

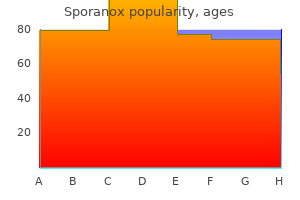
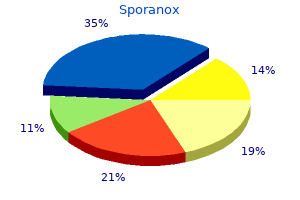
Sporanox
"Sporanox 100 mg order free shipping, antifungal extracts".
A. Rhobar, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Assistant Professor, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
As with histologic specimens fungus feet sporanox 100mg discount otc, probably the most frequent cytologic mimics are squamous metaplasia with reactive adjustments and atrophy fungus gnats pesticide cheap sporanox 100 mg without prescription. Squamous metaplastic cells commonly present gentle degrees of nuclear enlargement fungus games purchase sporanox 100mg amex, nuclear membrane irregularity, and even chromatin coarsening. Although atrophic squamous cells have a excessive nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, their nuclei are often very regular, with finely textured chromatin. The minimal hyperchromasia and the abundance of coffee-bean�shaped nuclei is a clue to the benign metaplastic nature of those cells. An different to loop is colposcopy with endocervical evaluation (evaluating the canal using the colposcope or tissue sampling). Proficiency on this distinction is an important talent of the cytology practitioner. With extra advanced tumors there can be again pain, sciatica, tenesmus, and hematuria. When related to hyperchromatic crowded teams of atypical cells or ample atypical keratinized cells with uncommon shapes ("tadpoles," "fiber cells"), the pattern is diagnostic. Slides from deeply invasive tumors show ample tumor diathesis, a granular precipitate of lysed blood and cell fragments. The benign atypia of atrophy accommodates scattered cells with large, darkish nuclei and eosinophilic or orangeophilic cytoplasm. Repair cells are recognized by their finely textured chromatin sample, the flatness and cohesion of the sheets. In some circumstances, information that the patient has a suspicious cervical mass or suspicious medical symptoms. Slides could show numerous isolated, keratinized cells with darkish, pleomorphic nuclei and huge nucleoli. Historically, administration options included a course of intravaginal estrogen cream. Carcinomas usually have a tumor diathesis and a lot of isolated atypical cells, features which may be usually absent in repair reactions. Small, keratinized squamous cells with mild variation in nuclear size and contour may characterize either a reactive course of or a significant squamous lesion. There are minor variations in the recommendations for younger (ages 21 to 24) and pregnant girls. Feathering, rosettes, and mitoses are just about never seen in menstrual endometrium. Both are characterised by hyperchromatic crowded groups, mitoses, apoptosis, and coarse chromatin. Some instances of adenocarcinoma are clearly invasive because the cells are massive, with ample cytoplasm and prominent nucleoli, and a tumor diathesis is present. Additional testing (imaging research, histologic sampling) is usually required for definitive classification and remedy. Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma of the endocervix represents approximately 20% to 25% of cervical cancers in the United States. Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinomas of the endocervix, endometrium, vagina, and even the ovaries and fallopian tubes are generally detected with the Pap test. Tumordiathesis on liquid-based preparations seems as clumps and as a granular ring around teams of malignant cells ("clingingdiathesis"). Glassy cell carcinoma is a poorly differentiated variant of adenosquamous carcinoma. Adenosquamous carcinoma is composed of malignant squamous and glandular cells arranged in sheets of enormous pleomorphic cells with abundant dense cytoplasm and outstanding macronucleoli. Clear cell carcinomas of the endocervix and vagina are morphologically identical: both are composed of spherical cells with pale nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and ample foamy or finely granular cytoplasm. The