

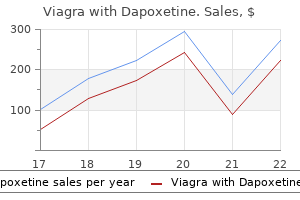
Viagra with Dapoxetine
"Viagra with dapoxetine 100/60 mg discount fast delivery, impotence pills".
I. Vigo, M.A., M.D.
Vice Chair, State University of New York Upstate Medical University
Examples embrace ultraradical debulking of ovarian cancer and cystectomy operations erectile dysfunction cause of divorce viagra with dapoxetine 50/30 mg purchase with visa. I n some centres using a postoperative epidural requires important care admission impotence merriam webster purchase viagra with dapoxetine 50/30mg on line. Anaesthetic implications of specific operations Emergency belly surgery Emergency abdominal surgical procedure is discussed in detail in Chapter forty four erectile dysfunction psychological treatment order 50/30 mg viagra with dapoxetine with mastercard. Elective stomach and pelvic surgical procedure A bdominal operations, especially cancer operations, are sometimes carried out on aged adults. Preoperative assessment ought to embody the potential comorbidities present within this group. Patients may be malnourished because of poor oral intake or recent crucial sickness. Chronic blood loss regarding ailments requiring cystectomy, hysterectomy or bowel cancer surgical procedure might mean the affected person is anaemic earlier than surgical procedure. O ther preoperative concerns embrace the potential for renal dysfunction caused by chemotherapy or ureteric obstruction or compression. Large pelvic tumours could cause stomach mass results similar to abdominal compartment syndrome, vena caval compression and diaphragmatic splinting. A ll patients are positioned supine, with decrease stomach and pelvic procedures requiring Lloyd-D avies and/or Trendelenburg, whilst upper stomach procedures, corresponding to cholecystectomy can require head-up, positioning. For both abdominal and laparoscopic approaches, tracheal intubation and mechanical air flow are required. The alternative of postoperative analgesia is dependent upon the premorbid condition of the patient and the incision used. Midline incisions extending past the umbilicus can also be managed this way, though epidurals are generally used. A lternatively, postoperative local anaesthetic wound infusion catheters may be used. Pelvic operations are sometimes extended and carry the chance of considerable blood loss. Extensive resection has the potential for marked physiological derangement, and invasive monitoring combined with postoperative important care admission is advisable. Examples include cystectomy, ovarian cancer debulking and extensive bowel tumour resection. Ultraradical debulking of extensive gynaecological cancers could require the excision of a number of buildings, and any peritoneal stripping may cause a profound inflammatory response requiring large-volume fluid resuscitation and/or vasopressors. Cystectomy operations, the place the ureters are diverted into a newly shaped ileal conduit, are particularly vulnerable to this complication. Vaginal hysterectomy causes much less trauma and postoperative ache than open stomach surgery. The diploma of postoperative pain as a end result of putting fallopian tube clips is tough to predict, however most sufferers require solely oral analgesics. Prostate surgery Prostate surgical procedure may be required for most cancers or benign prostatic hypertrophy. Both are strongly associated with growing age, and sufferers could also be frail or have comorbidities. I n addition, patients with benign prostatic hypertrophy typically present with acute urinary retention triggered by a medical insult such as latest surgery. Preoperative evaluation should notably aim to establish cardiovascular, respiratory or renal illnesses. Pre-existing metabolic derangements, specifically hyponatraemia, are additionally more likely to be exacerbated by surgery. Curative prostatic most cancers surgery (radical prostatectomy) requires transperitoneal or anteroperitoneal resection carried out using open, laparoscopic, or robotic methods. D uring laparoscopic radical prostatectomy the urethra is resected at the bladder base, and, inflicting diuresis by fluid-loading could obscure the surgical field. A sensory block to no much less than the T10�12 dermatomes is required to forestall discomfort brought on by bladder irrigation. For chosen instances, versatile endoscopic lasering with out anaesthetic could also be attainable. Glycine answer is essentially the most generally used hypotonic irrigation (approximately 200 mO smol L-1), and absorption of more than 2 L leads to fast decreasing of serum osmolality and sodium focus. I n addition, glycine displays toxic effects on the cardiovascular and central nervous techniques (including retinal neurotransmission). The most blatant clinical features and biochemical abnormality are altered consciousness, cardiovascular compromise and acute hyponatraemia. Unfortunately, delayed absorption from perivesicular tissue generally results in presentation after surgery. Hypertonic saline is required for sufferers with extreme neurological or myocardial dysfunction. Nephrectomy and renal surgery I ndications for nephrectomy include renal tumour, intractable an infection, trauma, calculous disease and renovascular hypertension or being a living donor. Renal tumours are related to preoperative renal tract blood loss and anaemia. Paraneoplastic syndromes sometimes happen in sufferers with renal