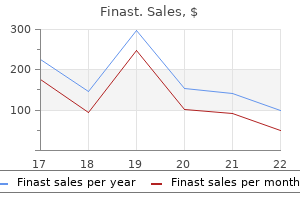
Longjack (Eurycoma Longifolia). Finast.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97076