rare, extremely well-differentiated tumor minimal deviation adenocarcinoma (or adenoma malignum) consists of mucinous glands that present little if any atypia, and yet, if untreated, invade deeply and metastasize. Frequently, even cervical biopsy specimens and endocervical curette scrapings are misinterpreted as benign. Adenocarcinomas of the cervix are treated in an analogous manner to squamous cancers. Less common sorts include serous and clear cell carcinomas, which current at a more advanced stage and have a worse prognosis. The mucinous sort of endometrial carcinoma, against this, behaves just like the endometrioid kind. Cervical Pap cytology is atypical, suspicious, or optimistic for malignancy in 38% to 90% of endometrial adenocarcinomas. These malignant cells present variation in nuclear dimension, with very distinguished nucleoli and coarsely granular chromatin. Nevertheless, the Pap check does fortuitously pick up cells from many endometrial cancers. Histiocytes frequently accompany the atypical cells and in some circumstances outnumber them. Cells from serous adenocarcinoma of the endometrium are sometimes very large, pleomorphic, and simply recognized as malignant. Compared with smears from the endometrioid kind, smears from serous carcinomas include more malignant cells. When adenocarcinoma cells are recognized on a Pap slide, the 2 principal suspects are endocervical and endometrial adenocarcinoma. Endometrial adenocarcinoma cells are rounder and tend to exfoliate as isolated cells and smaller clusters, often arranged as spheres, whereas the cells of endocervical adenocarcinomas are extra columnar and arranged as sheets. Histiocytes commonly accompany endometrial carcinomas and not endocervical carcinomas. Ultimately, the cytologist can normally solely recommend the probabilities, favoring one website over one other: the ultimate classification rests on histologic examination. Morphologic distinction can be inconceivable, and knowledge that the affected person has an endocervical polyp may be the only clue to right interpretation. Reactive cells form sheets however not often balls of cells, as is seen with many adenocarcinomas. There are instances, however, the place doubt stays: these are identified as "atypical glandular cells. If a tumor diathesis is current or the cells are round and have outstanding nucleoli, the tumor is greater than probably an invasive adenocarcinoma. Pemphigus vulgaris is a rare blistering dysfunction that involves mucous membranes, including the cervix. The squamous cells of the cervix lose their squamous construction and take on a pseudoglandular appearance, with a pale nucleus and distinguished nucleolus. For this purpose, "atypical endocervical cells" must be reserved for cells with a recognizably columnar morphology. Thesecellshave enlarged nuclei with slightly irregular contours and some infiltration by neutrophils. Like their counterparts in the lung, these cells are fragile and present nuclear smearing. Often poorly preserved, the cells are simply confused with menstrual endometrial cells. Nuclear smearing and mitoses, nevertheless, are very uncommon with endometrial cells and supply an excellent clue to the prognosis of a small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Atypical Endometrial Cells Atypical endometrial cells are isolated cells or rounded clusters of cells with an enlarged nucleus and one or more extra features of nuclear atypia. Tumor cells Other Malignant Neoplasms Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Tumors that resemble small cell carcinomas of the lung come up within the uterine cervix. Some have concomitant evidence of squamous differentiation and are a variant of poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Cytoplasm is scant or plentiful and in some cases demonstrates the telltale fantastic, brown granularity of melanin. Malignant Lymphoma Non-Hodgkin lymphoma incessantly entails the cervix and vagina when the illness is superior.