tumours, causing hypercalcaemia, hypertension, polyneuropathy or fever. I f the one functioning kidney is being eliminated, dialysis is required postoperatively and care should be taken to keep away from infusions of medicine prone to accumulate, similar to morphine. Care must also be taken to keep away from placing cannulae in forearm veins, which are likely to be needed for future fistulae. Partial nephrectomies might protect some renal function, but these have a lower fee of tumour clearance and the next incidence of perioperative haemorrhage. Large or vascular tumours might require radiological endovascular embolisation up to 24h earlier than surgery and an epidural block is often, inserted for procedural analgesia. D epending on the size of the tumour and complexity of resection, renal surgery may be carried out utilizing open or laparoscopic surgery. I n each eventualities the affected person shall be lateral, requiring tracheal intubation. Epidural or paravertebral blockade normally supplies good postoperative analgesia for open surgical procedure. Haemorrhage is the commonest complication, and tumour could impinge on the inferior vena cava, requiring it to be clamped during surgery. Pneumothoraces are usually self-limiting and resolve after laparoscopic insufflation is discontinued. The anaesthetic necessities for nephroureterectomy are similar to these for nephrectomy besides that sufferers initially require Lloyd-D avies positioning whilst the ureter is disconnected. Intrauterine and transurethral bladder surgical procedure Cervical and transcervical surgical procedure includes resection of tumours, endometrial ablation for menorrhagia, hysteroscopy and cervical dilatation and uterine cure age. Patients with a bladder tumour are often elderly and may have a historical past of cigare e smoking; cardiorespiratory comorbidities should be recognized preoperatively. A naesthesia for cystoscopy or uteroscopy has to facilitate irrigation however not all the time resection. S pinal anaesthesia is an effective various for higher-risk sufferers, although patients with respiratory illness may be more susceptible to coughing when lying in the Lloyd-D avies position, which might make surgical procedure doubtlessly hazardous. Resection of lateral bladder wall tumours can stimulate the obturator nerve, leading to sudden leg actions, rising the risk of bladder perforation. Bladder perforation may not be instantly obvious postoperatively, as spinal anaesthesia could masks any pain. Blood clots may cause postoperative catheter obstruction and urinary retention, even when irrigation is used. Care must be taken to avoid undue catheter rigidity and accidental displacement when transferring patients. Bladder spasm is frequent postoperatively, usually in catheter-naive sufferers who may benefit from i. Brachytherapy may be used to insert radioactive sources immediately into cancerous areas such as the prostate, uterus or cervix. A naesthesia is normally required for gynaecological brachytherapy together with spinal, epidural or, caudal analgesia if extended postoperative ache aid is required. I nstitutions enterprise brachytherapy have specific protocols designed to defend staff from ionising radiation.
Diseases
Repeated a empts at placement of regional blockade increases the chance of complication in addition to the probabilities of disrupting the sterile subject erectile dysfunction medicine in bangladesh 100/60mg viagra with dapoxetine order. I t is necessary to name for help if several a empts of placement have confirmed unsuccessful erectile dysfunction pump walgreens 50/30 mg viagra with dapoxetine with amex. The basic problems of regional anaesthesia are described in Chapters 25 and 26 list all erectile dysfunction drugs 50/30mg viagra with dapoxetine generic otc. A ny sheared portion of catheter is inert and sterile and thus unlikely to cause an issue, however a full account should be made within the medical document. I t might happen at the time of insertion of the epidural needle or be caused later by migration of the catheter into the intrathecal house (usually due to a defect within the dura brought on during insertion of the needle). The scientific presentation is of an occipital headache that may radiate anteriorly, aggravated by si ing and possibly associated with nausea, distorted hearing, photophobia and, not often diplopia ensuing, from stretching of the sixth cranial nerve because it passes through the dura. The differential diagnoses of meningitis, subarachnoid haemorrhage, subdural haematoma, sagi al sinus thrombosis and cerebral space-occupying lesions must be considered and excluded by history medical examination and, additional investigation if wanted. I f dural puncture is recognised on the time (clear fluid flowing from the Tuohy needle), there are two options. After insertion, all drugs must be given cautiously as a end result of some local anaesthetic could migrate intrathecally. Prophylactic bed rest and an epidural infusion of saline are not recommended. Oral fluids should be encouraged to forestall dehydration, and easy analgesics must be prescribed. The report also highlights the importance of follow-up and communications with the overall practitioner. Backache Backache is common after childbirth and affects 50% of girls throughout pregnancy. I nsertion of an epidural catheter may contribute to short-term acute again ache if it causes: � an