Amyloid deposits are seen in 80% of cases and may be confirmed with the Congo pink stain fungus gnats repellent sporanox 100 mg cheap mastercard. They are often uniform in measurement and form fungus under toenail cure 100mg sporanox discount visa, however many cases comprise no less than a number of alarmingly giant cells fungus gnats traps homemade sporanox 100 mg generic overnight delivery. Nuclei are eccentrically placed, which gives these cells a plasmacytoid look, and binucleation and multinucleation are common. In some instances the cells are decidedly spindle-shaped, and the eccentrically placed nucleus makes the cells look like a comet with a protracted cytoplasmic tail. Nuclei have a coarsely granular, "salt-and-pepper" chromatin texture and inconspicuous nucleoli. It is similar to colloid however may be distinguished with the Congo red stain, which exhibits apple-green dichroism with polarized gentle. A H�rthle cell neoplasm is a frequent consideration because the cells of each neoplasms are often dispersed as isolated cells with reasonable to ample cytoplasm. The identical applies for paraganglioma137 and sure metastatic tumors, notably melanoma. For patients with a germline mutation, a prophylactic complete thyroidectomy is beneficial by the age of 5 or when the mutation is recognized. Most patients present with a noticeably enlarging mass, and compressive symptoms (dyspnea, dysphagia, hoarseness) happen in about one-third. Other sorts, including major Hodgkin lymphoma of the thyroid, occur but are distinctly less common. Rare Primary Thyroid Tumors There are many main thyroid tumors which might be very rarely encountered. These include hematolymphoid tumors like Langerhans cell histiocytosis,141 Rosai-Dorfman disease, and follicular dendritic cell sarcoma; epithelial malignancies similar to mucoepidermoid carcinoma,142 sclerosing mucoepidermoid carcinoma with eosinophilia,143 mammary analogue secretory carcinoma,144 and spindle-shaped epithelial tumor with thymus-like differentiation145,146; and mesenchymal tumors such as paraganglioma. Parathyroid Tumors Parathyroid adenomas and the uncommon parathyroid carcinoma may be mistaken clinically for thyroid nodules. The follicular cell nuclei are enlarged and irregular in contour, however precise classification is challenging due to obscuring blood andclottingelements(Papanicolaoustain). Nuclei are spherical and have a coarsely granular chromatin pattern; nucleoli are small or outstanding. Parathyroid adenomas are regularly mistaken cytologically for a follicular or H�rthle cell neoplasm. Immunohistochemistry for thyroglobulin and parathyroid hormone could be useful if a parathyroid origin is suspected. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules: influence on thyroid follow and price of care. How does one separate mobile follicular lesions of the thyroid by fine-needle aspiration biopsy Fine-needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: a research of 4703 patients with histologic and medical correlations. Long-term assessment of a multidisciplinary approach to thyroid nodule diagnostic evaluation. Cost-effectiveness of quick specimen adequacy assessment of thyroid fine-needle aspirations. ThinPrep versus conventional smear cytologic preparations within the evaluation of thyroid fine-needle aspiration specimens. Conventional smears versus liquid-based preparations for thyroid fine-needle aspirates: a scientific review and meta-analysis. Long-term follow-up of sufferers with benign thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytologic diagnoses. Semiquantitative criteria for fineneedle biopsy prognosis: lowered false-negative diagnoses. Usefulness of fine-needle aspiration in the diagnosis of thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study in 37,895 sufferers. Accuracy of thyroid fine-needle aspiration utilizing receiver operator characteristic curves. Accuracy of fine-needle aspiration of thyroid: a review of 6226 cases and correlation with surgical or clinical end result. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of the thyroid: a 12-year expertise with 11,000 biopsies. Non-diagnostic fineneedle aspiration biopsy: a dilemma in administration of nodular thyroid disease. Impact of the multigene ThyroSeq next-generation sequencing assay on cancer analysis in thyroid nodules with Atypia of Undetermined Significance/Follicular Lesion of Undetermined Significance cytology. Highly correct analysis of cancer in thyroid nodules with follicular neoplasm/ suspicious for a follicular neoplasm cytology by ThyroSeq v2 nextgeneration sequencing assay. Evaluation of ThyroSeq v2 efficiency in thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology. Clinical performance of a next-generation sequencing assay (ThyroSeq v2) within the evaluation of indeterminate thyroid nodules. Performance of a genomic sequencing classifier for the preoperative diagnosis of cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: Definitions, Criteria, and Explanatory Notes. Nodular goiter: a histocytological research with some emphasis on pitfalls of fine-needle aspiration cytology. Diagnostic criteria and risk-adapted approach to indeterminate thyroid cytodiagnosis. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid: differential diagnosis by Videoplan picture evaluation. Planimetric research on fantastic needle aspirates from follicular adenoma and follicular carcinoma of the thyroid. Discriminating benign from malignant thyroid lesions utilizing artificial intelligence and statistical choice of morphometric features. Fine needle aspiration analysis of hyperplastic and neoplastic follicular nodules of the thyroid: a morphometric examine. Relationship between histopathologic typing and morphonuclear assessments of 238 thyroid lesions: digital cell image evaluation carried out on Feulgen-stained nuclei from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded supplies. Application of an immunodiagnostic method for bettering preoperative prognosis of nodular thyroid lesions. Cytological findings for the analysis of main thyroid mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma by nice needle aspiration. Restricted kappa/lambda mild chain ratio by flow cytometry in germinal heart B cells in Hashimoto thyroiditis. Subacute thyroiditis: scientific traits and treatment end result in fifty-six consecutive patients recognized between 1999 and 2005. Subacute thyroiditis: fine-needle aspiration cytology of 14 circumstances presenting with thyroid nodules. Multinucleated giant cells in fine-needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: their diagnostic significance. Amyloid goiter: a clinicopathologic examine of 14 circumstances and review of the literature. Cytologic findings in thyroid nodules after 131iodine remedy of hyperthyroidism. Cytologic modifications simulating malignancy in thyrotoxic goiters handled with carbimazole. Diagnosis of "follicular neoplasm": a grey zone in thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology. Preoperative cytologic analysis of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: a prospective evaluation. Fine needle aspiration of H�rthle cell lesions: a cytomorphologic strategy to analysis. Does the fine-needle aspiration analysis of "H�rthle-cell neoplasm/follicular neoplasm with oncocytic features" denote elevated threat of malignancy Does H�rthle cell lesion/neoplasm predict malignancy more than follicular lesion/neoplasm on thyroid fine-needle aspiration
Atractylis lancea (Atractylodes). Sporanox.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97043
Medial floor of ulna and interosseous membrane; provides rise to four tendons antifungal veterinary drugs sporanox 100mg buy line, which traverse the carpal tunnel and insert anteriorly onto the distal phalanges of digits 2 to 5 antifungal ear drops for dogs buy 100mg sporanox visa. Median nerve (C6-C7); the median nerve enters the forearm by coursing between the two heads antifungal meaning sporanox 100mg order line. The muscle tissue within the posterior compartment are divided into superficial and deep teams. Two heads (lateral epicondyle and supinator crest of ulna); inserts on lateral radius. Posterior interosseous nerve (radial nerve) (C6-C7); radial nerve programs between the 2 heads of the supinator to enter the posterior compartment of the forearm. Deep department of the radial nerve prior to traveling to the supinator muscle (C7-C8). Intertendinous connecting the tendons could additionally be current on the dorsum of the hand (location and number of connections may be variable). Lumbricals, dorsal interossei, and palmar interossei muscle tissue share a standard attachment to the dorsal digital enlargement. This damage is seen in almost 50% of tennis gamers (hence, the name "tennis elbow"); nonetheless, it may possibly affect anyone who participates in repetitive activity. A particular person with lateral epicondylitis will sometimes experience pain over the lateral epicondyle. The etiology of the pain is microtears of the proximal attachment of the extensor muscular tissues. A triangular melancholy on the posterolateral wrist formed by the abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollids brevis, and extensor pollids longus tendons. The scaphoid bone forms the floor of the snuffbox, the radial artery programs throughout the scaphoid bone, and the superficial radial nerve and cephalic vein course over the roofwithin the hypodermis. The posterior compartment of the forearm is innervated totally by the radial nerve. Innervates the flexor carpi ulnaris and the ulnar half of the flexor digitorum profundus. The ulnar nerve continues into the hand superficial to the carpal tunnel and courses by way of Guyon�s canal by the pisiform bone to enter the hand. Proximal to the wrist, the ulnar nerve provides rise to two cutaneous branches, a dorsal branch and a palmar department, which give cutaneous innervation to the dorsal medial aspect of the hand and the medial aspect of the palm, respectively. In the elbow, the median nerve courses by way of the cubital fossa, deep to the bicipital aponeurosis and between the two heads of the pronator teres, to enter the anterior compartment of the forearm. Courses between the flexor digitorum superficialis and the profundus muscular tissues; traverses the carpal tunnel to enter the hand. Symptoms are usually tingling and numbness in the cutaneous distribution of the ulnar nerve. In extreme cases, muscle weakness could additionally be apparent, with atrophy of the hypothenar eminence. Prior to traversing the carpal tunnel the median nerve gives rise to a palmar department. A syndrome attributable to the entrapment of the median nerve between the two heads ofthe pronator teres muscle. Depending on the severity of the damage, sensory modifications