epidural haematoma; � an epidural an infection inflicting abscess or meningitis; or � native bruising. The incidence of new-onset backache was on the order of 40%� 50%, but there was no difference within the incidence of backache at three months between those that had acquired an epidural and those that had not. There was a non-significantly barely larger probability of back pain on day 1, explained by minor local trauma. Bloody faucet Cannulation of an epidural vessel could happen with both the needle or catheter when performing an epidural. I t is necessary because, if undetected, it can lead to intravascular injection and thus native anaesthetic toxicity. A n epidural catheter may be positioned with its tip inside a blood vessel in the absence of a bloody tap, and a take a look at dose should always be used. Hypotension Hypotension is usually defined as a 25% lower in systolic or imply arterial stress or an absolute decrease in systolic pressure of 40mmHg. S mall decreases in stress are insignificant and could also be related to improved uteroplacental blood move if caused by vasodilatation. Neurological deficit N eurological deficit could additionally be caused by the medicine used for the process or by trauma from the needles or catheter. When neuropraxia is attributable to damage with the epidural needle or catheter, reassurance may be provided that these symptoms normally resolve over 3�6 months, however patients ought to be adopted up on an outpatient basis. S everal peripheral nerves may be injured throughout delivery and falsely a ributed to the epidural: � common peroneal nerve by stirrups, causing foot drop; � lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh by groin pressure from the lithotomy place, inflicting anterolateral thigh numbness; � femoral nerve or sciatic nerve by the lithotomy position, inflicting weak quadriceps with loss of knee reflex or pain in the again of the leg with loss of ankle reflex, respectively; and � sacral plexus and obturator nerves � these cross the pelvic rim and barely could additionally be broken by occipital presentation or forceps delivery. Effect on labour and mode of delivery Epidural analgesia for labour has been proven to delay the second stage of labour by 15. I t also increases the rate of instrumental supply although this threat could additionally be lowered by low-dose epidural methods. I n the 1970s�1980s, the variety of deaths immediately attributable to anaesthesia was 30�50 per one hundred,000 maternities; from 2009 this number has fallen to 2�4 per 100,000 maternities. The increasing security of anaesthesia in obstetrics is the outcome of many factors: � Increasing use of epidural analgesia in labour � Increasing use of regional anaesthesia for operative supply � Increase in dedicated advisor obstetric anaesthetic sessions � Improved teaching of obstetric anaesthesia � Improved help for the anaesthetist � Ongoing studying from triennial enquiries of maternal mortality Repeated a empts to intubate the trachea while dropping give consideration to oxygenation, unrecognised oesophageal intubation and gastric aspiration have been highlighted as direct causes of death in earlier reviews. General anaesthesia within the parturient is greater than 16 times extra prone to end in demise than a regional anaesthetic; that is additionally a reflection of the fact that general anaesthesia is usually carried out in emergency situations. The decreasing use of general anaesthesia in obstetric anaesthesia additional exacerbates this problem by lowering expertise and coaching alternatives. However, common anaesthesia continues to be required in the following situations: � In an excessive emergency. I t is essential that a thorough preanaesthetic evaluation is carried out, with airway analysis and planning in case a tough airway is encountered. I t is necessary that anaesthetists familiarise themselves with the working theatre and the anaesthetic tools, along with the rules and equipment which are out there for tough and failed intubation. D rugs and equipment ought to be checked at the beginning of every period of responsibility on the supply suite so that an emergency can be handled in a peaceful and ordered method. Technique of common anaesthesia in obstetric apply the tactic of performing speedy sequence induction is roofed elsewhere within the text; nonetheless, we spotlight some key elements of importance in obstetrics. There is a comparatively high incidence of failed intubation in obstetric patients (approximately 1 in 300 in contrast with 1 in 2220 in non-pregnant patients). The adjustments related to being pregnant and labour trigger a extra rapid fee of oxygen desaturation, which is additional compounded by the rising prevalence of weight problems. O ptimum positioning for intubation is of key significance, remembering to compensate for aortocaval compression. A dequate preoxygenation is often achieved by 3min of tidal respiratory with one hundred pc oxygen at high move by way of a tight-fi ing face mask. Consideration ought to be given to nasal oxygenation during induction, as nicely as mild face-mask air flow. I t is commonplace practice to use thiopental to induce anaesthesia, and a dose of no less than 5mgkg �1 is really helpful in healthy parturients. A short-acting opioid is usually used at induction to counteract the pressor response of laryngoscopy notably in pre-eclampsia, to reduce