in the distribution of the median nerve are more generally experienced In uncommon circumstances motor deficits in the distribution of the median nerve are skilled. In different words, the flexor pollicis longus muscle (flexes the thumb) and radial stomach of the flexor digitorum profundus (flexes digit 1 and 2) are affected. Travels alongside the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, pierces the membrane, and supplies the deep extensor muscular tissues. Travels alongside the posterior surface of the interosseous membrane and supplies the superficial extensors. Forms anastomoses with the recurrent interosseous artery vascular community of the elbow. Travels in a superior course, posterior to the elbow complicated, and varieties an anastomosis with the center collateral artery. The pulse of the radial artery is commonly felt on the lateral, palmar surface of the wrist. The radial artery terminates in the hand as the deep and superficial radial palmar arches. Courses in a superior path anterior to the medial epicondyle and types an anastomosis with the inferior ulnar collateral artery. Courses in a superior path posterior to the medial epicondyle and forms an anastomosis with the superior ulnar collateral artery. Courses toward the interosseous membrane and bifurcates into the anterior and posterior interosseous branches. Courses anteriorly to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus to anastomose with the radial collateral artery. The wrist complicated could be very versatile due to the synovial joint between the radius and the proximal row of carpal bones (radiocarpal joint) and the proximal and the distal row of carpal bones (midcarpal joint). Radiocarpal ioint Articulation between the radius and the radioulnar disc (triangular fibrocartilage complex) with the proximal row of carpal bones (scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum). Midcarpal ioint Articulation between the proximal row of carpal bones (scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum) with the distal row of carpal bones (trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate). Reinforces the anterior capsule and attaches proximally to the distal radius and distally to the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and capitate. Articulation between the ulnar notch of the radius, the articular disc, and the pinnacle of the ulna. A fibrocartilaginous construction located within the medial aspect ofthe wrist joint distal to the ulna; cushions and supports the carpal bones. Attaches proximally to the ulnar styloid course of and the triangular fibrocartilage advanced and distally to the lunate and triquetrum. Reinforces the posterior capsule and attaches proximally to the distal radius and distally to the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum. The distal radioulnar joint is supported by two ligaments that originate from the dorsal and palmar elements of the ulnar notch of the radius and lengthen to the bottom of the styloid process of the ulna. The interosseous membrane is a wide sheet of connective tissue that connects the radius and ulna and features to assist each the proximal and distal radioulnar joints. The association of the fibers allows for the transmission of forces from the hand and radius to the ulna. Muscles of the Forearm Muscle Anterior foreann Pronator teres Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Action Innervation Humeral head: medial epicondyle and supracondylar ridge of humerus Ulnar head: coronoid process of ulna Midshaft of radius Pronation and flexion of elbow Median n. Muscles of the Forearm (continued) Muscle Posterior foreann Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Action Innervation Anconeus Lateral epicondyle of humerus Lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus Olecranon means of the ulna Styloid strategy of the radius Metacarpal 2 Extension of elbow Radial n. In the hand, the fascia varies in thickness and divides the hand into five separate compartments that correspond with the five digits and have similar blood supply, innervation, and actions. Located between the thenar and hypothenar compartments and incorporates the flexor tendons and the lumbrical muscle tissue. Located between the metacarpals and contains the dorsal and palmar interossei muscular tissues. Thnnels composed of dense collagenous connective tissue that encloses the flexor tendons of digits 2 to 5 and the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus muscle (digit 1) and their related synovial sheaths. A band of dense collagenous connective tissue that types a roof over the concavity of the carpal bones thus forming the carpal tunnel; anchors to the pisiform and the hook of the hamate (medially) and the scaphoid and trapezium (laterally). The carpal tunnel has the following contents: � Four flexor digitorum superficialis tendons (and associated synovial sheaths). An aponeurosis masking the dorsum of the digits and attaches distal to the distal phalanx. Moving the metacarpal towards the palm (flexion) and away from the palm (extension). Form the bones of the wrist arranged in the following method: � Abduction and adduction. Described in relation to digit three; abduction is spreading fingers away from digit 3; adduction is shifting fingers towards digit 3. Boat-shaped bone that articulates with the radius; varieties the floor of the anatomical snu1Jbox.