the danger of, hypertensive disaster at induction. There is also a growing variety of obstetric anaesthetists who use propofol and rocuronium (1mgkg�1) for induction. The use of suxamethonium originated from the fast motion and brief duration of motion enabling a quick achievement of paralysis sufficient for intubation and early return of spontaneous air flow in the event of failed intubation. However, life-threatening desaturation might happen earlier than return of neuromuscular operate after the administration of suxamethonium. D uring this era, circumstances for intubation and ventilation additionally become suboptimal, necessitating an additional dose of paralysis. Rapid reversal of rocuronium necessitates the use of sugammadex, which has further value. The Fifth N ational Audit Project (N A P5) has highlighted the difficulty of consciousness in obstetric anaesthesia, with an estimated incidence of 1:670 in general anaesthesia for caesarean section, larger than most other forms of surgical procedure. S everal elements enhance the danger of awareness in obstetrics, including use of decrease doses of anaesthetic brokers for fear of uterine leisure or neonatal compromise, the quick period of time between induction and surgical incision, the elevated incidence of failed intubation and the omission of opioids. The debate has also reopened the query of using propofol for induction, which has been linked to fewer circumstances of consciousness. Propofol has lower dangers of syringe swap in contrast with thiopental, which can be confused with other drugs. A naesthesia is maintained using nitrous oxide and a unstable anaesthetic agent in oxygen, utilizing positive stress air flow. I soflurane or sevoflurane are commonly used and should be administered to obtain a total end-tidal focus (volatile and nitrous oxide) of a minimal of 1. Higher concentrations trigger extreme uterine leisure, whereas decrease concentrations predispose the woman to consciousness. More conventionally, gas ratios of nitrous oxide and oxygen of 66:33 are used after intubation. A fter the delivery of the baby, an opioid, corresponding to morphine, could also be given with S yntocinon. Residual neuromuscular block should be antagonised earlier than tracheal extubation, with the girl within the lateral place and with a slight head-down tilt, or si ing up to scale back the risk of aspiration. Routine postoperative care in an appropriately staffed, fully outfitted recovery area is crucial. At this time, postoperative pain aid should be optimised and the baby ought to be given to the mother every time potential. The effect of the physiological changes of being pregnant on the disease have to be recognised and appropriate investigations instigated. Women with cardiac or respiratory illness require careful assessment as a result of the physiological adjustments of pregnancy and supply might have a profound effect on the disease. Many of those women have good reserves for regular day-to-day activities in being pregnant however are unable to cope with the added stress of labour.
Diseases
Which one of many following sequence modifications would most probably be the pathogenic variant detected on this patient A 6-year-old boy was delivered to erectile dysfunction doctor karachi viagra with dapoxetine 100/60 mg generic otc a clinic by his mom for fatigue and multiple infections erectile dysfunction for young adults buy discount viagra with dapoxetine 50/30mg on-line, including two pneumonias in 1 month beta blocker causes erectile dysfunction viagra with dapoxetine 50/30mg buy with amex. Her unsteady gait had increased progressively, main her to be wheelchair-bound. The household historical past was remarkable because her youngest brother and maternal uncle had an analogous sickness. Her maternal uncle had seizures and was wheelchair-bound on the age of 12 and died on the age of 35 from respiratory tract an infection. The physical examination revealed that the woman was small for her age and had gray hairs. Which one of the following problems would this patient most probably have if she had a genetic situation A 12-year-old woman was referred to a genetics clinic by her pediatrician for progressive neck swelling and fever for 1 month and unsteady gait and seizures for two years. The physical examination revealed that the woman was small for her age, with gray hairs. Features of cerebellar dysfunction corresponding to cerebellar ataxia, dyssynergia, dysarthria, and intentional tremors had been current. Which one of many following diseases would the mom have an elevated risk of growing in her lifetime A 6-year-old boy was delivered to a clinic for progressive gait and truncal ataxia beginning at 2 years old, progressively slurred speech, and oculocutaneous telangiectasia. The mother had been pregnant for 6 weeks (calculated from the first day of her final period), and he or she requested in regards to the risk of the fetus having the identical situation. Which one of many following assays would most probably be used to diagnose Bloom syndrome in this affected person Spots of hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation were observed on the trunk and limbs. The mother had been pregnant for six weeks (calculated from the first day of her final period), and asked in regards to the danger of the fetus having the identical condition. A 10-year-old Ashkenazi Jewish girl was referred to a genetics clinic for short stature. The spots of hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation had been noticed on the trunk and limbs. Bloom syndrome is an inherited disorder characterized by short stature, a skin rash that develops after publicity to the sun, and a tremendously elevated threat of most cancers. It occurs hardly ever in all nationwide and ethnic teams however is relatively less rare in Ashkenazi Jews. A 6-year-old Ashkenazi Jewish lady was dropped at a genetics clinic for short standing, developmental delay, and mental incapacity. She had extreme global delay, bilateral cataracts, and severe sensorineural hearing loss. Which one of many following assays would the medical geneticist most probably have ordered to affirm the analysis in this affected person She was born to nonconsanguineous dad and mom after a normal supply with a good Apgar rating and low delivery weight. She had severe global delay, bilateral cataracts, and severe sensorineural deafness. A 6-year-old lady was brought to a genetics clinic for short status, developmental delay, and mental incapacity. Which one of the following genes would more than likely be included in the molecular genetic check to confirm the analysis in this patient The medical geneticist suspected that the affected person had Cockayne syndrome and ordered a genetic take a look at to affirm the prognosis. Which one of many following malignancies would the patient have an increased threat of growing in her lifetime The dermatologist suspected that the patient had dyskeratosis congenita and ordered a genetic test for the affected person after consulting with a medical geneticist. Which one of many following assays would the dermatologist more than likely order to confirm the diagnosis in this affected person The dermatologist suspected that the affected person had dyskeratosis congenita, and ordered a genetic test for the affected person after consulting a medical geneticist. Which of the next assays could be the most delicate one to rule out dyskeratosis congenita in this patient One of her uncles from her mother aspect, whom she had never met, died of a hematological cancer abroad. A 7th-grade boy was brought to a dermatology clinic by his dad and mom for abnormally shaped fingernails and toenails, white patches contained in the mouth, and adjustments in pores and skin coloring round his neck and chest. The dermatologist suspected that the patient had dyskeratosis congenita and ordered a genetic test for the affected person after consulting a medical geneticist. Which one of the genes would more than likely harbor a pathogenic variant if the patient had dyskeratosis congenita A 6th-grade boy was dropped at a dermatology clinic by his parents for abnormally shaped fingernails and toenails, white patches inside the mouth, and adjustments in skin coloring around his neck and chest. Her father died of a hematological cancer right after her family moved to America when she was 5 years old. Which of the following genes would most probably be included in the genetic take a look at to rule out dyskeratosis congenita on this affected person During the bodily examination, she observed that the patient was small for his age. Which one of the following genetic assays can be the most appropriate initial take a look at for this affected person The patient also had developmental delay, broad thumbs and great toes, bilateral undescended testes, and a heart murmur. A molecular sequencing check was ordered, and the outcomes turned out to be adverse. The mother is pregnant and she needs to learn how doubtless it will be for her unborn youngster to have the same situation. A 2-year-old boy is delivered to a dermatology clinic by his dad and mom for extreme sunburn after being on a beach for lower than half-hour. A 4-year-old boy is referred to a surgeon for an abdominal mass discovered by ultrasound. After surgical removing of a half of the left kidney, the boy is identified with unilateral and unicentric Wilms tumor. The mother and father ask for the estimated recurrent danger for his or her next baby, since the mother is at present pregnant. Which one of the following is the empiric risk of Wilms tumor to the unborn baby A 1-year-old boy was referred to a genetics clinic by his pediatrician for a historical past of developmental delay with an incapability to transfer the left limbs and a lump in the left facet of the abdomen. The physical examination revealed facial dysmorphic features, aniridia, bilateral undescended testes, and a palpable mass situated within the left flank, which was immobile on respiration. The gyral enhancement in right parieto-occipital region was suggestive of angiomatosis. Which one of many following genetic assays would more than likely be used for the genetic analysis to confirm/rule out genetic etiologies in this affected person Which one of many following hereditary cancer predisposition syndromes would this affected person more than likely have An 18-month-old girl was delivered to an emergency department by her mother and father for shortness of breath. After consulting with a medical geneticist, the physician ordered a sequencing check for the patient. Which one of many following genes would most probably be sequenced to rule out genetic etiologies on this affected person The pathological examination of a biopsy of the cysts confirmed the analysis of pleuropulmonary blastoma.